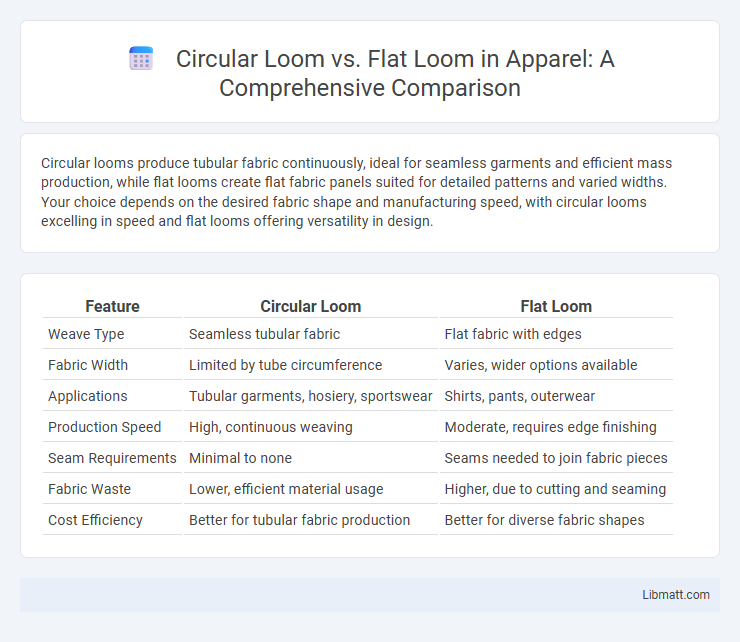
Circular looms produce tubular fabric continuously, ideal for seamless garments and efficient mass production, while flat looms create flat fabric panels suited for detailed patterns and varied widths. Your choice depends on the desired fabric shape and manufacturing speed, with circular looms excelling in speed and flat looms offering versatility in design.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Circular Loom | Flat Loom |
|---|---|---|
| Weave Type | Seamless tubular fabric | Flat fabric with edges |
| Fabric Width | Limited by tube circumference | Varies, wider options available |
| Applications | Tubular garments, hosiery, sportswear | Shirts, pants, outerwear |
| Production Speed | High, continuous weaving | Moderate, requires edge finishing |
| Seam Requirements | Minimal to none | Seams needed to join fabric pieces |
| Fabric Waste | Lower, efficient material usage | Higher, due to cutting and seaming |
| Cost Efficiency | Better for tubular fabric production | Better for diverse fabric shapes |
Introduction to Circular Looms and Flat Looms
Circular looms produce tubular fabric by rotating yarns around a central axis, enabling seamless construction for items like sacks and bags. Flat looms weave fabric in a flat, rectangular shape ideal for sheets, garments, and upholstery, offering versatility in width and pattern design. Your choice between circular and flat looms depends on the desired fabric form and application requirements.
Key Differences Between Circular and Flat Looms
Circular looms produce tubular fabrics by continuously weaving in a circular motion, ideal for creating seamless garments such as T-shirts and hosiery. Flat looms weave fabric in a linear fashion, producing flat textiles primarily used for apparel, home furnishings, and technical textiles. The key differences lie in fabric construction, production speed, and the range of products, with circular looms offering faster output of seamless tubular fabrics and flat looms providing versatility in fabric width and pattern complexity.
How Circular Looms Work
Circular looms operate by continuously weaving fabric in a tubular form using multiple shuttles or no shuttles, simultaneously inserting weft threads around a rotating warp beam. The warp yarns are arranged in a circular frame, facilitating seamless fabric production ideal for making seamless tubes, bags, and sleeves. This mechanism ensures rapid fabric creation with minimal waste compared to traditional flat looms, which weave fabric in flat sheets.
How Flat Looms Operate
Flat looms operate by weaving fabric in a horizontal plane, using a shuttle that moves back and forth to interlace warp and weft threads in a precise, controlled pattern. This method allows for the creation of wide, flat textile pieces with consistent tension across the fabric, ideal for producing detailed designs and varied textures. Your choice of a flat loom enables customization in fabric width and pattern complexity, making it suitable for diverse weaving projects.
Advantages of Circular Looms
Circular looms offer higher weaving speed and efficiency compared to flat looms, enabling continuous fabric production with minimal downtime. Their design reduces fabric distortion, resulting in consistent tubular fabrics ideal for seamless garments and industrial applications. Maintenance costs are generally lower as circular looms have fewer moving parts, contributing to increased productivity and cost-effectiveness in textile manufacturing.
Benefits of Flat Loom Design
Flat looms offer superior control over fabric tension and pattern precision, making them ideal for intricate designs and uniform weave quality. Their ergonomic design reduces operator fatigue and allows easy adjustments, enhancing productivity in textile manufacturing. Unlike circular looms, flat looms facilitate a wider variety of fabric widths and weaving techniques, optimizing versatility in production.
Applications of Circular Looms in Industry
Circular looms are widely used in industrial applications for producing tubular fabrics such as sacks, bags, and nets, making them essential in packaging, agriculture, and fishing industries. Their ability to continuously weave seamless tubes increases efficiency and reduces labor costs compared to flat looms. Your manufacturing processes can benefit from circular looms when uniform tubular fabric is required for high-volume production.
Industrial Uses for Flat Looms
Flat looms are extensively used in industrial textile manufacturing for producing a wide range of woven fabrics such as upholstery, denim, and technical textiles due to their ability to create complex patterns and precise weaves. These looms offer enhanced control over yarn tension and fabric width, making them ideal for applications requiring consistent quality and intricate designs. Your production efficiency benefits from the flat loom's capacity to handle high-speed operations with minimal defects in fabrics destined for automotive, home furnishing, and apparel industries.
Cost and Efficiency Comparison
Circular looms generally offer higher efficiency by enabling continuous fabric production, which reduces downtime and labor costs compared to flat looms that operate in a start-and-stop manner. While flat looms have lower initial investment costs, their slower production rates and manual intervention needs increase operational expenses over time. Consequently, circular looms present better cost-efficiency for large-scale textile manufacturing despite higher upfront expenditures.
Choosing the Right Loom for Your Needs
Selecting the right loom depends on your weaving goals, as a Circular Loom excels in creating seamless tubes and rounded fabrics ideal for making hats, bags, or socks, while a Flat Loom is better suited for producing flat textiles such as scarves, blankets, and tapestries with precise patterns. Circular Looms optimize continuous weaving with minimal seams, enhancing durability, whereas Flat Looms offer more versatility in intricate designs and larger fabric widths. Evaluate your project requirements, fabric type, and desired final product shape to determine the optimal loom for efficiency and quality.
Circular Loom vs Flat Loom Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com