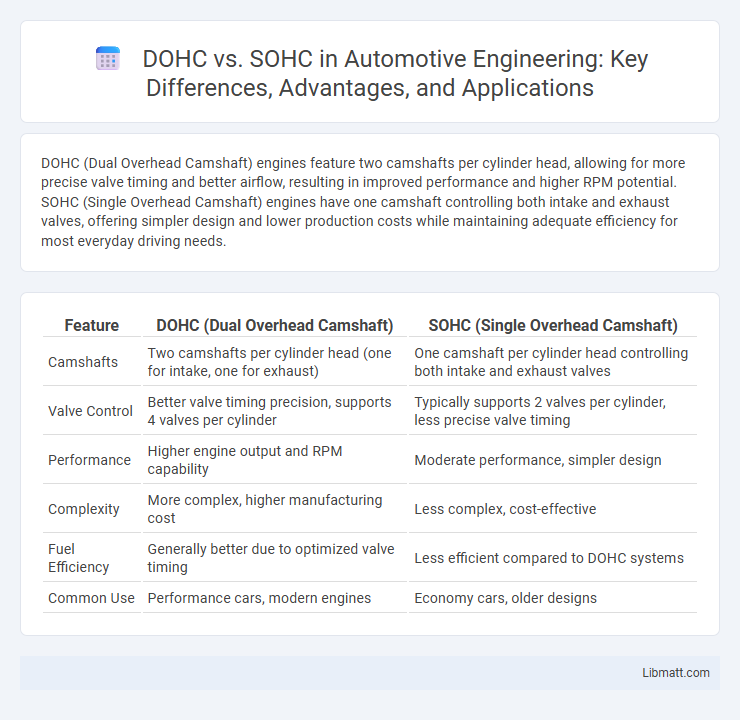
DOHC (Dual Overhead Camshaft) engines feature two camshafts per cylinder head, allowing for more precise valve timing and better airflow, resulting in improved performance and higher RPM potential. SOHC (Single Overhead Camshaft) engines have one camshaft controlling both intake and exhaust valves, offering simpler design and lower production costs while maintaining adequate efficiency for most everyday driving needs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | DOHC (Dual Overhead Camshaft) | SOHC (Single Overhead Camshaft) |
|---|---|---|
| Camshafts | Two camshafts per cylinder head (one for intake, one for exhaust) | One camshaft per cylinder head controlling both intake and exhaust valves |
| Valve Control | Better valve timing precision, supports 4 valves per cylinder | Typically supports 2 valves per cylinder, less precise valve timing |
| Performance | Higher engine output and RPM capability | Moderate performance, simpler design |
| Complexity | More complex, higher manufacturing cost | Less complex, cost-effective |
| Fuel Efficiency | Generally better due to optimized valve timing | Less efficient compared to DOHC systems |
| Common Use | Performance cars, modern engines | Economy cars, older designs |
Introduction to DOHC and SOHC Engines
DOHC (Dual Overhead Camshaft) and SOHC (Single Overhead Camshaft) engines differ primarily in the number of camshafts controlling the intake and exhaust valves. DOHC engines feature two camshafts per cylinder bank, allowing better airflow and higher performance, while SOHC engines use a single camshaft, offering simpler design and reduced manufacturing costs. Understanding these differences can help you choose the right engine type for your vehicle's performance and efficiency needs.
What is a SOHC (Single Overhead Camshaft)?
A Single Overhead Camshaft (SOHC) engine features one camshaft positioned above the cylinder head, responsible for operating both intake and exhaust valves. SOHC designs simplify valve operation compared to DOHC setups, often resulting in fewer moving parts and lower production costs. This configuration provides a balance between performance and efficiency, commonly used in compact engines for everyday vehicles.
What is a DOHC (Dual Overhead Camshaft)?
A DOHC (Dual Overhead Camshaft) engine features two camshafts located in the cylinder head, with one camshaft controlling the intake valves and the other controlling the exhaust valves. This configuration allows for more precise valve timing and improved airflow, leading to better engine performance and higher RPM capabilities. DOHC designs are commonly used in modern high-performance and efficiency-focused engines due to their ability to optimize valve operation.
Key Differences Between DOHC and SOHC
DOHC (Dual Overhead Camshaft) engines feature two camshafts per cylinder bank, enabling precise control of intake and exhaust valves for improved performance and higher RPM capabilities. SOHC (Single Overhead Camshaft) engines use one camshaft per cylinder bank, simplifying design and reducing manufacturing costs but limiting valve timing flexibility. DOHC configurations typically support multi-valve setups, enhancing airflow and combustion efficiency, whereas SOHC designs often have fewer valves, impacting overall engine output and fuel efficiency.
Performance Comparison: DOHC vs SOHC
DOHC (Dual Overhead Camshaft) engines typically deliver higher performance due to better valve control, allowing for increased airflow and higher RPM capabilities compared to SOHC (Single Overhead Camshaft) engines. The presence of two camshafts in DOHC designs enables independent operation of intake and exhaust valves, enhancing engine efficiency and power output. SOHC engines, while simpler and more compact, generally produce less peak power and have limited high-speed performance relative to DOHC configurations.
Fuel Efficiency Considerations
DOHC engines typically offer better fuel efficiency due to precise valve timing and improved air intake control, enhancing combustion. SOHC engines, while simpler and lighter, may experience less optimal fuel atomization and airflow, potentially reducing fuel efficiency. The ability of DOHC configurations to support technologies like variable valve timing further contributes to superior fuel economy in many applications.
Maintenance and Reliability Aspects
DOHC engines generally require more complex maintenance due to having two camshafts per cylinder head, increasing the number of components prone to wear. SOHC engines offer simpler designs with fewer moving parts, often resulting in lower maintenance costs and improved long-term reliability. Regular timing belt or chain inspections are critical in both types to prevent engine damage and maintain performance.
Cost Factors: DOHC vs SOHC
DOHC (Double Overhead Camshaft) engines generally incur higher production costs compared to SOHC (Single Overhead Camshaft) engines due to their more complex design, requiring additional camshafts and components. The increased precision machining and assembly time elevate manufacturing expenses, leading to a higher retail price. SOHC engines, with fewer moving parts and simpler construction, offer cost-effective solutions ideal for budget-conscious applications while maintaining adequate performance.
Popular Applications and Examples
DOHC (Dual Overhead Camshaft) engines are widely used in high-performance sports cars and motorcycles, such as the Honda Civic Type R and Yamaha YZF-R1, due to their ability to optimize valve timing and improve engine efficiency at high RPMs. SOHC (Single Overhead Camshaft) engines find popularity in everyday vehicles like the Toyota Corolla and Honda Accord, offering a simpler design with fewer parts, which enhances reliability and reduces manufacturing costs. Both configurations serve distinct market needs, with DOHC favored for enhanced power and SOHC chosen for economy and durability.
Choosing the Right Engine: DOHC or SOHC?
Choosing between a DOHC (Dual Overhead Camshaft) and SOHC (Single Overhead Camshaft) engine depends on performance and efficiency needs. DOHC engines offer better valve control with separate cams for intake and exhaust, resulting in higher power output and improved fuel efficiency, ideal for sports or high-performance vehicles. SOHC engines provide simpler design, lower manufacturing costs, and adequate performance for daily commuting or economy-focused vehicles, making them suitable for budget-conscious drivers.
DOHC vs SOHC Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com