A crossmember is a structural component that supports the engine or suspension and connects opposite sides of a vehicle's chassis, providing rigidity and alignment. Your vehicle's subframe is a larger assembly that houses multiple components like the engine, suspension, and transmission, isolating them from the main body to reduce noise and improve safety.
Table of Comparison
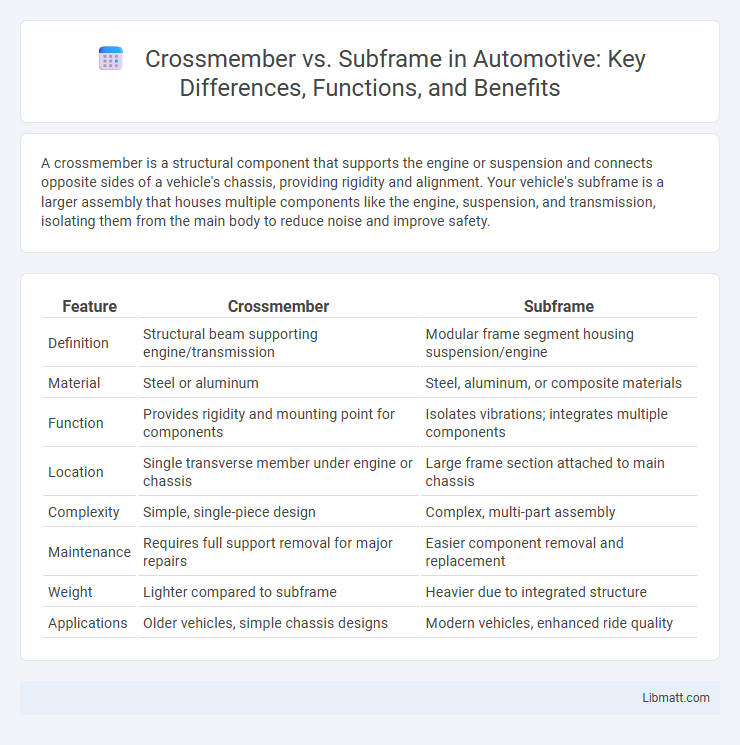
| Feature | Crossmember | Subframe |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Structural beam supporting engine/transmission | Modular frame segment housing suspension/engine |
| Material | Steel or aluminum | Steel, aluminum, or composite materials |
| Function | Provides rigidity and mounting point for components | Isolates vibrations; integrates multiple components |
| Location | Single transverse member under engine or chassis | Large frame section attached to main chassis |
| Complexity | Simple, single-piece design | Complex, multi-part assembly |
| Maintenance | Requires full support removal for major repairs | Easier component removal and replacement |
| Weight | Lighter compared to subframe | Heavier due to integrated structure |
| Applications | Older vehicles, simple chassis designs | Modern vehicles, enhanced ride quality |
Introduction to Crossmember and Subframe
A crossmember is a structural component in a vehicle's chassis that provides support and rigidity by spanning across the frame, often serving as a mounting point for the engine, transmission, or suspension parts. A subframe is a separate, often detachable, assembly that supports the engine, suspension, or drivetrain components, designed to isolate vibrations and improve structural integrity without adding significant weight. Both crossmembers and subframes play crucial roles in vehicle safety, handling, and overall chassis performance.
Definition of Crossmember
A crossmember is a structural component of a vehicle's chassis that spans the width of the frame, providing support and stiffness by connecting opposing sides. It serves as a mounting point for various suspension and drivetrain components, helping to distribute loads and maintain alignment under dynamic conditions. Unlike a subframe, which is a larger assembly often detachable and housing major systems, the crossmember is typically integral to the main vehicle frame.
Definition of Subframe
A subframe is a structural component of a vehicle that supports the engine, suspension, and other key systems, isolating them from the main body to improve ride quality and reduce noise and vibration. Unlike a crossmember, which is typically a single transverse beam providing structural support, the subframe is a more comprehensive assembly that can be bolted or welded to the vehicle's chassis. Subframes enhance vehicle safety and handling by distributing loads evenly and allowing easier repair and replacement of major components.
Key Differences Between Crossmember and Subframe
Crossmembers are structural components that provide support and rigidity to the vehicle's chassis by spanning across the frame, primarily serving as attachment points for suspension and engine components. Subframes are larger, modular assemblies that integrate multiple suspension and drivetrain components, isolating vibrations and improving ride quality by mounting to the vehicle's unibody or frame with bushings. The key differences lie in their scope and function: crossmembers act as individual support beams, whereas subframes serve as comprehensive support modules enhancing structural integrity and noise isolation.
Structural Roles in Vehicle Chassis
A crossmember provides essential lateral support by connecting the vehicle's frame rails, enhancing torsional rigidity and distributing loads across the chassis. A subframe serves as a modular assembly that isolates the engine, suspension, or drivetrain components, improving ride quality and reducing NVH (noise, vibration, and harshness). Both components are critical in maintaining structural integrity, with crossmembers reinforcing primary chassis strength while subframes offer flexibility in mounting key mechanical systems.
Materials Used in Crossmembers and Subframes
Crossmembers are typically constructed from high-strength steel or aluminum alloys to provide structural support and absorb impact in vehicle frames, while subframes often use stamped steel or hydroformed steel sections for enhanced rigidity and weight reduction. Composite materials, such as carbon fiber-reinforced plastics, are increasingly integrated into subframes for luxury or performance vehicles to improve strength-to-weight ratio. Understanding the materials used in your vehicle's crossmembers and subframes can help optimize durability and crash safety.
Common Applications in Automobiles
Crossmembers provide essential structural support by connecting the vehicle's frame rails, commonly found in trucks and SUVs to enhance chassis rigidity and absorb impact forces. Subframes are typically used in passenger cars and compact vehicles, serving as modular units that mount engines and suspensions, improving crash safety and simplifying assembly. Understanding these differences helps you identify which component contributes to your vehicle's stability and handling performance.
Advantages of Crossmembers
Crossmembers provide increased structural rigidity and support by connecting key points of the vehicle chassis, enhancing overall stability during driving. They are typically lighter and easier to manufacture than subframes, contributing to weight reduction and improved fuel efficiency. You will benefit from better alignment and impact distribution with crossmembers, which helps maintain vehicle integrity in collisions.
Benefits of Using Subframes
Subframes provide enhanced structural support by isolating the suspension and drivetrain from the vehicle's main body, resulting in improved ride comfort and noise reduction. They simplify assembly and repair processes, making maintenance more efficient compared to conventional crossmembers. Your vehicle gains increased durability and crash energy absorption due to the subframe's ability to distribute loads more evenly.
Choosing Between Crossmember and Subframe
Choosing between a crossmember and a subframe depends on vehicle design requirements and performance goals. Crossmembers provide structural rigidity by supporting key components like the engine and suspension within the unibody, ideal for lighter vehicles or simpler designs. Subframes offer enhanced modularity and noise isolation by mounting entire assemblies separately from the main frame, preferred in complex or high-performance vehicles requiring easier repairs and improved crash absorption.
Crossmember vs Subframe Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com