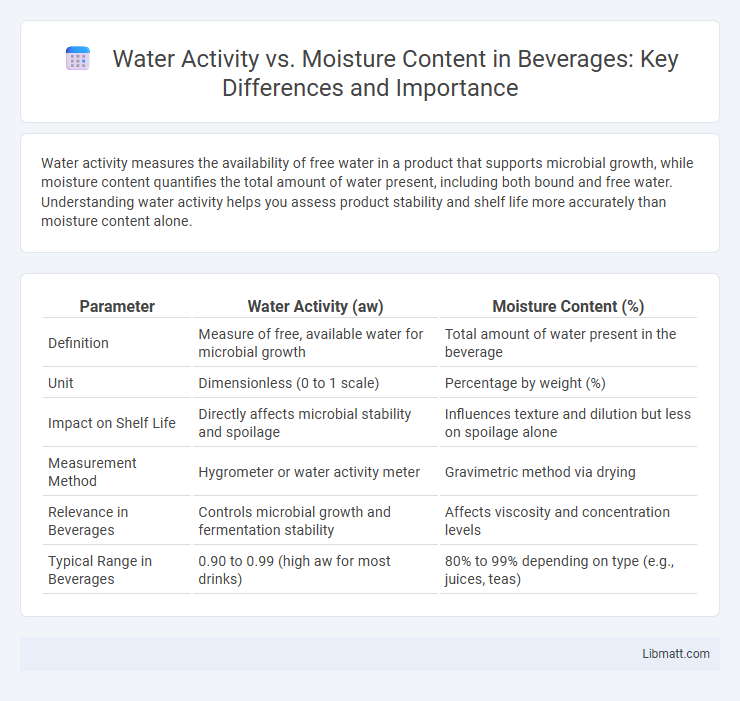
Water activity measures the availability of free water in a product that supports microbial growth, while moisture content quantifies the total amount of water present, including both bound and free water. Understanding water activity helps you assess product stability and shelf life more accurately than moisture content alone.
Table of Comparison
| Parameter | Water Activity (aw) | Moisture Content (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measure of free, available water for microbial growth | Total amount of water present in the beverage |
| Unit | Dimensionless (0 to 1 scale) | Percentage by weight (%) |
| Impact on Shelf Life | Directly affects microbial stability and spoilage | Influences texture and dilution but less on spoilage alone |
| Measurement Method | Hygrometer or water activity meter | Gravimetric method via drying |
| Relevance in Beverages | Controls microbial growth and fermentation stability | Affects viscosity and concentration levels |
| Typical Range in Beverages | 0.90 to 0.99 (high aw for most drinks) | 80% to 99% depending on type (e.g., juices, teas) |
Introduction to Water Activity and Moisture Content
Water activity (aw) measures the availability of free water in a product for microbial growth, chemical reactions, and enzymatic activity, while moisture content quantifies the total amount of water present. Both parameters are critical in food preservation, safety, and quality control, influencing shelf life and texture. Understanding water activity helps you predict microbial stability better than moisture content alone, as it reflects the water's chemical potential and usability in the product.
Defining Water Activity in Foods
Water activity (aw) in foods measures the availability of free water for microbial growth and chemical reactions, distinct from total moisture content. It is quantified on a scale from 0 to 1, representing the ratio of the vapor pressure of water in the food to that of pure water under the same conditions. Controlling water activity is crucial for ensuring food safety, shelf life, and quality stability, as it directly influences microbial spoilage and enzymatic activity.
Understanding Moisture Content
Moisture content refers to the percentage of water present in a material, crucial for assessing food quality, stability, and shelf life. Unlike water activity, which measures the availability of water for microbial growth, moisture content quantifies total water regardless of its state or binding. Accurate determination of moisture content ensures proper processing, packaging, and preservation in various industries, particularly food production.
Key Differences Between Water Activity and Moisture Content
Water activity (aw) measures the availability of free water for microbial growth and chemical reactions, ranging from 0 to 1, whereas moisture content quantifies the total amount of water, including bound and free water, as a percentage of the product's weight. Water activity directly influences food stability, shelf life, and safety by controlling microbial growth, while moisture content alone does not predict spoilage or microbial risk. Understanding the distinction between aw and moisture content is crucial for optimizing food processing, packaging, and storage conditions.
How Water Activity Influences Food Safety
Water activity (aw) directly impacts microbial growth and food safety by determining the availability of free water for bacteria, yeast, and mold, with most pathogens requiring an aw above 0.85 to proliferate. Foods with low moisture content can still have high water activity, posing a risk if aw exceeds safe thresholds, while controlling aw through drying, salting, or adding humectants effectively inhibits spoilage and pathogenic microbes. Managing your product's water activity is essential to extend shelf life and prevent foodborne illnesses by controlling microbial contamination.
The Role of Moisture Content in Product Quality
Moisture content significantly influences product quality by directly affecting water activity, which governs microbial growth, enzymatic reactions, and chemical stability. Precise control of moisture content ensures optimal water activity levels, reducing spoilage and extending shelf life. In food and pharmaceutical products, maintaining appropriate moisture content is critical for preserving texture, flavor, and overall safety.
Measurement Methods: Water Activity vs Moisture Content
Water activity is commonly measured using dew point hygrometers or capacitance sensors that detect the vapor pressure of water in a product, providing insight into microbial stability and shelf life. Moisture content is determined through methods such as oven drying, Karl Fischer titration, or near-infrared spectroscopy, quantifying the total amount of water present in a sample. While water activity reflects the availability of free water for microbial growth, moisture content measures the absolute water quantity, making these complementary metrics crucial for food safety and quality control.
Impact on Shelf Life and Spoilage
Water activity (aw) directly influences the shelf life and spoilage rate of food products by controlling microbial growth and enzymatic reactions, while moisture content measures the total water present without indicating availability for these processes. Low water activity inhibits bacterial, yeast, and mold growth, extending shelf life even if moisture content is relatively high, making aw a more critical factor in food preservation. Your ability to manage water activity effectively ensures reduced spoilage risks and prolonged product stability compared to relying solely on moisture content data.
Applications in the Food Industry
Water activity (aw) and moisture content critically influence food quality, safety, and shelf life, with water activity directly affecting microbial growth and enzymatic reactions while moisture content determines texture and weight. Food industry applications use water activity measurements to control preservation methods, optimize packaging, and prevent spoilage, ensuring product stability and consumer safety. Understanding these parameters allows you to tailor processing and storage conditions for diverse products like baked goods, dairy, and dried fruits, enhancing both product performance and regulatory compliance.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Parameter
Water activity (aw) is a critical parameter for predicting microbial growth, chemical stability, and shelf life, whereas moisture content quantifies the total water present in a product. Selecting the right parameter depends on the specific application: water activity is preferred for assessing food safety and quality control, while moisture content is useful for processing and formulation purposes. Accurate measurement of water activity provides better insight into product stability and spoilage risk compared to moisture content alone.
Water activity vs moisture content Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com