Naturally aspirated engines rely solely on atmospheric pressure to draw air into the combustion chamber, resulting in linear power delivery and simpler maintenance. Forced induction systems, such as turbochargers or superchargers, compress incoming air to increase engine power and efficiency, enhancing your vehicle's performance especially at higher rpm ranges.
Table of Comparison
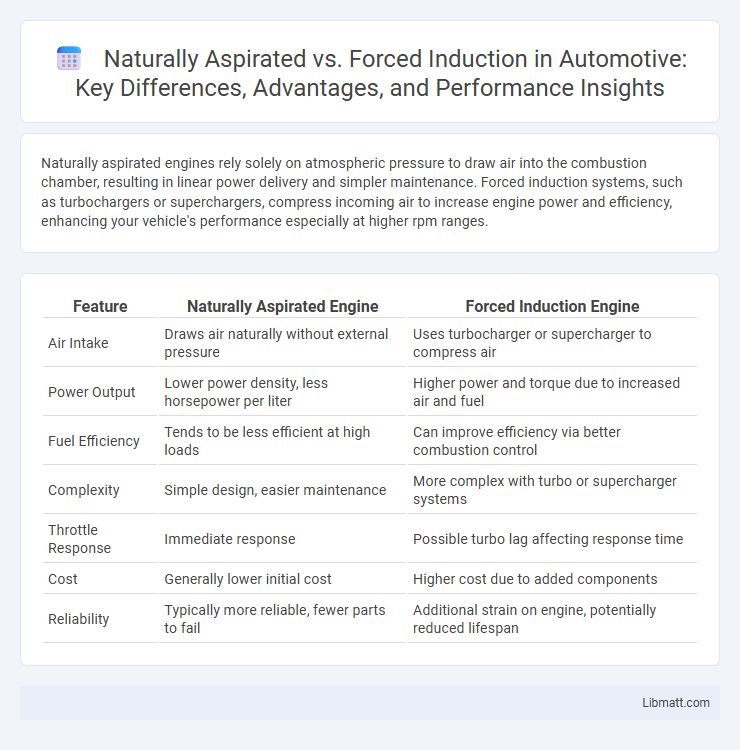
| Feature | Naturally Aspirated Engine | Forced Induction Engine |
|---|---|---|
| Air Intake | Draws air naturally without external pressure | Uses turbocharger or supercharger to compress air |
| Power Output | Lower power density, less horsepower per liter | Higher power and torque due to increased air and fuel |
| Fuel Efficiency | Tends to be less efficient at high loads | Can improve efficiency via better combustion control |
| Complexity | Simple design, easier maintenance | More complex with turbo or supercharger systems |
| Throttle Response | Immediate response | Possible turbo lag affecting response time |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost | Higher cost due to added components |
| Reliability | Typically more reliable, fewer parts to fail | Additional strain on engine, potentially reduced lifespan |
Introduction to Engine Induction Methods
Engine induction methods determine how air is supplied to the combustion chamber, directly impacting performance and efficiency. Naturally aspirated engines rely on atmospheric pressure to draw air in, leading to simpler design and linear throttle response but limited power output. Forced induction, including turbocharging and supercharging, compresses air before entering the combustion chamber, significantly increasing engine power and torque by improving air density and oxygen availability.
What is a Naturally Aspirated Engine?
A naturally aspirated engine relies on atmospheric pressure to draw air into the combustion chamber without using forced induction devices like turbochargers or superchargers. This type of engine typically offers linear throttle response and predictable power delivery, favored for its simplicity and reliability. It usually provides lower peak power compared to forced induction engines but excels in smooth performance and ease of maintenance.
Understanding Forced Induction: Turbochargers and Superchargers
Forced induction systems, such as turbochargers and superchargers, significantly boost engine performance by increasing the amount of air delivered to the combustion chamber, resulting in higher power output compared to naturally aspirated engines. Turbochargers utilize exhaust gas energy to spin a turbine, compressing air efficiently without engine power loss, while superchargers are belt-driven and provide immediate boost at lower RPMs but can reduce fuel efficiency. Understanding these differences helps optimize your vehicle's performance and fuel economy based on your driving needs and engine design.
Key Differences: Naturally Aspirated vs Forced Induction
Naturally aspirated engines rely on atmospheric pressure to draw air into the combustion chamber, resulting in linear throttle response and simpler mechanical design. Forced induction systems, such as turbochargers and superchargers, compress incoming air to increase oxygen density, significantly boosting power output and efficiency. Key differences include complexity, power potential, fuel efficiency, and lag characteristics, with forced induction offering higher performance at the cost of added mechanical components and heat management challenges.
Performance Comparison: Power and Efficiency
Naturally aspirated engines rely on atmospheric pressure for air intake, resulting in linear power delivery but generally lower peak horsepower compared to forced induction systems. Forced induction, such as turbocharging or supercharging, compresses the intake air, significantly increasing power output and improving engine efficiency by extracting more energy from the same fuel amount. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize consistent throttle response and simplicity or enhanced performance and fuel economy through advanced air compression technology.
Reliability and Maintenance Considerations
Naturally aspirated engines generally offer greater reliability and lower maintenance costs due to their simpler design, lacking components like turbochargers or superchargers that can wear out or fail. Forced induction systems increase engine complexity, requiring more frequent maintenance of parts such as intercoolers, turbo seals, and boost control systems to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Proper care and timely servicing of forced induction components are crucial to prevent issues like increased thermal stress and potential engine knock.
Fuel Economy: Which System Wins?
Naturally aspirated engines generally offer better fuel economy due to their simpler design and lower operating pressures, which reduce pumping losses and improve efficiency at steady speeds. Forced induction systems, like turbochargers and superchargers, increase power by compressing intake air, often leading to higher fuel consumption under heavy load despite better performance. Your choice impacts fuel costs and efficiency, with naturally aspirated engines typically winning in everyday driving scenarios focused on fuel economy.
Driving Experience and Sound Characteristics
Naturally aspirated engines deliver a linear throttle response and a more organic, mechanical sound that enhances the purity of your driving experience. Forced induction engines, such as turbocharged or supercharged systems, provide increased power and torque, often accompanied by a distinctive turbo whistle or supercharger whine that adds intensity to engine note. The choice between naturally aspirated and forced induction profoundly shapes your vehicle's acceleration feel and acoustic personality on the road.
Tuning Potential and Aftermarket Modifications
Boosted engines with forced induction offer significantly greater tuning potential due to their ability to increase air intake pressure, allowing for substantial horsepower gains through upgraded turbochargers or superchargers. Naturally aspirated engines typically require precision modifications like camshaft upgrades, intake manifolds, and exhaust enhancements to optimize airflow but have more limited power growth compared to forced induction setups. Your choice between these setups influences the scope and cost of aftermarket modifications tailored to maximize performance gains.
Choosing the Right Induction Method for Your Needs
Choosing the right induction method depends on your performance goals, driving conditions, and maintenance preferences. Naturally aspirated engines offer linear power delivery and simpler mechanics, making them ideal for daily driving and reliability. Forced induction systems, like turbochargers or superchargers, provide significant power boosts and efficiency benefits, perfect for enthusiasts seeking higher horsepower and torque.
Naturally Aspirated vs Forced Induction Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com