Antimicrobials actively kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria and other microbes to prevent contamination and infection, while odor-resistant materials are specifically designed to neutralize or reduce unpleasant smells caused by bacterial activity. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize hygiene and health benefits (antimicrobials) or maintaining freshness and odor control in fabrics or products.
Table of Comparison
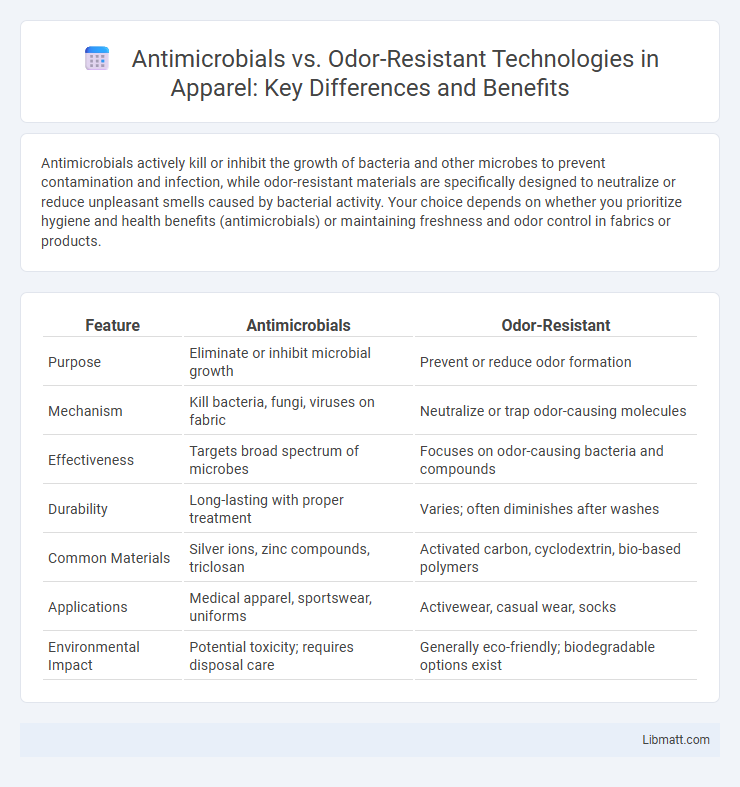
| Feature | Antimicrobials | Odor-Resistant |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Eliminate or inhibit microbial growth | Prevent or reduce odor formation |
| Mechanism | Kill bacteria, fungi, viruses on fabric | Neutralize or trap odor-causing molecules |
| Effectiveness | Targets broad spectrum of microbes | Focuses on odor-causing bacteria and compounds |
| Durability | Long-lasting with proper treatment | Varies; often diminishes after washes |
| Common Materials | Silver ions, zinc compounds, triclosan | Activated carbon, cyclodextrin, bio-based polymers |
| Applications | Medical apparel, sportswear, uniforms | Activewear, casual wear, socks |
| Environmental Impact | Potential toxicity; requires disposal care | Generally eco-friendly; biodegradable options exist |
Understanding Antimicrobials: Definition and Function
Antimicrobials are agents designed to kill or inhibit the growth of microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, and viruses, playing a crucial role in infection control and hygiene maintenance. Their function extends beyond odor control by actively reducing microbial populations on surfaces or fabrics. Understanding this distinction is essential when comparing antimicrobials to odor-resistant technologies, which primarily aim to neutralize or mask odors without necessarily targeting microbial activity.
What Does Odor-Resistant Mean?
Odor-resistant refers to materials or products designed to inhibit the buildup of odor-causing bacteria, keeping your environment fresher for longer periods. Unlike antimicrobials, which actively kill or stop the growth of microbes, odor-resistant features primarily prevent unpleasant smells without necessarily eliminating all bacteria. This distinction is crucial when selecting products for maintaining hygiene and comfort in daily use.
Key Differences Between Antimicrobial and Odor-Resistant Technologies
Antimicrobial technologies actively inhibit or kill bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms to prevent growth on surfaces, while odor-resistant technologies primarily neutralize or mask odors caused by microbial activity or sweat. Antimicrobials target the source of microbial contamination, effectively reducing potential health risks, whereas odor-resistant treatments focus on improving comfort by controlling unpleasant smells. Your choice depends on whether you need to address microbial contamination directly or simply want to manage odors for freshness.
How Antimicrobials Prevent Microbial Growth
Antimicrobials prevent microbial growth by disrupting the cellular processes of bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms, inhibiting their ability to reproduce and thrive on surfaces. These agents interfere with cell wall synthesis, protein production, or DNA replication, effectively reducing microbial populations and preventing odor-causing bacteria proliferation. In contrast to odor-resistant technologies that mask smells, antimicrobials target and eliminate the root cause of odor by eradicating microbes responsible for decomposition and unpleasant smells.
Mechanisms Behind Odor-Resistant Fabrics
Odor-resistant fabrics utilize antimicrobial agents such as silver ions, triclosan, or copper nanoparticles to inhibit the growth of odor-causing bacteria by disrupting their cellular processes and protein functions. These antimicrobial mechanisms prevent the production of volatile sulfur compounds and other metabolites responsible for unpleasant smells, thereby maintaining fabric freshness. Advanced textiles incorporate microencapsulation or bonding techniques to ensure long-lasting odor resistance without compromising breathability or comfort.
Applications: Where Are Antimicrobial and Odor-Resistant Products Used?
Antimicrobial products are widely used in healthcare settings, food processing, and household items to inhibit the growth of harmful bacteria, viruses, and fungi, enhancing hygiene and safety. Odor-resistant products find applications primarily in athletic wear, footwear, and textiles where moisture and sweat accumulation typically cause unpleasant smells, ensuring prolonged freshness. Both technologies are increasingly integrated into consumer goods such as bedding, upholstery, and personal care items to improve user experience and product longevity.
Effectiveness: Antimicrobial vs Odor-Resistant Performance
Antimicrobials target and eliminate bacteria and microbes directly, reducing the source of odors, while odor-resistant materials primarily block or neutralize odor molecules without killing microbes. Your choice depends on whether you need active bacterial control, as antimicrobials provide a more effective solution against microbial growth than odor-resistant treatments. For environments prone to bacterial buildup, antimicrobial performance offers superior long-term odor control compared to odor-resistant options.
Safety and Environmental Impact of Antimicrobial Treatments
Antimicrobial treatments often involve chemicals like triclosan and silver nanoparticles, which may pose risks to human health and contribute to environmental pollution through water contamination and bioaccumulation. Odor-resistant technologies typically rely on physical barriers or natural fibers like bamboo charcoal, offering safer alternatives that minimize ecological harm while maintaining effectiveness. Your choice of odor-resistant products can reduce exposure to potentially harmful antimicrobials and support more sustainable consumption.
Choosing Between Antimicrobial and Odor-Resistant Solutions
Choosing between antimicrobial and odor-resistant solutions depends on the primary need: antimicrobial treatments target bacteria, fungi, and viruses to prevent infections and material degradation, while odor-resistant solutions primarily neutralize or inhibit odor-causing microbes. Antimicrobial products often contain agents like silver ions or triclosan that provide broad-spectrum protection, whereas odor-resistant materials focus on maintaining freshness and eliminating unpleasant smells through chemical or natural additives. Selecting the appropriate solution requires evaluating the environment's exposure to pathogens versus odor concerns, with healthcare or high-contact surfaces benefiting more from antimicrobial properties and athletic or everyday wear favoring odor-resistant technologies.
Future Trends: Innovations in Microbial and Odor Control Technologies
Innovations in antimicrobial and odor-resistant technologies are rapidly advancing with the integration of nanomaterials and bioengineered peptides that target specific microbial strains while neutralizing odor-causing compounds. Smart textiles embedded with sensors are emerging to monitor and respond to microbial growth and odor levels in real time, enhancing personal hygiene and product longevity. You can expect future products to offer more sustainable, non-toxic solutions that combine both antimicrobial efficacy and superior odor control.
antimicrobials vs odor-resistant Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com