Cane sugar and beet sugar are chemically similar, both primarily composed of sucrose, but they differ in taste nuances and agricultural origins, with cane sugar derived from sugarcane and beet sugar from sugar beets. Your choice between the two may depend on factors like environmental impact, processing methods, and personal preference for flavor subtlety.
Table of Comparison
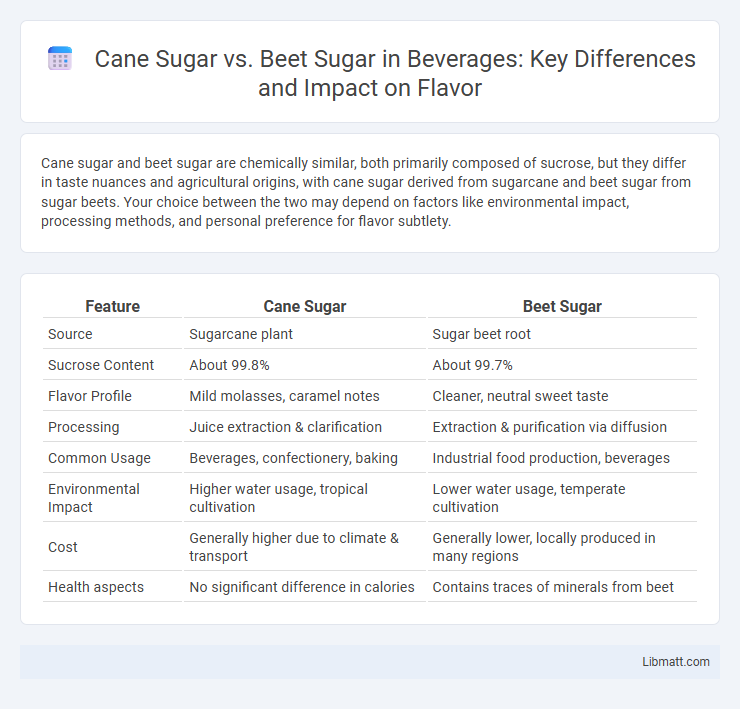
| Feature | Cane Sugar | Beet Sugar |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Sugarcane plant | Sugar beet root |
| Sucrose Content | About 99.8% | About 99.7% |
| Flavor Profile | Mild molasses, caramel notes | Cleaner, neutral sweet taste |
| Processing | Juice extraction & clarification | Extraction & purification via diffusion |
| Common Usage | Beverages, confectionery, baking | Industrial food production, beverages |
| Environmental Impact | Higher water usage, tropical cultivation | Lower water usage, temperate cultivation |
| Cost | Generally higher due to climate & transport | Generally lower, locally produced in many regions |
| Health aspects | No significant difference in calories | Contains traces of minerals from beet |
Introduction to Cane Sugar and Beet Sugar
Cane sugar and beet sugar are two primary sources of sucrose derived from different plants: sugarcane and sugar beets. Both undergo refining processes that produce chemically identical white granulated sugar, yet their agricultural origins influence flavor nuances and production sustainability. Understanding the distinction between cane and beet sugar helps you make informed choices based on sourcing, environmental impact, and taste preferences.
Botanical Origins and Growth Regions
Cane sugar is derived from the tall tropical and subtropical grass species Saccharum officinarum, predominantly cultivated in countries like Brazil, India, and Thailand. Beet sugar comes from the root crop Beta vulgaris, grown mainly in temperate regions such as Europe, Russia, and the United States. Understanding these distinct botanical origins and growth regions helps you make informed choices about the source and environmental impact of your sugar.
Extraction and Production Processes
Cane sugar is extracted from sugarcane through crushing, juice clarification, evaporation, and crystallization, emphasizing high fiber removal and molasses separation. Beet sugar production involves slicing beets, diffusing sugar through hot water, purifying the juice via carbonation or liming, then evaporating and crystallizing, highlighting beet pulp utilization and waste by-products management. Both methods rely on refining steps to produce sucrose, but differ in raw material processing and energy consumption patterns.
Chemical Composition Differences
Cane sugar and beet sugar both contain sucrose as their primary chemical component, but they differ in minor impurities and trace elements due to their botanical origins. Cane sugar often contains higher levels of molasses impurities, such as calcium, potassium, and magnesium salts, which can affect flavor and crystallization. Beet sugar typically exhibits a higher ash content and different nitrogen compounds, influencing its refining process and end-product characteristics.
Flavor Profiles and Culinary Uses
Cane sugar offers a rich, complex flavor with subtle molasses notes, making it ideal for baking and beverages where depth of taste is desired. Beet sugar has a cleaner, more neutral sweetness, suitable for recipes requiring a pure sugar result without altering the flavor profile. Understanding these distinctions helps you choose the best sugar for your culinary creations, enhancing the final taste and texture.
Nutritional Value Comparison
Cane sugar and beet sugar are nearly identical in nutritional value, both containing about 16 calories per teaspoon and consisting primarily of sucrose with no significant vitamins or minerals. Minor differences in trace elements exist due to their plant origin, but these variations are nutritionally negligible and do not impact blood sugar levels differently. Your choice between cane and beet sugar should focus on taste preference or processing methods rather than nutritional benefits.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Cane sugar production generally requires more water and land compared to beet sugar, contributing to deforestation and habitat loss in tropical regions where sugarcane is cultivated. Beet sugar, grown in temperate climates, typically has a lower environmental footprint due to more efficient use of water and less pesticide application. If you prioritize sustainability, choosing beet sugar may reduce your environmental impact while supporting more eco-friendly agricultural practices.
Economic Aspects and Global Trade
Cane sugar dominates global sugar production, accounting for approximately 80% of the market, driven by favorable growing conditions in tropical regions such as Brazil and India, which are the top exporters. Beet sugar, primarily produced in temperate climates like the European Union and the United States, benefits from government subsidies and supports local economies but faces higher production costs compared to cane sugar. Your choice between cane and beet sugar may influence economic outcomes depending on regional availability, price fluctuations, and trade policies affecting international sugar markets.
Health Considerations and Myths
Cane sugar and beet sugar have nearly identical chemical compositions, primarily sucrose, making their health effects similar when consumed in moderation. Some myths suggest beet sugar may contain harmful residues from pesticides or have a lower nutritional value, but rigorous testing ensures both types meet food safety standards and provide no significant nutritional difference. Understanding these facts helps you make informed choices without being misled by misconceptions about their health impacts.
Choosing Between Cane Sugar and Beet Sugar
Choosing between cane sugar and beet sugar depends on factors such as flavor, processing, and environmental impact. Cane sugar often has a slightly richer taste and is preferred in gourmet baking, while beet sugar is typically more cost-effective and has a similar sweetness level. Consumers concerned with sustainability might consider cane sugar from certified organic farms or beet sugar produced with energy-efficient methods.
Cane sugar vs beet sugar Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com