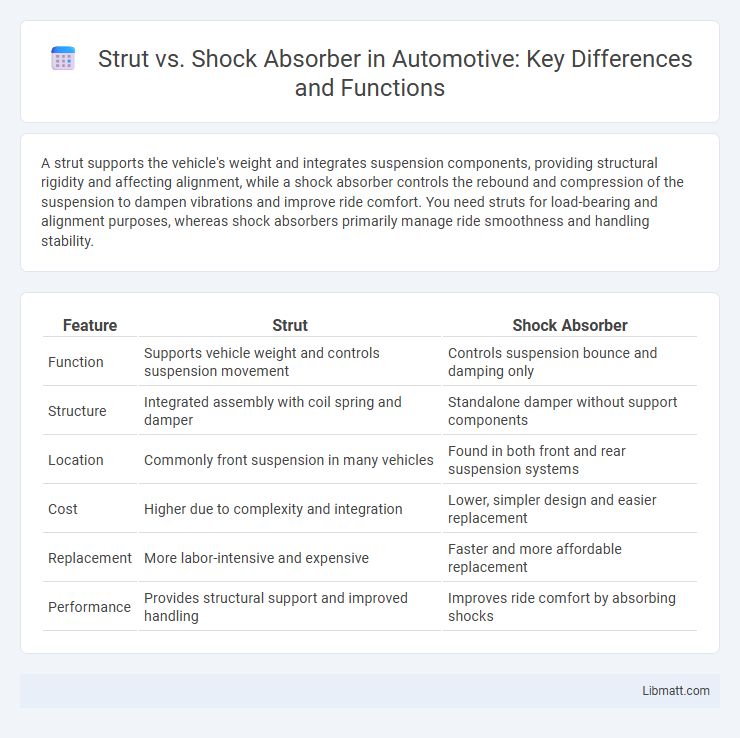
A strut supports the vehicle's weight and integrates suspension components, providing structural rigidity and affecting alignment, while a shock absorber controls the rebound and compression of the suspension to dampen vibrations and improve ride comfort. You need struts for load-bearing and alignment purposes, whereas shock absorbers primarily manage ride smoothness and handling stability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Strut | Shock Absorber |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Supports vehicle weight and controls suspension movement | Controls suspension bounce and damping only |
| Structure | Integrated assembly with coil spring and damper | Standalone damper without support components |
| Location | Commonly front suspension in many vehicles | Found in both front and rear suspension systems |
| Cost | Higher due to complexity and integration | Lower, simpler design and easier replacement |
| Replacement | More labor-intensive and expensive | Faster and more affordable replacement |
| Performance | Provides structural support and improved handling | Improves ride comfort by absorbing shocks |
Introduction to Struts and Shock Absorbers
Struts and shock absorbers are essential components of a vehicle's suspension system designed to improve ride quality and handling. Struts provide structural support, integrating the shock absorber with other suspension parts, while shock absorbers primarily control the impact and rebound movement of the springs. Understanding the differences helps you make informed decisions about maintenance and replacements for optimal vehicle performance.
Role of Struts in Vehicle Suspension Systems
Struts serve as a critical structural component in vehicle suspension systems, combining the functions of a shock absorber and a coil spring to support the vehicle's weight while absorbing road impacts. They provide a mounting point for the suspension and help maintain wheel alignment, directly influencing handling, steering stability, and ride comfort. Unlike standalone shock absorbers, struts are integral to the suspension geometry, making them essential for both shock absorption and vehicle control.
Function of Shock Absorbers Explained
Shock absorbers play a crucial role in controlling the unwanted spring motion by dampening the impact and vibrations from road irregularities, ensuring a smooth and stable ride. Unlike struts, which combine suspension and structural support, shock absorbers focus solely on absorbing and dissipating energy to prevent excessive bouncing and improve vehicle handling. Your vehicle's safety and comfort depend significantly on the proper functioning of shock absorbers.
Key Differences Between Struts and Shock Absorbers
Struts serve as a structural component of a vehicle's suspension system, providing both support for the vehicle's weight and damping to absorb road shocks, whereas shock absorbers primarily control spring movement and improve ride quality without bearing structural loads. Struts integrate a coil spring and damping unit into a single assembly, impacting alignment and handling, while shock absorbers function as standalone components attached to the suspension. The key differences include struts' role in maintaining suspension geometry and steering, contrasted with shock absorbers' focus solely on controlling unwanted spring oscillations.
Signs of Worn Struts vs Shock Absorber Failure
Worn struts often cause uneven tire wear, a noticeable knocking noise when driving over bumps, and poor vehicle alignment, while shock absorber failure typically results in excessive bouncing, reduced braking efficiency, and fluid leaks around the shock. Your vehicle may also experience increased body roll during turns or a generally rougher ride with worn struts compared to shock absorbers. Identifying these signs early helps maintain safety and prolongs suspension system life.
Impact on Ride Quality: Strut vs Shock Absorber
Struts and shock absorbers both play crucial roles in vehicle suspension, but struts provide structural support to the suspension system, directly affecting alignment and handling, which enhances overall ride quality. Shock absorbers control the rebound and compression of the springs, primarily smoothing out road vibrations and bumps for a comfortable ride. Your choice between struts and shock absorbers influences the balance between ride comfort and vehicle stability on various road conditions.
Cost Comparison: Replacing Struts vs Shock Absorbers
Replacing struts typically costs more than replacing shock absorbers due to their complex design and integration with suspension components. Shock absorber replacement generally requires less labor and fewer parts, making it a more affordable option for maintaining your vehicle's ride quality. Understanding the cost difference helps you budget effectively for suspension repairs and choose the best solution for your car's needs.
Maintenance Tips for Struts and Shock Absorbers
Regular inspection of struts and shock absorbers for leaks, dents, or worn bushings ensures optimal vehicle suspension performance and safety. Replacing these components every 50,000 to 75,000 miles prevents uneven tire wear and improves handling on various road conditions. Maintaining proper tire pressure and alignment enhances the lifespan of struts and shock absorbers by reducing undue stress and vibration.
When to Replace Struts or Shock Absorbers
Replace struts or shock absorbers when you notice signs such as excessive bouncing, poor handling, uneven tire wear, or fluid leaks from the components. Struts generally require replacement every 50,000 to 100,000 miles depending on driving conditions, while shock absorbers may last about 50,000 miles but should be inspected regularly for performance degradation. Prompt replacement ensures improved vehicle stability, safety, and ride comfort.
Choosing the Right Suspension Component for Your Vehicle
Selecting the appropriate suspension component depends on your vehicle's design and driving needs, as struts combine a shock absorber and coil spring for structural support, while shock absorbers solely dampen vibrations without bearing weight. Struts are often used in front suspension systems to provide stability and alignment control, particularly in front-wheel-drive cars, whereas shock absorbers are common in rear suspension setups or vehicles prioritizing ride comfort. Understanding the differences in function, load-bearing capacity, and vehicle compatibility ensures optimal performance and safety when replacing suspension components.
strut vs shock absorber Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com