GDI (Global Development Index) measures overall socio-economic progress, while TBI (Traumatic Brain Injury) refers to physical brain damage caused by external force. Understanding the distinction between GDI and TBI is crucial for interpreting data in development studies versus medical contexts.
Table of Comparison
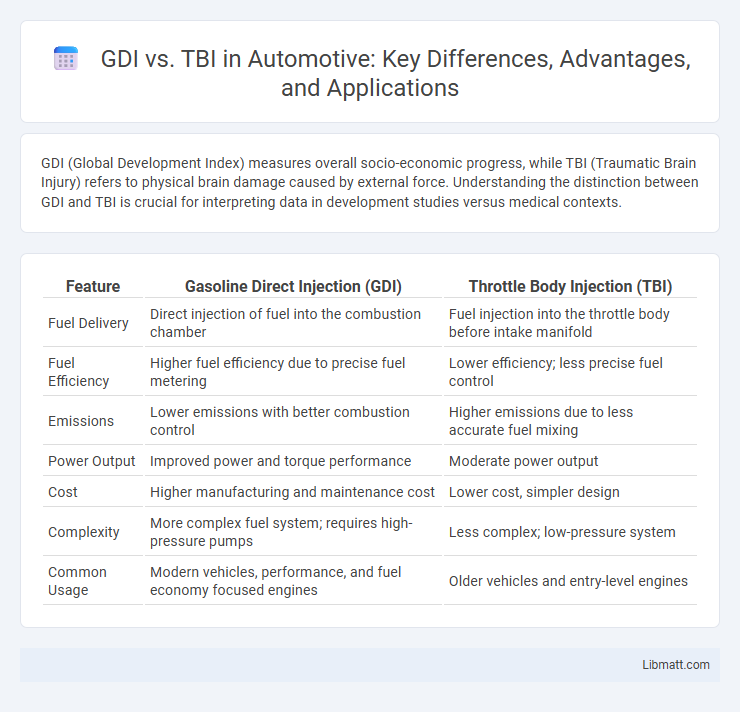
| Feature | Gasoline Direct Injection (GDI) | Throttle Body Injection (TBI) |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Delivery | Direct injection of fuel into the combustion chamber | Fuel injection into the throttle body before intake manifold |
| Fuel Efficiency | Higher fuel efficiency due to precise fuel metering | Lower efficiency; less precise fuel control |
| Emissions | Lower emissions with better combustion control | Higher emissions due to less accurate fuel mixing |
| Power Output | Improved power and torque performance | Moderate power output |
| Cost | Higher manufacturing and maintenance cost | Lower cost, simpler design |
| Complexity | More complex fuel system; requires high-pressure pumps | Less complex; low-pressure system |
| Common Usage | Modern vehicles, performance, and fuel economy focused engines | Older vehicles and entry-level engines |
Introduction to GDI and TBI Technologies
GDI (Gasoline Direct Injection) and TBI (Throttle Body Injection) are fuel delivery technologies used in internal combustion engines to optimize performance and efficiency. GDI injects fuel directly into the combustion chamber, allowing for precise fuel metering and improved power output, while TBI delivers fuel into the throttle body, mixing it with air before entering the intake manifold. Understanding the differences between GDI and TBI can help you make informed decisions about engine tuning and fuel system maintenance.
How Gasoline Direct Injection (GDI) Works
Gasoline Direct Injection (GDI) operates by injecting fuel directly into the combustion chamber at high pressure, enabling precise control over the air-fuel mixture for improved combustion efficiency. Unlike Throttle Body Injection (TBI) that sprays fuel into the intake manifold, GDI's direct spray enhances atomization and promotes better fuel vaporization, resulting in increased power output and reduced emissions. This advanced technology also contributes to better throttle response and fuel economy by optimizing injection timing and quantity based on real-time engine demands.
Understanding Turbocharged Direct Injection (TBI)
Turbocharged Direct Injection (TBI) integrates the benefits of turbocharging with direct fuel injection technology, delivering precise fuel delivery directly into the combustion chamber. This results in improved fuel atomization, enhanced power output, and increased fuel efficiency compared to conventional port fuel injection systems. Understanding TBI helps you appreciate how this combination maximizes engine performance while reducing emissions.
Key Differences Between GDI and TBI
Gasoline Direct Injection (GDI) systems deliver fuel directly into the combustion chamber, enhancing fuel atomization and combustion efficiency, while Throttle Body Injection (TBI) injects fuel into the intake manifold, mixing with air before entering the cylinders. GDI offers improved power output, better fuel economy, and lower emissions compared to TBI, due to precise fuel metering and higher injection pressure. However, TBI systems are simpler, cheaper to maintain, and less prone to carbon buildup issues than GDI engines.
Fuel Efficiency Comparison: GDI vs TBI
GDI (Gasoline Direct Injection) systems deliver fuel directly into the combustion chamber, resulting in more precise fuel metering and improved combustion efficiency compared to TBI (Throttle Body Injection). This precision often translates to better fuel economy and reduced emissions, making GDI engines more fuel-efficient under various driving conditions. Your vehicle can achieve enhanced mileage and lower fuel consumption when equipped with GDI technology versus traditional TBI systems.
Performance Outcomes of GDI and TBI
Gasoline Direct Injection (GDI) engines deliver higher fuel efficiency and improved power output by injecting fuel directly into the combustion chamber, resulting in better combustion control and reduced fuel consumption. Throttle Body Injection (TBI) systems, while simpler and less expensive, generally provide less precise fuel metering leading to comparatively lower performance and fuel economy. Studies show GDI engines often achieve up to 15% better fuel efficiency and increased torque, making them more suitable for modern performance and emission standards.
Emissions and Environmental Impact
Gasoline Direct Injection (GDI) engines typically produce lower carbon dioxide emissions due to improved fuel efficiency but can generate higher particulate matter and nitrogen oxide (NOx) pollutants compared to Throttle Body Injection (TBI) systems. TBI engines generally emit more carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons due to less precise fuel delivery, contributing to greater smog formation. Advances in GDI technology, such as particulate filters and improved combustion control, are mitigating environmental impacts and enabling compliance with stringent emission standards.
Maintenance and Reliability Considerations
GDI engines require more frequent maintenance due to carbon buildup on intake valves, which can impact reliability if untreated, while TBI systems tend to have fewer carbon-related issues, leading to simpler upkeep. Fuel quality and regular use of fuel system cleaners are essential for maintaining optimal GDI performance and preventing injector clogging. You should monitor GDI components closely to ensure longevity, whereas TBI systems are generally more forgiving but may sacrifice some efficiency and emissions performance.
Cost Analysis: GDI vs TBI
Gasoline Direct Injection (GDI) engines generally have higher upfront costs compared to Throttle Body Injection (TBI) systems due to advanced fuel delivery components and precision engineering. Maintenance expenses for GDI can be greater over time because of issues like carbon buildup on intake valves, requiring specialized cleaning methods. In contrast, TBI systems offer lower initial costs and simpler maintenance, making them more cost-effective for budget-conscious vehicle owners despite less fuel efficiency.
Choosing the Best Technology for Your Vehicle
When choosing between GDI (Gasoline Direct Injection) and TBI (Throttle Body Injection) for your vehicle, consider fuel efficiency and performance; GDI systems offer more precise fuel delivery, resulting in better power output and lower emissions. TBI systems are simpler and typically more affordable to maintain, making them suitable for older or less performance-oriented vehicles. Evaluate your vehicle's engine type, driving habits, and maintenance preferences to select the most suitable fuel injection technology.
GDI vs TBI Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com