Glycerin and propylene glycol are both common humectants used in skincare and food products to retain moisture and improve texture. Your choice depends on skin sensitivity and product formulation, as glycerin is natural and gentle, while propylene glycol is synthetic and can occasionally cause irritation.
Table of Comparison
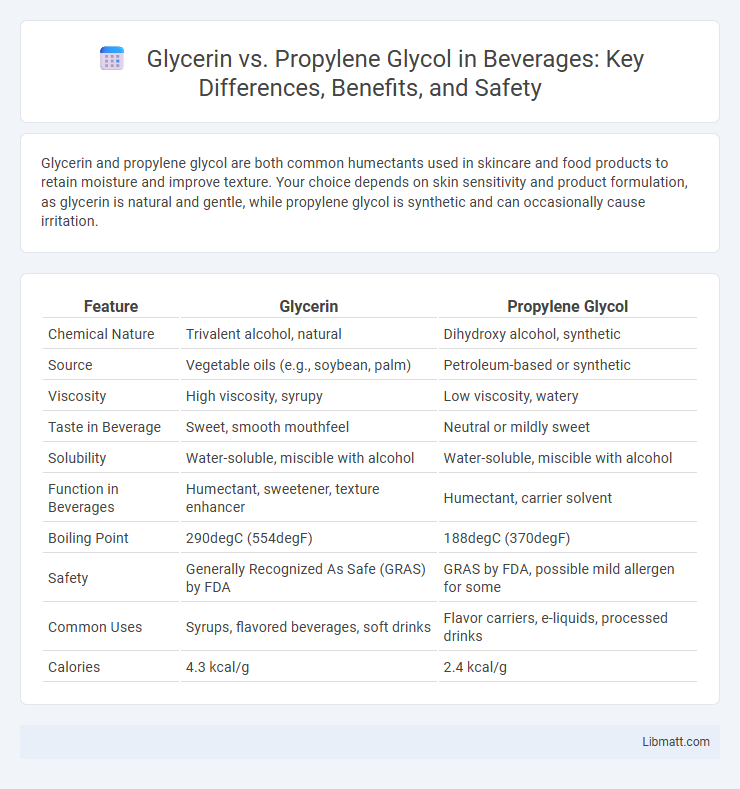
| Feature | Glycerin | Propylene Glycol |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Nature | Trivalent alcohol, natural | Dihydroxy alcohol, synthetic |
| Source | Vegetable oils (e.g., soybean, palm) | Petroleum-based or synthetic |
| Viscosity | High viscosity, syrupy | Low viscosity, watery |
| Taste in Beverage | Sweet, smooth mouthfeel | Neutral or mildly sweet |
| Solubility | Water-soluble, miscible with alcohol | Water-soluble, miscible with alcohol |
| Function in Beverages | Humectant, sweetener, texture enhancer | Humectant, carrier solvent |
| Boiling Point | 290degC (554degF) | 188degC (370degF) |
| Safety | Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS) by FDA | GRAS by FDA, possible mild allergen for some |
| Common Uses | Syrups, flavored beverages, soft drinks | Flavor carriers, e-liquids, processed drinks |
| Calories | 4.3 kcal/g | 2.4 kcal/g |
Understanding Glycerin and Propylene Glycol
Glycerin and propylene glycol are common humectants used in skincare and pharmaceutical formulations, each with distinct chemical structures and moisturizing properties. Glycerin is a natural, plant-derived compound known for its superior ability to attract and retain moisture, making it ideal for hydrating dry or sensitive skin. Propylene glycol, a synthetic compound, functions effectively as a solvent and preservative, enhancing product stability while providing moderate hydration for your skin.
Chemical Structure and Properties
Glycerin (C3H8O3) is a trihydroxy alcohol with three hydroxyl groups, making it highly hygroscopic and viscous, commonly used for its moisturizing and solvent properties. Propylene glycol (C3H8O2) is a diol with two hydroxyl groups, less viscous and more volatile than glycerin, offering excellent solvent capabilities and lower hygroscopicity. The difference in hydroxyl group count directly impacts their solubility, viscosity, and applications in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food industries.
Common Uses in Industry and Products
Glycerin is widely used in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, food products, and personal care items due to its moisturizing and humectant properties. Propylene glycol is commonly found in antifreeze formulations, food flavorings, pharmaceuticals, and tobacco products as a solvent and preservative. Both compounds serve vital roles in the formulation of skincare products, but glycerin is preferred for its natural origin and skin compatibility, while propylene glycol is valued for its ability to stabilize and dissolve active ingredients.
Safety and Toxicity Profiles
Glycerin and propylene glycol both exhibit low toxicity and are generally recognized as safe for use in food, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals by regulatory agencies such as the FDA. Glycerin is a natural compound derived from fats and oils, offering excellent biocompatibility and minimal allergenic potential, making it suitable for sensitive skin applications. Propylene glycol, a synthetic organic compound, may cause mild skin irritation or allergic reactions in some individuals but remains safe at approved concentrations and is metabolized efficiently by the human body.
Effects on Skin and Health
Glycerin is a natural humectant that attracts moisture to the skin, enhancing hydration and promoting a soft, smooth texture without causing irritation. Propylene glycol, a synthetic compound, functions as both a humectant and penetration enhancer but can sometimes cause allergic reactions or skin sensitivity in sensitive individuals. Both substances are widely used in skincare, but glycerin is generally considered safer and gentler for prolonged topical use.
Glycerin vs Propylene Glycol in Food and Beverages
Glycerin and propylene glycol serve as common humectants and solvents in food and beverages, with glycerin favored for its natural origin and sweet taste that enhances flavor profiles, while propylene glycol is prized for its ability to maintain moisture and stability in beverages without altering taste significantly. Both substances are Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS) by the FDA, but glycerin is often preferred in products aiming for a cleaner label or natural appeal. You can select between them based on the desired taste, texture, and product labeling requirements in your formulation.
Applications in Pharmaceuticals and Cosmetics
Glycerin and propylene glycol are widely used humectants in pharmaceuticals and cosmetics, valued for their moisturizing and solvent properties. Glycerin is favored for its natural origin and excellent skin compatibility, making it ideal for lotions, creams, and oral syrups. Propylene glycol, with its superior penetration and antimicrobial effects, is commonly utilized in topical medications and deodorants to enhance formulation stability and skin absorption.
Environmental Impact and Biodegradability
Glycerin is derived from natural sources like vegetable oils and is readily biodegradable, making it an environmentally friendly option with minimal ecological footprint. Propylene glycol, while synthetic, is also biodegradable but tends to degrade more slowly and may have a slightly higher environmental persistence. Choosing glycerin over propylene glycol can reduce your product's environmental impact due to its sustainable sourcing and faster biodegradation rate.
Cost and Availability Comparison
Glycerin typically costs more than propylene glycol due to its natural origin and more complex extraction process, impacting overall formulation budgets. Propylene glycol is widely available and produced on a large industrial scale, resulting in lower prices and easier procurement for manufacturers. Your choice between these two humectants should consider budget constraints and supply chain stability.
Which is Best: Glycerin or Propylene Glycol?
Glycerin and propylene glycol both serve as effective humectants in skincare and cosmetic formulations, but glycerin excels in moisturizing due to its natural origin and superior water retention properties. Propylene glycol, a synthetic compound, offers better skin penetration and stability in formulations, making it ideal for delivering active ingredients efficiently. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize intense hydration with glycerin or enhanced absorption and formulation versatility with propylene glycol.
Glycerin vs propylene glycol Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com