Shrinkage refers to the reduction in fabric dimensions due to exposure to heat, moisture, or mechanical action during washing or drying, often causing the material to become smaller overall. Puckering occurs when seams or stitches cause the fabric to gather or wrinkle unevenly, affecting the smooth appearance of your garment rather than its overall size.
Table of Comparison
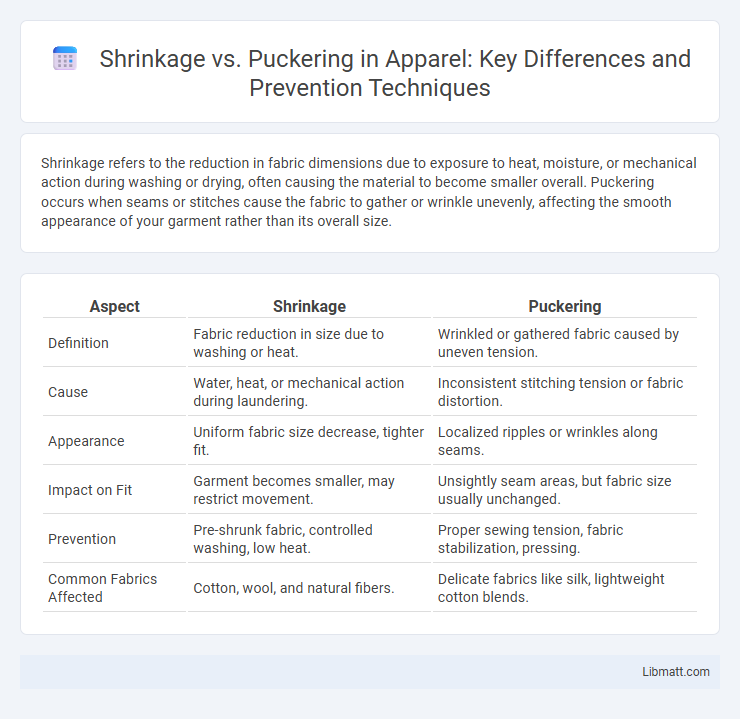
| Aspect | Shrinkage | Puckering |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fabric reduction in size due to washing or heat. | Wrinkled or gathered fabric caused by uneven tension. |
| Cause | Water, heat, or mechanical action during laundering. | Inconsistent stitching tension or fabric distortion. |
| Appearance | Uniform fabric size decrease, tighter fit. | Localized ripples or wrinkles along seams. |
| Impact on Fit | Garment becomes smaller, may restrict movement. | Unsightly seam areas, but fabric size usually unchanged. |
| Prevention | Pre-shrunk fabric, controlled washing, low heat. | Proper sewing tension, fabric stabilization, pressing. |
| Common Fabrics Affected | Cotton, wool, and natural fibers. | Delicate fabrics like silk, lightweight cotton blends. |
Understanding Shrinkage and Puckering
Shrinkage refers to the reduction in fabric size due to factors like washing, drying, or fiber contraction, often causing garments to become tighter or smaller. Puckering occurs when fabric or seams bunch up unevenly, resulting from tension imbalance, improper stitching, or incompatible fabric-thread combinations. Understanding shrinkage and puckering is crucial for garment manufacturers to ensure proper fit and aesthetic quality in finished products.
Key Differences Between Shrinkage and Puckering
Shrinkage refers to the reduction in fabric size caused by washing or drying, while puckering is the distortion of fabric surface resulting in uneven, raised areas along seams or stitches. The key differences lie in their causes--shrinkage is a dimensional change due to fiber contraction, whereas puckering arises from improper tension, stitch length, or fabric handling during sewing. Understanding these distinctions helps you prevent fabric defects and achieve a smooth, professional finish in garment production.
Causes of Fabric Shrinkage
Fabric shrinkage primarily results from the relaxation of tension within the fibers after exposure to moisture, heat, or mechanical agitation during washing or drying. Natural fibers like cotton and wool are more susceptible to dimensional changes due to their inherent fiber structure absorbing water and swelling. Improper drying techniques and high temperatures can exacerbate shrinkage by further contracting the fiber networks.
Common Reasons for Fabric Puckering
Fabric puckering commonly results from uneven tension during sewing, such as improperly adjusted machine settings or inconsistent thread tension. Using incompatible thread and fabric types or stitching at inappropriate speeds also contributes to puckering. Poor-quality fabric or pre-shrunk material that hasn't been properly stabilized before sewing can exacerbate puckering issues.
Types of Shrinkage in Textiles
Shrinkage in textiles primarily occurs due to relaxation shrinkage, felting shrinkage, and progressive shrinkage, each affecting fabric differently. Relaxation shrinkage happens when fibers regain their natural length after manufacturing tension is released, common in cotton and wool. Felting shrinkage is specific to wool fibers, caused by the movement and entanglement of scales on the fiber surface during washing, leading to a denser fabric, while progressive shrinkage occurs gradually with repeated laundering.
Identifying Puckering in Garments
Puckering in garments appears as uneven, raised lines or small gathers along seams caused by fabric tension or improper stitching techniques. Identifying puckering involves closely examining seams for distorted fabric and uneven stitching that disrupt garment smoothness. Your ability to spot puckering early helps improve garment quality and ensures a polished final product.
Prevention Tips for Shrinkage
To prevent shrinkage in fabrics, always prewash your materials following the care instructions provided by the manufacturer. Use cold water washing and low heat settings in dryers to minimize fabric contraction during laundering. Your garments maintain their original size longer when you avoid high temperatures and consider air-drying delicate items.
Solutions to Minimize Puckering
Minimizing puckering involves selecting the right thread tension, using a proper needle size, and stabilizing the fabric with appropriate backing materials to prevent fabric distortion during sewing. Adjusting machine settings such as stitch length and using techniques like pressing seams can further reduce puckering on delicate or stretchy fabrics. Proper fabric handling and choosing compatible thread types also play crucial roles in achieving smooth, professional seams without puckering.
Impact on Fabric Quality and Appearance
Shrinkage reduces fabric size uniformly, leading to a tighter, more compact texture that may distort garment fit and cause uneven seams, negatively impacting fabric quality. Puckering creates small, unwanted wrinkles or gathers along seams that disrupt the smooth surface, diminishing the fabric's visual appeal and professional finish. Your choice of materials and sewing techniques directly influences the degree to which shrinkage or puckering affects fabric quality and appearance.
Best Practices for Care and Maintenance
Shrinkage and puckering in fabrics result from improper washing and drying techniques, so using cold water and gentle cycles is essential for preserving garment integrity. To minimize these issues, always follow the care label instructions and avoid high heat settings in dryers, which can distort fabric fibers and cause permanent deformation. Your best practice includes air drying or using a low-heat setting to maintain the garment's shape and texture over time.
Shrinkage vs puckering Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com