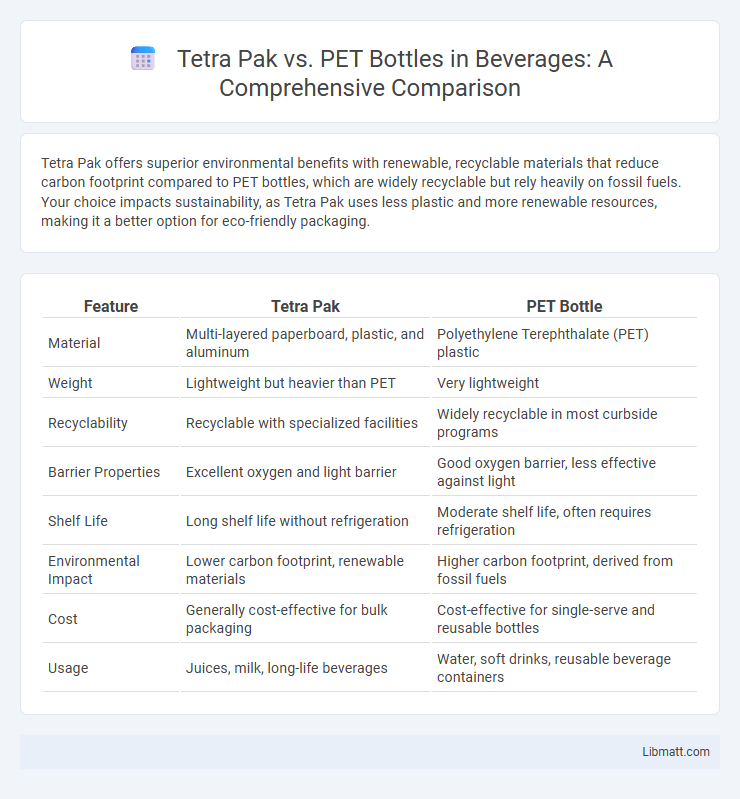
Tetra Pak offers superior environmental benefits with renewable, recyclable materials that reduce carbon footprint compared to PET bottles, which are widely recyclable but rely heavily on fossil fuels. Your choice impacts sustainability, as Tetra Pak uses less plastic and more renewable resources, making it a better option for eco-friendly packaging.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Tetra Pak | PET Bottle |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Multi-layered paperboard, plastic, and aluminum | Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) plastic |
| Weight | Lightweight but heavier than PET | Very lightweight |
| Recyclability | Recyclable with specialized facilities | Widely recyclable in most curbside programs |
| Barrier Properties | Excellent oxygen and light barrier | Good oxygen barrier, less effective against light |
| Shelf Life | Long shelf life without refrigeration | Moderate shelf life, often requires refrigeration |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint, renewable materials | Higher carbon footprint, derived from fossil fuels |
| Cost | Generally cost-effective for bulk packaging | Cost-effective for single-serve and reusable bottles |
| Usage | Juices, milk, long-life beverages | Water, soft drinks, reusable beverage containers |
Introduction: Tetra Pak vs PET Bottle
Tetra Pak cartons offer superior environmental benefits compared to PET bottles, as they are primarily made from renewable materials and are designed for efficient recycling. PET bottles, while lightweight and transparent, rely heavily on fossil fuels and contribute significantly to plastic pollution due to lower recycling rates. The choice between Tetra Pak and PET bottles impacts sustainability, carbon footprint, and waste management practices in packaging industries.
Material Composition and Structure
Tetra Pak cartons are primarily composed of layers of paperboard, polyethylene, and aluminum foil, providing a lightweight yet durable multi-material barrier that protects liquid products from light, oxygen, and contamination. PET bottles consist of polyethylene terephthalate, a single plastic polymer known for its clarity, strength, and recyclability but with less barrier protection against oxygen and light compared to Tetra Pak. Your selection between Tetra Pak or PET bottles will depend on the need for product preservation, shelf life, and environmental impact considerations related to material composition and structure.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Tetra Pak cartons generally have a lower carbon footprint compared to PET bottles due to their renewable paperboard content and lighter weight, which reduces transportation emissions. While PET bottles are widely recyclable, they often face lower recycling rates and frequently contribute to plastic pollution in oceans and landfills. Your choice of packaging significantly influences environmental sustainability by promoting materials that minimize waste and resource consumption.
Cost Comparison: Production and Transportation
Tetra Pak cartons typically incur higher production costs due to their composite materials and complex manufacturing process compared to PET bottles, which benefit from lower raw material expenses and faster production cycles. Transportation costs favor Tetra Pak as its lightweight, flat-pack design reduces volume and weight, leading to more efficient shipping and lower carbon emissions relative to bulky PET bottles. The overall cost-effectiveness depends on balancing Tetra Pak's savings in logistics against PET's lower initial production expenditure.
Shelf Life and Product Preservation
Tetra Pak cartons provide extended shelf life for beverages and perishable products by offering excellent barrier protection against oxygen, light, and moisture, effectively preserving freshness without refrigeration. PET bottles, while recyclable and clear for product visibility, have limited barrier properties, resulting in shorter shelf life and faster flavor degradation when exposed to air and light. Your choice between Tetra Pak and PET bottles directly impacts product preservation and storage requirements, especially for sensitive liquid products.
Consumer Safety and Health Considerations
Tetra Pak cartons utilize multiple layers including paperboard, polyethylene, and aluminum foil to create a strong barrier protecting contents from light, air, and bacteria, which helps maintain product freshness and reduces the risk of contamination. PET bottles are made from polyethylene terephthalate, a recyclable plastic known for its durability but can potentially leach antimony or bisphenol A under certain conditions, raising concerns about chemical migration into beverages. Both packaging types undergo rigorous food safety testing, though Tetra Pak's multi-layer protection offers enhanced shielding against microbial contamination and prolonged shelf life without preservatives.
Recycling and Waste Management
Tetra Pak cartons combine paperboard, polyethylene, and aluminum layers, requiring specialized facilities for effective recycling, leading to limited recycling rates in some regions. PET bottles are widely accepted in curbside recycling programs and can be reprocessed into new containers or polyester fibers with high recovery efficiency. Waste management strategies prioritize PET bottles for their straightforward sorting and recycling processes, while Tetra Pak's composite materials pose challenges that demand investment in advanced separation technologies.
Convenience and Usability for Consumers
Tetra Pak cartons offer lightweight, resealable packaging that enhances convenience for consumers on the go, with easy storage and minimal spillage compared to rigid PET bottles. PET bottles provide transparency, allowing you to see the product inside, and feature screw caps that enable easy resealing and portability. Both options cater to usability, but Tetra Pak's slim design optimizes shelf space, while PET bottles excel in durability and recyclability.
Industry Adoption and Market Trends
Tetra Pak packaging has gained significant adoption in the dairy and beverage industries due to its sustainability and extended shelf life benefits, with global market shares exceeding 40% in liquid food packaging segments. PET bottles dominate the bottled water and carbonated soft drink markets, driven by consumer preference for transparency and recyclability, capturing over 60% of single-serve beverage packaging demand worldwide. Emerging market trends indicate a rising shift towards eco-friendly alternatives, with innovations in recyclable polymers and bioplastics promoting Tetra Pak and PET bottle use in circular economy models.
Future Innovations and Emerging Technologies
Future innovations in Tetra Pak packaging emphasize biodegradable materials and smart packaging technologies, such as embedded sensors for freshness monitoring and blockchain-enabled supply chain transparency. PET bottles are advancing with enhanced recyclability via chemical recycling and lightweighting technologies that reduce carbon footprint without compromising durability. Your choice between Tetra Pak and PET bottles will hinge on emerging eco-friendly solutions and digital innovations driving sustainability in packaging.
Tetra Pak vs PET bottle Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com