Cold extraction preserves delicate flavors and nutrients by avoiding heat, making it ideal for sensitive ingredients like herbs and fresh fruits. Hot extraction uses heat to accelerate solubility and release more robust flavors, perfect for extracting oils, caffeine, or compounds from tougher materials.
Table of Comparison
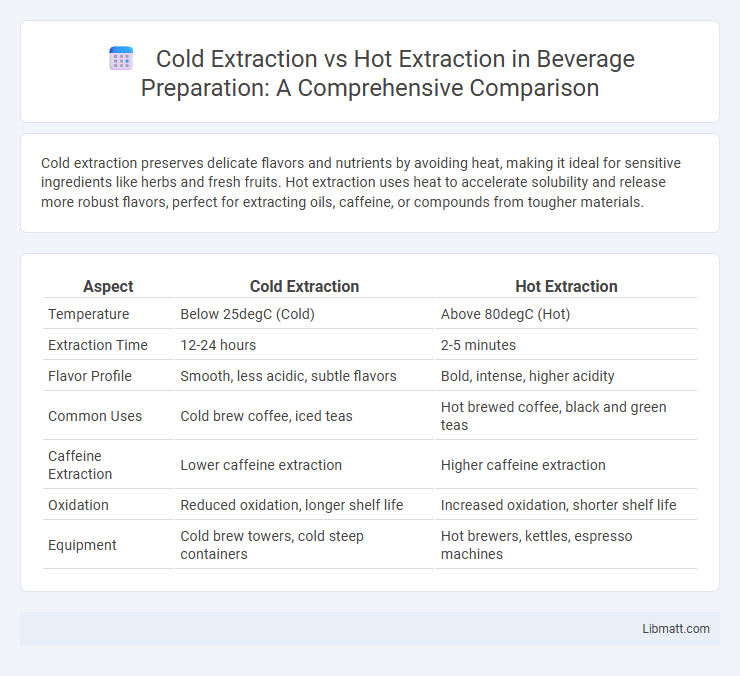
| Aspect | Cold Extraction | Hot Extraction |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Below 25degC (Cold) | Above 80degC (Hot) |
| Extraction Time | 12-24 hours | 2-5 minutes |
| Flavor Profile | Smooth, less acidic, subtle flavors | Bold, intense, higher acidity |
| Common Uses | Cold brew coffee, iced teas | Hot brewed coffee, black and green teas |
| Caffeine Extraction | Lower caffeine extraction | Higher caffeine extraction |
| Oxidation | Reduced oxidation, longer shelf life | Increased oxidation, shorter shelf life |
| Equipment | Cold brew towers, cold steep containers | Hot brewers, kettles, espresso machines |
Introduction to Extraction Methods
Cold extraction preserves delicate flavors and nutrients by using low temperatures, preventing heat-sensitive compounds from degrading. Hot extraction accelerates the process through higher temperatures, enhancing the release of oils, caffeine, or active compounds but may compromise subtle flavors. Understanding these differences helps you select the optimal method for maximizing quality and potency in your extraction.
Understanding Cold Extraction
Cold extraction preserves the natural flavors and nutritional compounds of ingredients by using lower temperatures, preventing degradation and oxidation. This method is especially beneficial for extracting volatile oils, antioxidants, and delicate nutrients found in herbs, fruits, and coffee. Cold extraction yields a smoother, less bitter taste compared to hot extraction, which uses heat to speed up the process but can alter flavor profiles and reduce nutrient content.
Understanding Hot Extraction
Hot extraction uses elevated temperatures to increase the solubility and release of compounds from plant materials, enhancing the yield and potency of the extract. This method is ideal for extracting heat-stable bioactive compounds efficiently, often utilized in herbal tinctures and essential oil production. Your choice of hot extraction affects the flavor profile and concentration, making it essential for tailored herbal preparations.
Key Differences Between Cold and Hot Extraction
Cold extraction preserves delicate flavors and nutrients by using low temperatures, preventing heat-sensitive compounds from degradation, making it ideal for fresh herbs and delicate materials. Hot extraction uses elevated temperatures to expedite the release of compounds, increasing yield and efficiency but potentially altering flavor profiles and reducing heat-sensitive nutrient content. Understanding these key differences helps you choose the most suitable method for your desired quality and extraction goals.
Impact on Nutrient Preservation
Cold extraction preserves delicate nutrients such as vitamin C, antioxidants, and enzymes by minimizing exposure to heat, which can degrade these sensitive compounds. Hot extraction often leads to nutrient loss due to thermal degradation but enhances the availability of certain phytochemicals like polyphenols and carotenoids through heat-induced cell wall breakdown. Balancing extraction methods can optimize nutrient retention depending on the desired bioactive compounds in juices or herbal preparations.
Flavor and Aroma Variations
Cold extraction preserves delicate flavor compounds and volatile aromatics, resulting in brighter, more nuanced coffee profiles with enhanced floral and fruity notes. Hot extraction intensifies bold flavors and robust aromas through higher temperature infusion, often producing richer, more caramelized and smoky undertones. These temperature-driven differences significantly influence the sensory experience, dictating whether the coffee emphasizes subtle complexity or full-bodied intensity.
Extraction Efficiency and Yield
Cold extraction preserves delicate compounds by using low temperatures, resulting in higher-quality extracts with better flavor and aroma but typically lower yield compared to hot extraction. Hot extraction increases extraction efficiency by utilizing heat to dissolve more compounds quickly, maximizing yield but potentially degrading sensitive phytochemicals. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize extraction efficiency and maximum yield or preserving the integrity of heat-sensitive components.
Equipment and Energy Requirements
Cold extraction requires specialized equipment such as cold press machines or ultrasonic extractors that operate at low temperatures to preserve bioactive compounds, resulting in lower energy consumption compared to hot extraction. Hot extraction involves the use of heated vessels like reflux extractors, Soxhlet apparatus, or autoclaves, which demand higher energy input to maintain elevated temperatures and prolonged extraction cycles. Energy efficiency varies significantly between these methods, with cold extraction favoring thermal-sensitive materials and reduced operational costs, while hot extraction achieves faster solvent penetration but incurs higher energy expenses.
Applications in Food and Beverage Industries
Cold extraction preserves delicate flavors and nutrients, making it ideal for producing premium-quality juices, cold brew coffee, and herbal infusions in the food and beverage industries. Hot extraction accelerates the release of compounds like caffeine and essential oils, which is beneficial for making teas, broths, and flavored syrups where robust flavors and higher extraction yields are desired. The choice between cold and hot extraction affects product taste profiles, nutrient retention, and shelf life, influencing formulation strategies in beverage manufacturing and food processing.
Choosing the Right Extraction Method
Choosing the right extraction method depends on the desired flavor profile, chemical composition, and application of the product. Cold extraction preserves delicate compounds and aromas by using low temperatures, ideal for teas, oils, and herbal infusions, while hot extraction uses heat to maximize yield and extract robust flavors or active ingredients from raw materials like coffee or spices. Understanding your specific needs for aroma, potency, and stability will guide you in selecting the optimal extraction technique for your product.
Cold extraction vs hot extraction Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com