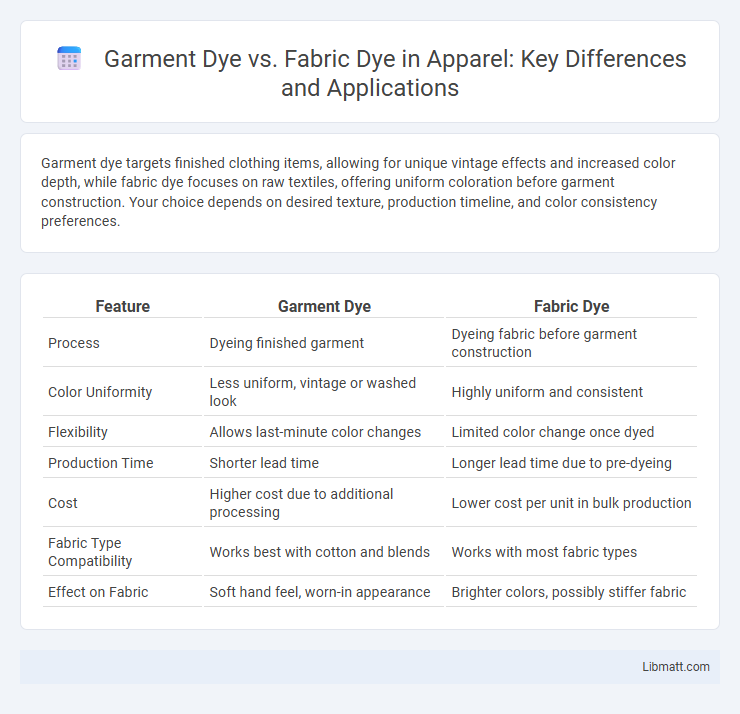
Garment dye targets finished clothing items, allowing for unique vintage effects and increased color depth, while fabric dye focuses on raw textiles, offering uniform coloration before garment construction. Your choice depends on desired texture, production timeline, and color consistency preferences.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Garment Dye | Fabric Dye |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Dyeing finished garment | Dyeing fabric before garment construction |
| Color Uniformity | Less uniform, vintage or washed look | Highly uniform and consistent |
| Flexibility | Allows last-minute color changes | Limited color change once dyed |
| Production Time | Shorter lead time | Longer lead time due to pre-dyeing |
| Cost | Higher cost due to additional processing | Lower cost per unit in bulk production |
| Fabric Type Compatibility | Works best with cotton and blends | Works with most fabric types |
| Effect on Fabric | Soft hand feel, worn-in appearance | Brighter colors, possibly stiffer fabric |
Introduction to Garment Dye and Fabric Dye
Garment dyeing involves dyeing the finished clothing item, allowing for unique color effects and variations in each piece, while fabric dyeing colors the fabric before it is cut and sewn, ensuring uniformity across the material. Your choice between garment dye and fabric dye impacts the texture, colorfastness, and overall appearance of the garment. Understanding these methods helps in selecting the best dyeing technique for desired aesthetic and production outcomes.
What Is Garment Dye?
Garment dye is a textile coloring process where fully constructed clothing is dyed after sewing, allowing for unique color variations and a softer hand feel. This method enhances fabric texture and is commonly used for casual wear like t-shirts, sweatshirts, and outerwear, providing vibrant, washed-in looks that fade naturally over time. Compared to fabric dyeing, garment dyeing offers greater flexibility in inventory and design, as it allows manufacturers to produce garments in neutral colors and dye them in small batches according to market demand.
What Is Fabric Dye?
Fabric dye refers to the process of coloring the raw textile material before it is cut and sewn into a garment, ensuring color consistency throughout the fabric. This method allows for uniform and vibrant hues that penetrate the fibers deeply, making the color more durable and less prone to fading. Fabric dyeing is commonly used for producing large batches of clothing with consistent coloration and quality control.
Key Differences Between Garment Dye and Fabric Dye
Garment dye involves coloring the finished clothing item, allowing for deeper color saturation, unique vintage effects, and greater flexibility in production. Fabric dye colors the textile before it is cut and sewn, ensuring uniform color consistency and better control over colorfastness. Your choice between garment dye and fabric dye depends on the desired aesthetic, production timeline, and durability requirements.
Pros and Cons of Garment Dye
Garment dye offers vibrant, rich colors and softer textures by dyeing finished pieces, enhancing the look and feel of your apparel with a unique, lived-in aesthetic. The process allows greater flexibility in color choices and customization but may result in slight size and fit variations due to shrinkage. However, garment dyeing can increase production costs and limit fabric options, making it less ideal for designs requiring precise measurements or delicate materials.
Pros and Cons of Fabric Dye
Fabric dye offers vibrant and consistent coloration throughout the textile, ensuring long-lasting color retention and uniformity before garment construction. It allows for efficient large-scale dyeing processes, reducing production costs and minimizing color variations across different fabric batches. However, fabric dye limits flexibility in design customization after assembly and may result in wasted material if patterns or styles change post-dyeing.
Applications and Popular Uses
Garment dye is widely used for creating casual and fashion-forward apparel, offering unique color variations and a soft, worn-in feel ideal for T-shirts, hoodies, and denim. Fabric dye is preferred in industrial textile production, where consistent coloring is critical for large quantities of fabrics used in uniforms, home textiles, and upholstery. Your choice between garment dye and fabric dye depends on whether you prioritize texture and one-off design effects or uniformity and large-scale fabric processing.
Impact on Fabric Quality and Appearance
Garment dye enhances fabric softness and flexibility by dyeing the finished product, allowing for a vintage, worn-in look with subtle color variations that add character to your clothing. Fabric dye, applied before garment construction, ensures uniform color but can result in a stiffer texture and less variation in shading. The choice impacts not only the appearance but also the durability and hand feel of the fabric, influencing how your garment ages over time.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
Fabric dyeing generally consumes more water and energy due to large-scale processing before garment construction, increasing environmental impact. Garment dyeing offers a sustainable alternative by dyeing finished products in smaller batches, reducing waste and allowing for on-demand production. Your choice of garment dyeing supports lower water usage and chemical discharge, contributing to more eco-friendly fashion practices.
Choosing the Right Dyeing Method for Your Needs
Selecting between garment dye and fabric dye depends on your production goals and desired final appearance. Fabric dyeing offers precise color control and consistency across large fabric batches, ideal for uniformity in mass production. Garment dyeing provides unique, vintage-inspired looks with slight color variations, perfect if you want to create distinct, customized pieces that stand out.
garment dye vs fabric dye Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com