Private label products are created by a manufacturer and sold under your brand name, allowing you to control branding and marketing without handling production. Co-manufacturing involves collaborating with a manufacturer to produce products according to your specifications, offering greater customization and input in the product development process.
Table of Comparison
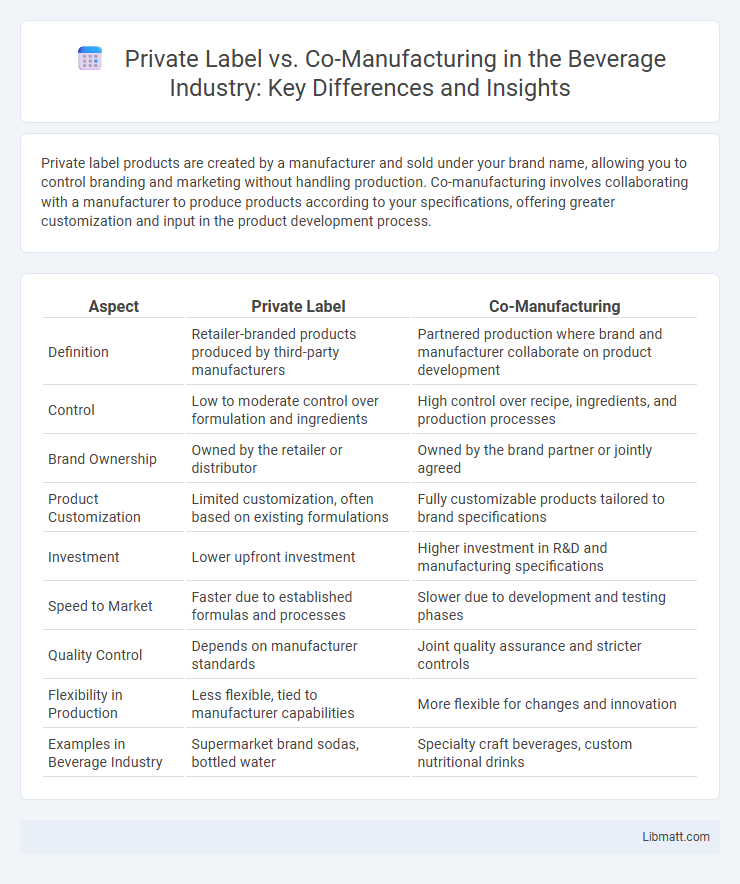
| Aspect | Private Label | Co-Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Retailer-branded products produced by third-party manufacturers | Partnered production where brand and manufacturer collaborate on product development |
| Control | Low to moderate control over formulation and ingredients | High control over recipe, ingredients, and production processes |
| Brand Ownership | Owned by the retailer or distributor | Owned by the brand partner or jointly agreed |
| Product Customization | Limited customization, often based on existing formulations | Fully customizable products tailored to brand specifications |
| Investment | Lower upfront investment | Higher investment in R&D and manufacturing specifications |
| Speed to Market | Faster due to established formulas and processes | Slower due to development and testing phases |
| Quality Control | Depends on manufacturer standards | Joint quality assurance and stricter controls |
| Flexibility in Production | Less flexible, tied to manufacturer capabilities | More flexible for changes and innovation |
| Examples in Beverage Industry | Supermarket brand sodas, bottled water | Specialty craft beverages, custom nutritional drinks |
Introduction to Private Label and Co-Manufacturing
Private label products are manufactured by one company and sold under another brand's name, allowing retailers to offer exclusive items without owning production facilities. Co-manufacturing involves collaboration between a brand owner and a manufacturer to develop and produce customized products, sharing expertise and resources. Both strategies enable businesses to expand product lines and reduce manufacturing costs while maintaining control over branding and quality.
Defining Private Label: An Overview
Private label refers to products manufactured by one company and sold under another company's brand, allowing retailers to offer exclusive items without managing production. This strategy enables control over product design, pricing, and marketing while leveraging the manufacturer's expertise. Private label products often enhance brand identity and improve profit margins for retailers.
What is Co-Manufacturing?
Co-manufacturing involves partnering with a third-party manufacturer to produce products according to your specifications, allowing you to maintain control over branding and product development while leveraging their production expertise. This arrangement helps you scale manufacturing without investing in your own facilities, optimizing cost-efficiency and speed to market. Unlike private labeling, co-manufacturing provides more customization and involvement in the product formulation process.
Key Differences Between Private Label and Co-Manufacturing
Private label involves a retailer branding and selling products created by a third-party manufacturer under their own label, allowing control over marketing and pricing while outsourcing production. Co-manufacturing entails a partnership where both the brand owner and manufacturer collaborate on product design, formulation, and production processes, sharing expertise and responsibilities. Key differences include the level of control over product innovation, with private label focusing on brand identity and co-manufacturing emphasizing joint development and customization.
Cost Implications: Private Label vs Co-Manufacturing
Private label products typically offer lower upfront costs as companies purchase finished goods ready for branding, reducing expenses related to production facilities and labor. Co-manufacturing involves higher initial investment due to customization, quality control, and collaboration with manufacturers on product development, which can lead to increased per-unit costs. Evaluating cost implications requires balancing lower initial expenditures of private label options against potential long-term benefits and pricing flexibility offered by co-manufacturing partnerships.
Control and Customization Options
Private label offers limited control and customization since products are pre-made by manufacturers, allowing minimal changes to formulations or packaging. Co-manufacturing provides extensive control, enabling Your brand to tailor product specifications, ingredients, and packaging design to meet specific market demands. This flexibility in co-manufacturing ensures a unique product that aligns closely with Your brand identity and customer preferences.
Time-to-Market Comparison
Private label products typically offer a faster time-to-market because the designs and formulations are pre-established, allowing brands to quickly customize packaging and launch. Co-manufacturing often involves longer lead times due to collaboration on product development, formulation adjustments, and quality control processes. Your choice will impact how quickly your product reaches consumers, balancing customization needs against speed.
Quality Assurance and Compliance
Private label products rely on the retailer's specifications, making quality assurance dependent on the manufacturer's adherence to set standards and certifications. Co-manufacturing involves a collaborative process where both parties actively ensure compliance with industry regulations, enhancing product consistency and safety. Your business benefits from co-manufacturing by gaining greater control and transparency in quality assurance and regulatory compliance.
Choosing the Right Strategy for Your Business
Selecting between private label and co-manufacturing hinges on factors such as control over product development, production capacity, and brand differentiation. Private label allows businesses to market pre-existing products under their brand, optimizing speed to market and lower costs. Co-manufacturing involves partnering with manufacturers to create custom products, offering enhanced customization and innovation aligned with specific business goals.
Conclusion: Which Approach Suits Your Brand?
Choosing between private label and co-manufacturing depends on your brand's control preferences and customization needs. Private label offers faster market entry with pre-designed products, ideal for brands prioritizing speed and lower development costs. Co-manufacturing suits brands seeking unique formulations and greater product differentiation, allowing deeper involvement in product development and quality assurance.
Private label vs co-manufacturing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com