Unibody construction integrates the vehicle's frame and body into a single cohesive structure, offering enhanced rigidity, reduced weight, and improved fuel efficiency, ideal for passenger cars and crossovers. Body-on-frame design consists of a separate frame supporting the body, providing greater durability and off-road capability, making it suitable for trucks and SUVs.
Table of Comparison
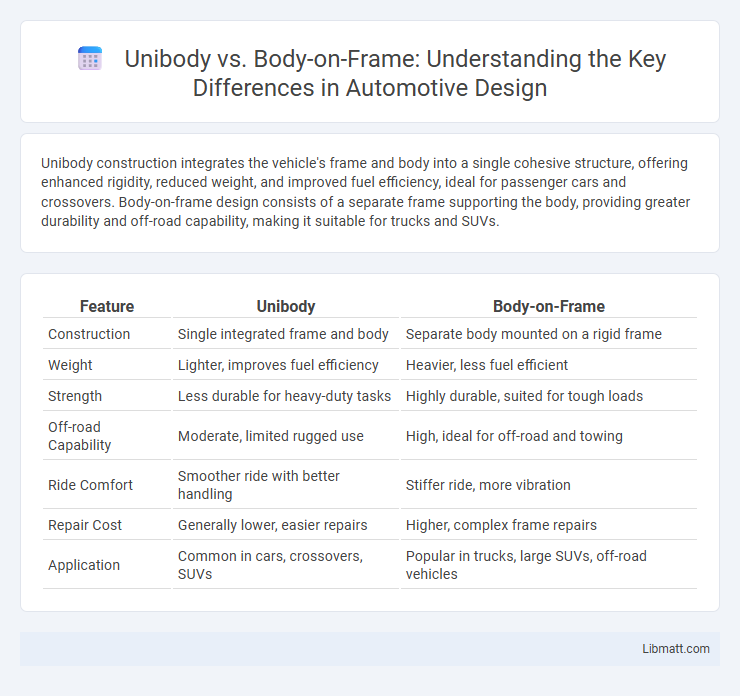
| Feature | Unibody | Body-on-Frame |
|---|---|---|
| Construction | Single integrated frame and body | Separate body mounted on a rigid frame |
| Weight | Lighter, improves fuel efficiency | Heavier, less fuel efficient |
| Strength | Less durable for heavy-duty tasks | Highly durable, suited for tough loads |
| Off-road Capability | Moderate, limited rugged use | High, ideal for off-road and towing |
| Ride Comfort | Smoother ride with better handling | Stiffer ride, more vibration |
| Repair Cost | Generally lower, easier repairs | Higher, complex frame repairs |
| Application | Common in cars, crossovers, SUVs | Popular in trucks, large SUVs, off-road vehicles |
Introduction to Unibody and Body-on-frame Designs
Unibody design integrates the vehicle's body and frame into a single, cohesive structure, enhancing rigidity and reducing weight for improved fuel efficiency and handling. Body-on-frame construction involves mounting the body separately on a robust frame, offering superior durability and off-road capability, ideal for heavy-duty trucks and SUVs. Understanding these differences helps you choose the right vehicle based on performance, safety, and intended use.
Structural Differences: Unibody vs Body-on-frame
Unibody construction integrates the vehicle's body and frame into a single, cohesive structure, enhancing rigidity and reducing overall weight, which improves fuel efficiency and handling. Body-on-frame design separates the frame and body, with the frame supporting the drivetrain and suspension, providing superior durability and off-road capability for heavy-duty applications. Your choice between these depends on whether you prioritize ride comfort and efficiency (Unibody) or toughness and towing capacity (Body-on-frame).
Historical Evolution of Vehicle Construction
Vehicle construction transitioned from body-on-frame designs, dominant in early 20th-century automobiles due to manufacturing simplicity and durability, to unibody structures that emerged in the 1930s, offering enhanced safety, reduced weight, and improved fuel efficiency. The unibody's integration of chassis and body increased structural rigidity and became prevalent in passenger cars by the mid-20th century, while body-on-frame remained preferred for trucks and SUVs requiring superior load-bearing capacity. Advances in materials and manufacturing technologies accelerated unibody adoption, shaping modern automotive engineering and design standards.
Weight and Efficiency Comparisons
Unibody construction typically results in lighter vehicle weight compared to body-on-frame designs, enhancing fuel efficiency and handling performance. Body-on-frame vehicles, while heavier due to separate chassis and body components, offer superior durability and towing capacity but often sacrifice fuel economy. Automakers prioritize unibody designs for passenger cars to maximize weight savings and efficiency, whereas body-on-frame remains common in trucks and SUVs where strength outweighs fuel considerations.
Safety and Crash Performance
Unibody construction integrates the body and frame into a single structure, enhancing crash energy absorption and reducing cabin intrusion during collisions, which typically results in higher safety ratings. Body-on-frame designs, while generally stronger in handling heavy impacts and off-road conditions, often experience greater deformation in crashes, potentially compromising passenger protection. Modern unibody vehicles frequently incorporate advanced crumple zones and reinforced safety cages that improve occupant survival rates compared to traditional body-on-frame trucks and SUVs.
Ride Comfort and Handling
Unibody construction offers superior ride comfort and handling due to its integrated frame and body design that allows for enhanced flexibility and reduced weight, resulting in smoother rides and better steering response. Body-on-frame frames provide greater durability for off-road and heavy-duty use but often sacrifice ride comfort with increased body roll and vibrations. The choice impacts vehicle dynamics significantly, with unibody excelling in everyday driving conditions and body-on-frame favoring rugged terrain performance.
Off-road Capability and Durability
Unibody construction provides improved handling and fuel efficiency but sacrifices off-road durability and ruggedness compared to body-on-frame designs, which excel in withstanding extreme terrain and heavy impacts. Body-on-frame vehicles offer superior structural integrity, making them ideal for serious off-road driving and heavy-duty use. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize off-road capability and durability or urban driving comfort and efficiency.
Maintenance and Repair Considerations
Unibody vehicles generally offer lower maintenance costs due to integrated construction, resulting in fewer components prone to wear and simpler repairs after minor collisions. Body-on-frame vehicles, favored for heavy-duty use, often require more frequent maintenance on suspension and frame parts but allow easier replacement of damaged components without compromising structural integrity. You should consider your usage and repair budget, as unibody designs simplify routine maintenance while body-on-frame systems provide durability and easier frame repairs in off-road or commercial settings.
Popular Vehicles Featuring Each Frame Type
Popular unibody vehicles include the Honda CR-V, Toyota RAV4, and Tesla Model 3, known for their lightweight construction and improved fuel efficiency. Body-on-frame designs are commonly found in trucks and SUVs like the Ford F-150, Toyota Tacoma, and Jeep Wrangler, offering enhanced durability and off-road capability. The choice between unibody and body-on-frame often depends on the vehicle's intended use, with unibody favored for everyday driving and body-on-frame preferred for heavy-duty tasks.
Choosing the Right Frame for Your Needs
Choosing the right frame depends on your vehicle usage and driving preferences. Unibody frames provide better fuel efficiency, handling, and comfort, ideal for daily commuting and city driving. Body-on-frame designs offer superior durability and off-road capability, making them suitable for towing, heavy loads, and rugged terrain.
Unibody vs Body-on-frame Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com