Artificial sweeteners offer low-calorie alternatives that can help you reduce sugar intake without sacrificing sweetness, while natural sweeteners like honey and maple syrup provide trace nutrients and antioxidants but often contain higher calorie content. Choosing between them depends on your dietary goals, taste preferences, and any health considerations such as blood sugar management or digestive sensitivity.
Table of Comparison
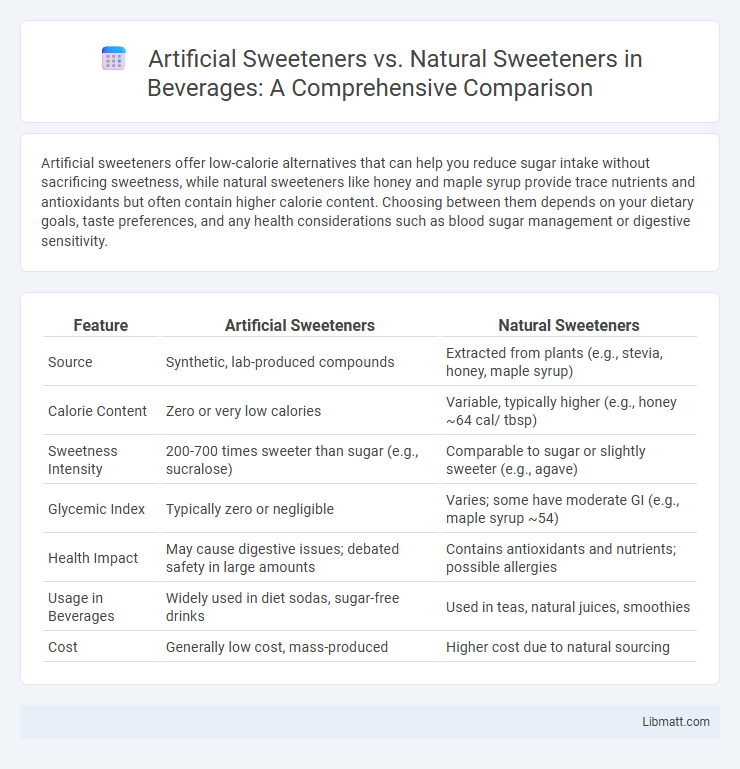
| Feature | Artificial Sweeteners | Natural Sweeteners |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Synthetic, lab-produced compounds | Extracted from plants (e.g., stevia, honey, maple syrup) |
| Calorie Content | Zero or very low calories | Variable, typically higher (e.g., honey ~64 cal/ tbsp) |
| Sweetness Intensity | 200-700 times sweeter than sugar (e.g., sucralose) | Comparable to sugar or slightly sweeter (e.g., agave) |
| Glycemic Index | Typically zero or negligible | Varies; some have moderate GI (e.g., maple syrup ~54) |
| Health Impact | May cause digestive issues; debated safety in large amounts | Contains antioxidants and nutrients; possible allergies |
| Usage in Beverages | Widely used in diet sodas, sugar-free drinks | Used in teas, natural juices, smoothies |
| Cost | Generally low cost, mass-produced | Higher cost due to natural sourcing |
Understanding Artificial vs. Natural Sweeteners
Artificial sweeteners, such as aspartame, sucralose, and saccharin, provide intense sweetness without the calories found in natural sweeteners like honey, maple syrup, or agave nectar. Natural sweeteners typically contain trace nutrients and antioxidants, while artificial sweeteners are synthetic compounds created to mimic sugar's taste without impacting blood sugar levels. Understanding the differences in origin, calorie content, and metabolic effects can help you make informed choices that align with your dietary goals and health needs.
Common Types of Artificial Sweeteners
Common types of artificial sweeteners include aspartame, sucralose, saccharin, and acesulfame potassium, each offering intense sweetness with minimal or zero calories. These synthetic compounds are widely used in diet sodas, sugar-free gums, and low-calorie desserts to replace sugar without raising blood glucose levels. Understanding the differences between your options can help you make informed choices for managing calorie intake and controlling sweetness in your diet.
Popular Natural Sweetener Options
Popular natural sweetener options include honey, maple syrup, agave nectar, and stevia, each offering unique flavors and varying glycemic indexes. These sweeteners provide antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals absent in artificial alternatives, supporting a more nutrient-rich diet. You can choose the best natural sweetener based on taste preference, caloric content, and impact on blood sugar levels.
Health Effects: Artificial Sweeteners
Artificial sweeteners, such as aspartame, sucralose, and saccharin, provide a low-calorie alternative to sugar, but their health effects remain debated. Studies indicate that some artificial sweeteners may alter gut microbiota and influence glucose metabolism, potentially affecting insulin sensitivity and weight management. You should consider current research findings and consult healthcare professionals when choosing between artificial and natural sweeteners for optimal health.
Health Benefits and Risks of Natural Sweeteners
Natural sweeteners like honey, maple syrup, and agave nectar offer antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals that can support immune health and provide anti-inflammatory properties. However, these sweeteners still contain sugars that can contribute to blood sugar spikes and weight gain if consumed in excess. You should balance the health benefits of natural sweeteners with their caloric content and potential impact on metabolic health.
Caloric Content and Weight Management
Artificial sweeteners contain little to no calories, making them a popular choice for weight management and reducing overall caloric intake. Natural sweeteners like honey, maple syrup, and agave nectar provide calories and can contribute to increased energy consumption. Studies indicate that substituting sugar with low-calorie artificial sweeteners may support weight loss or maintenance by lowering daily calorie intake.
Impact on Blood Sugar Levels
Artificial sweeteners like aspartame, sucralose, and stevia typically have minimal to no impact on blood sugar levels, making them suitable for individuals with diabetes. Natural sweeteners such as honey, maple syrup, and agave nectar contain carbohydrates that can raise blood glucose, albeit often at lower glycemic indexes than refined sugar. Monitoring the glycemic response and individual tolerance is crucial for effective blood sugar management when choosing between artificial and natural sweeteners.
Safety and Regulatory Status
Artificial sweeteners like aspartame, sucralose, and saccharin are approved by regulatory agencies such as the FDA and EFSA, with extensive safety evaluations confirming their use within established acceptable daily intake limits. Natural sweeteners like stevia and monk fruit extract are generally recognized as safe (GRAS) but may have varying regulatory statuses depending on the country. Your choice between artificial and natural sweeteners should consider these safety assessments and regulatory approvals to ensure safe consumption.
Taste and Culinary Uses
Artificial sweeteners like aspartame and sucralose provide intense sweetness with minimal calories, often delivering a taste profile that can be slightly metallic or bitter, making them ideal for low-calorie beverages and sugar-free products. Natural sweeteners such as honey, maple syrup, and agave offer complex flavors and varying sweetness levels, enhancing baked goods, sauces, and beverages with their rich, distinctive taste. Culinary use depends on heat stability and flavor compatibility; natural sweeteners generally caramelize and add moisture, while artificial sweeteners maintain sweetness without altering texture but may lose potency or develop off-flavors when heated.
Choosing the Right Sweetener for Your Needs
Choosing the right sweetener depends on your health goals, dietary restrictions, and taste preferences. Natural sweeteners like honey, maple syrup, and stevia offer antioxidants and minerals but can impact blood sugar levels differently than artificial sweeteners such as aspartame or sucralose, which provide sweetness without calories. Understanding how each sweetener interacts with your metabolism ensures you make an informed choice that aligns with your lifestyle and nutritional needs.
Artificial sweeteners vs natural sweeteners Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com