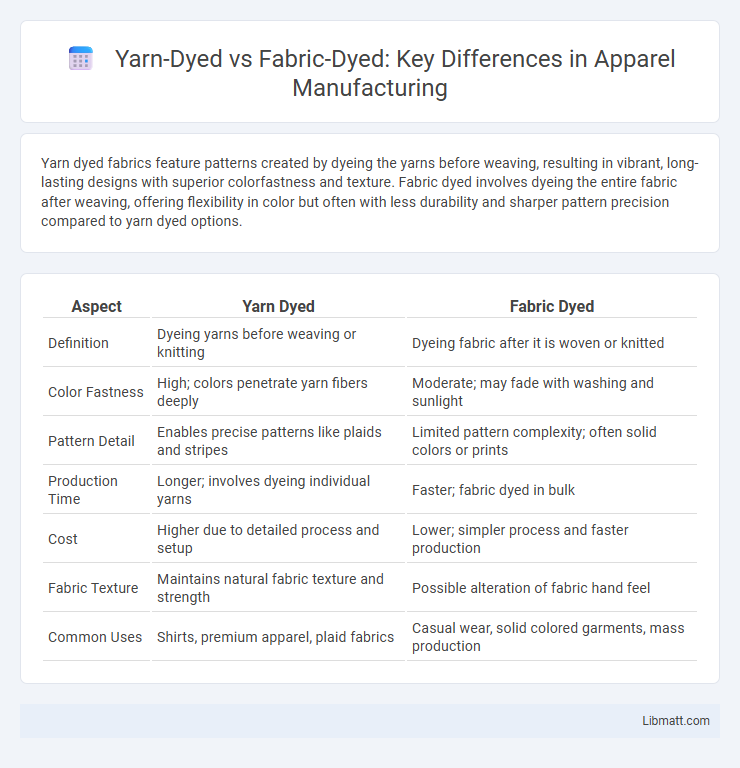
Yarn dyed fabrics feature patterns created by dyeing the yarns before weaving, resulting in vibrant, long-lasting designs with superior colorfastness and texture. Fabric dyed involves dyeing the entire fabric after weaving, offering flexibility in color but often with less durability and sharper pattern precision compared to yarn dyed options.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Yarn Dyed | Fabric Dyed |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Dyeing yarns before weaving or knitting | Dyeing fabric after it is woven or knitted |
| Color Fastness | High; colors penetrate yarn fibers deeply | Moderate; may fade with washing and sunlight |
| Pattern Detail | Enables precise patterns like plaids and stripes | Limited pattern complexity; often solid colors or prints |
| Production Time | Longer; involves dyeing individual yarns | Faster; fabric dyed in bulk |
| Cost | Higher due to detailed process and setup | Lower; simpler process and faster production |
| Fabric Texture | Maintains natural fabric texture and strength | Possible alteration of fabric hand feel |
| Common Uses | Shirts, premium apparel, plaid fabrics | Casual wear, solid colored garments, mass production |
Introduction to Yarn Dyed and Fabric Dyed Techniques
Yarn dyed techniques involve coloring the yarns before weaving or knitting, resulting in vibrant, long-lasting patterns such as plaids and stripes with excellent colorfastness. Fabric dyed refers to dyeing the whole fabric after it has been woven or knitted, allowing for rich, uniform hues or piece-dyeing effects but sometimes with less color precision than yarn dyeing. You can choose between these methods based on desired pattern sharpness and production efficiency for your textile projects.
Understanding the Yarn Dyeing Process
Yarn dyeing involves coloring the yarns before they are woven into fabric, resulting in vibrant patterns and enhanced colorfastness compared to fabric dyeing. This process allows precise control over color placement and consistency across the textile, ideal for creating intricate designs such as plaids or stripes. Understanding the yarn dyeing process helps you choose textiles that offer durability and aesthetic appeal tailored to your specific project needs.
How Fabric Dyeing Differs from Yarn Dyeing
Fabric dyeing involves coloring the entire fabric after it has been woven or knitted, allowing for uniform or patterned color application, while yarn dyeing colors the individual yarns before fabric construction, enabling more precise and complex patterns like plaids or stripes. The choice between fabric dyed and yarn dyed depends on the desired design intricacy, colorfastness, and texture, with yarn dyeing generally offering better color durability and sharper patterns. Your decision on this process impacts the final garment's appearance and quality, especially in textiles where pattern definition and color consistency are critical.
Visual and Aesthetic Differences
Yarn dyed fabrics showcase intricate patterns and color variations due to the dyeing of individual yarns before weaving, resulting in sharper, more vibrant designs like plaids and stripes. Fabric dyed materials exhibit uniform color across the surface, offering a consistent and smooth appearance but lacking the visual depth found in yarn dyed textiles. The choice between yarn dyed and fabric dyed directly impacts the texture perception and colorfastness, influencing the overall aesthetic appeal and garment durability.
Durability and Color Fastness Comparison
Yarn dyed fabrics exhibit superior durability due to the color being integrated into the yarn before weaving, allowing colors to endure repeated washing and exposure without significant fading. Fabric dyed textiles undergo color application after weaving, which can result in less color fastness and a higher tendency to fade or bleed over time. Consequently, yarn dyed materials are preferable for long-lasting color retention and improved resistance to wear and tear.
Common Applications in Textile Industry
Yarn dyed fabrics are predominantly used in high-quality shirting, upholstery, and denim where colorfast patterns like plaids, stripes, and checks are essential for durability and design precision. Fabric dyed textiles find common applications in mass-produced garments, home textiles, and casual wear due to their versatility in achieving uniform solid colors with cost-effective dyeing processes. The textile industry favors yarn dyed methods for products requiring intricate, long-lasting patterns, while fabric dyed techniques are preferred for quick turnarounds and broad color ranges in everyday fabric production.
Cost and Production Time Analysis
Yarn dyed fabrics incur higher production costs and longer lead times due to the intricate process of dyeing individual yarns before weaving, which involves multiple dyeing batches and quality control steps. Fabric dyed methods are generally more cost-effective and quicker, as the entire fabric is dyed in bulk post-weaving, reducing labor intensity and minimizing production stages. Manufacturers balance cost and production time by choosing yarn dyed for high-quality, durable color clarity and fabric dyed for faster, economical large-volume orders.
Environmental Impact of Each Dyeing Method
Yarn dyed fabric typically has a lower environmental impact than fabric dyed, as the dyeing process occurs before weaving, reducing water and chemical usage during fabric production. Fabric dyed involves immersing finished fabric in dye baths, consuming more water, energy, and generating higher levels of chemical effluents. The yarn dyed method also allows for precise color control, minimizing dye wastage and pollution compared to the batch dyeing processes used in fabric dyeing.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Project
Yarn dyed fabrics offer vibrant, long-lasting colors with intricate patterns ideal for designs requiring high durability and colorfastness, making them perfect for upholstery or detailed textiles. Fabric dyed methods provide greater flexibility and cost-efficiency for large runs with solid colors or simpler designs, suitable for fashion and home textiles where quick turnaround is essential. Your project's needs for color intensity, pattern complexity, and production scale should guide the choice between yarn dyed and fabric dyed techniques.
Conclusion: Yarn Dyed vs Fabric Dyed – Which is Better?
Yarn dyed fabrics offer superior colorfastness, intricate patterns, and higher durability compared to fabric dyed materials, making them ideal for premium textiles and detailed designs. Fabric dyed processes provide greater flexibility in color choices and are more cost-effective for large batch production with simple patterns. Choosing between yarn dyed and fabric dyed depends on the specific needs of the project, balancing quality, design complexity, and budget constraints.
Yarn dyed vs fabric dyed Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com