Nitrogen infusion creates smaller, smoother bubbles that give your beverage a creamier texture and a rich, velvety mouthfeel, while carbonation produces larger bubbles resulting in a sharper, more effervescent fizz. Choosing between nitrogen and carbonation depends on the desired taste and texture experience you want in your drink.
Table of Comparison
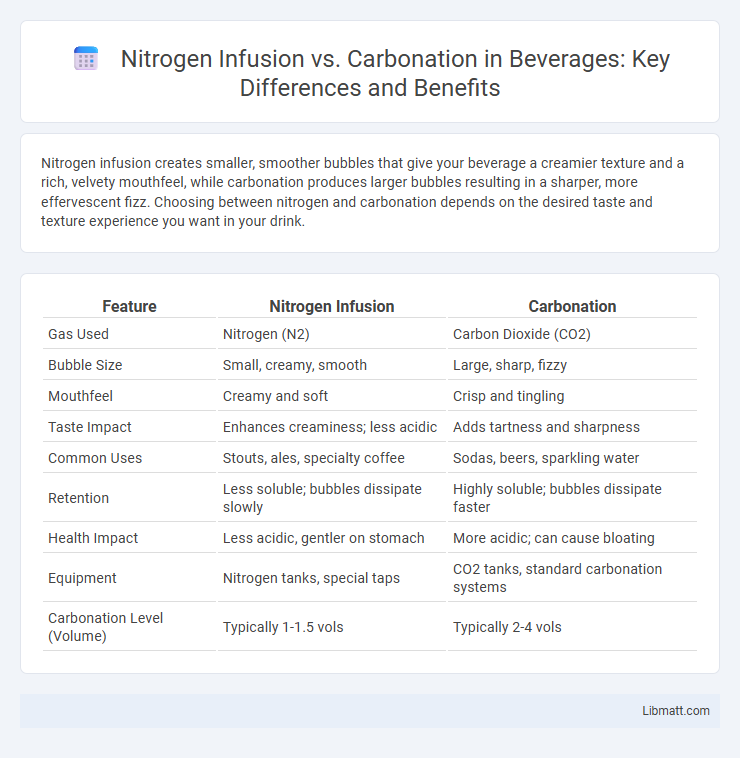
| Feature | Nitrogen Infusion | Carbonation |
|---|---|---|
| Gas Used | Nitrogen (N2) | Carbon Dioxide (CO2) |
| Bubble Size | Small, creamy, smooth | Large, sharp, fizzy |
| Mouthfeel | Creamy and soft | Crisp and tingling |
| Taste Impact | Enhances creaminess; less acidic | Adds tartness and sharpness |
| Common Uses | Stouts, ales, specialty coffee | Sodas, beers, sparkling water |
| Retention | Less soluble; bubbles dissipate slowly | Highly soluble; bubbles dissipate faster |
| Health Impact | Less acidic, gentler on stomach | More acidic; can cause bloating |
| Equipment | Nitrogen tanks, special taps | CO2 tanks, standard carbonation systems |
| Carbonation Level (Volume) | Typically 1-1.5 vols | Typically 2-4 vols |
Introduction to Nitrogen Infusion and Carbonation
Nitrogen infusion involves dissolving nitrogen gas into beverages, creating smaller bubbles that result in a creamier texture and smoother mouthfeel, commonly found in stouts and cold brews. Carbonation, on the other hand, uses carbon dioxide to produce larger bubbles that give drinks a sharper, more effervescent sensation, typical in sodas and sparkling waters. Both techniques influence flavor perception and texture but achieve distinct sensory experiences through different gas properties and solubility levels.
The Science Behind Nitrogen Infusion
Nitrogen infusion involves dissolving nitrogen gas into a liquid under high pressure, creating smaller bubbles that result in a smoother, creamier texture compared to carbonation, which uses carbon dioxide to produce larger, fizzier bubbles. The lower solubility of nitrogen gas in liquid causes a dense, velvety mouthfeel and a cascading visual effect when poured. This science-driven infusion technique enhances sensory experience by altering bubble size, gas solubility, and fluid dynamics.
How Traditional Carbonation Works
Traditional carbonation works by dissolving carbon dioxide (CO2) gas into liquid under high pressure, creating bubbles that give beverages their fizzy and tangy texture. This process involves infusing CO2 until it reaches equilibrium, resulting in the characteristic sharp effervescence of sodas and sparkling waters. Understanding how traditional carbonation operates helps you appreciate the smoother, creamier mouthfeel that nitrogen infusion provides as an alternative.
Key Differences: Nitrogen Infusion vs Carbonation
Nitrogen infusion results in smaller, denser bubbles that create a smoother, creamier mouthfeel compared to carbonation, which produces larger, sharper bubbles that add a fizzy, effervescent texture. Nitrogen-infused beverages, such as stouts and cold brews, offer a rich, velvety taste due to nitrogen's lower solubility and slower dissolution in liquid, whereas carbonation relies on dissolved carbon dioxide to achieve a tangy, crisp sensation. The dispensing process for nitrogen typically requires specialized equipment like a nitrogen widget or gas blend, while carbonation can be achieved with simpler CO2 systems.
Effects on Beverage Texture and Mouthfeel
Nitrogen infusion produces smaller bubbles than carbonation, creating a smooth, creamy texture and a velvety mouthfeel that enhances the perception of richness in beverages. Carbonation generates larger, sharper bubbles that provide a crisp, effervescent sensation, adding a refreshing and lively feel to drinks. The choice between nitrogen and carbonation significantly influences the tactile experience, with nitrogen favoring softness and carbonation emphasizing buoyancy and sparkle.
Flavor Profile: Nitrogen vs Carbon Dioxide
Nitrogen infusion creates a smoother, creamier mouthfeel with subtle, rounded flavors compared to the sharp, tangy notes produced by carbon dioxide carbonation. Your beverage infused with nitrogen tends to have a less acidic taste and a richer, velvety texture, enhancing malt and chocolate undertones in drinks like stouts. Carbonation, on the other hand, delivers a bright, crisp sensation and pronounced acidity that highlights fruity and citrus flavors in sodas and ales.
Popular Beverages Utilizing Nitrogen Infusion
Popular beverages utilizing nitrogen infusion include stout beers like Guinness, cold brew coffee, and certain craft sodas that deliver a smooth, creamy texture and rich mouthfeel. Nitrogen bubbles are smaller than carbon dioxide, creating a dense, velvety foam and less acidity compared to traditional carbonation, which enhances flavor without overwhelming bitterness. Your experience with nitrogen-infused drinks often highlights a unique tactile sensation and a visually appealing cascading effect that distinguishes them from carbonated alternatives.
Health and Preservation Aspects
Nitrogen infusion reduces oxidation in beverages, preserving flavor and freshness longer than carbonation, which introduces dissolved CO2 that can lower pH and potentially accelerate spoilage in some cases. Nitrogen bubbles create a smooth texture without acidity, beneficial for sensitive stomachs and reducing bloating compared to carbonated drinks. Preservation with nitrogen also minimizes microbial growth by limiting oxygen exposure, enhancing shelf life without relying on preservatives.
Consumer Preferences and Trends
Consumer preferences reveal a growing demand for nitrogen-infused beverages due to their smooth, creamy texture and reduced bitterness, especially in coffee and beer markets. Market trends indicate a rising interest in nitrogenated drinks among millennials and Gen Z, who value unique sensory experiences and premium quality. While carbonation remains popular for its effervescence and refreshing qualities, the niche appeal of nitrogen infusion continues to expand, driven by innovative flavors and artisanal brands.
Future Innovations in Beverage Infusion
Future innovations in beverage infusion will likely enhance nitrogen and carbonation techniques by integrating advanced microbubble technology to improve texture and flavor retention. Research into hybrid gas infusions combining nitrogen and CO2 aims to create unique sensory profiles and increased shelf stability. Smart infusion systems using AI-driven controls promise precise gas blending tailored to consumer preferences and beverage types.
Nitrogen infusion vs carbonation Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com