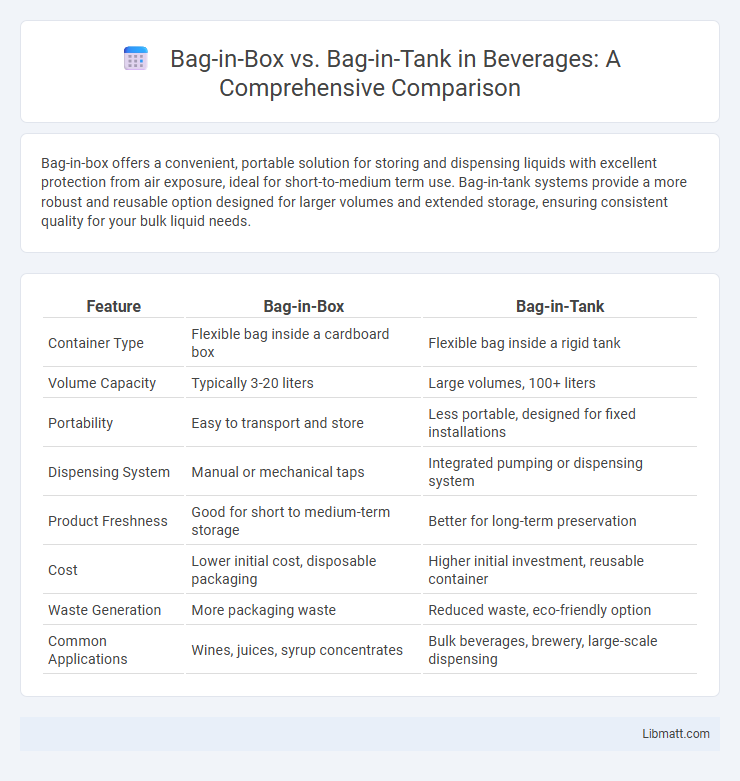
Bag-in-box offers a convenient, portable solution for storing and dispensing liquids with excellent protection from air exposure, ideal for short-to-medium term use. Bag-in-tank systems provide a more robust and reusable option designed for larger volumes and extended storage, ensuring consistent quality for your bulk liquid needs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bag-in-Box | Bag-in-Tank |
|---|---|---|
| Container Type | Flexible bag inside a cardboard box | Flexible bag inside a rigid tank |
| Volume Capacity | Typically 3-20 liters | Large volumes, 100+ liters |
| Portability | Easy to transport and store | Less portable, designed for fixed installations |
| Dispensing System | Manual or mechanical taps | Integrated pumping or dispensing system |
| Product Freshness | Good for short to medium-term storage | Better for long-term preservation |
| Cost | Lower initial cost, disposable packaging | Higher initial investment, reusable container |
| Waste Generation | More packaging waste | Reduced waste, eco-friendly option |
| Common Applications | Wines, juices, syrup concentrates | Bulk beverages, brewery, large-scale dispensing |
Overview of Bag-in-Box and Bag-in-Tank Systems
Bag-in-Box (BiB) systems consist of a flexible plastic bladder housed inside a cardboard box, commonly used for storing and dispensing liquids like wine, juice, or chemicals efficiently while minimizing oxidation and contamination. Bag-in-Tank (BiT) systems integrate a flexible bag within a rigid tank structure, offering enhanced durability and greater volume capacity for industrial liquids, oils, or beverages, with improved protection against punctures and environmental conditions. Both systems optimize storage and distribution by reducing packaging waste and ensuring product freshness, but BiT is favored for heavy-duty applications requiring robust containment.
Key Differences Between Bag-in-Box vs Bag-in-Tank
Bag-in-box packaging features a flexible plastic bag housed within a cardboard box, allowing for easy storage, portability, and cost-effective shipping, while bag-in-tank systems utilize a sealed, rigid container designed for industrial-scale dispensing and long-term storage of liquids. Bag-in-box solutions are commonly used in food and beverage industries for products like wine, juice, and sauces, emphasizing convenience and preservation, whereas bag-in-tank systems cater to sectors requiring bulk liquid handling, such as chemicals or pharmaceuticals, prioritizing safety and contamination control. The primary differences lie in scale, application, and material rigidity, with bag-in-box optimized for consumer-friendly packaging and bag-in-tank suited for large-volume, controlled dispensing.
Packaging Materials and Structural Design
Bag-in-box packaging uses a flexible plastic bag encased in a sturdy cardboard box, offering excellent protection from air and light to preserve product freshness. Bag-in-tank systems incorporate a flexible liner within a rigid tank, providing greater durability and suitability for larger-volume storage or transportation while maintaining airtight conditions. Your choice depends on packaging material preferences and structural design needs for shelf life and handling efficiency.
Space Efficiency and Storage Considerations
Bag-in-box packaging offers superior space efficiency by compactly storing liquids in flexible bags within sturdy boxes, allowing for easy stacking and optimal use of storage areas, especially in retail or warehouse settings. In contrast, bag-in-tank systems require more substantial structural support and space due to rigid tanks, which may limit storage density and increase footprint. Your choice between the two should align with available storage space and handling logistics to maximize operational efficiency.
Dispensing Methods and User Convenience
Bag-in-box systems utilize a collapsible bag inside a carton, allowing gravity or pump dispensing that reduces oxidation and prolongs product freshness, making it suitable for wines and liquid foods. Bag-in-tank solutions integrate flexible bags directly within stainless steel tanks, enabling more precise control with automated pumps and carbonation for beverages like craft beers. Both methods enhance user convenience by minimizing waste and simplifying refills, but bag-in-tank offers superior pressure management and consistent pour quality.
Product Preservation and Shelf Life
Bag-in-box packaging utilizes an airtight, collapsible bag that prevents oxygen exposure, significantly extending the product's shelf life by reducing oxidation and contamination risks. Bag-in-tank systems maintain product freshness by enclosing the liquid within a sealed bag inside a pressurized tank, allowing for controlled dispensing without introducing air. Both methods offer superior preservation compared to traditional packaging, but bag-in-tank often provides enhanced protection in high-volume or industrial dispensing scenarios.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Bag-in-box packaging significantly reduces plastic waste due to its lightweight and collapsible design, which lowers transportation emissions compared to rigid containers. Bag-in-tank systems enhance sustainability by allowing bulk dispensing, minimizing single-use packaging and reducing overall material consumption. Both solutions promote lower carbon footprints, but bag-in-tank proves more efficient for large-scale operations by optimizing refill processes and minimizing packaging waste.
Cost Comparison and Economic Benefits
Bag-in-box packaging generally offers lower upfront costs due to simpler materials and established manufacturing processes, making it a cost-effective option for businesses with moderate volume needs. Bag-in-tank systems, while initially more expensive due to durable tank components, provide long-term economic benefits through reduced waste, lower contamination risks, and extended product shelf life. Your choice between the two depends on balancing immediate expenses with potential savings in storage, handling, and product preservation.
Typical Applications in the Food and Beverage Industry
Bag-in-box packaging is commonly used for liquid food products such as wine, juice, and sauces, offering convenience and extended freshness through airtight sealing. Bag-in-tank systems are ideal for larger-scale applications like dairy, brewing, and industrial beverage processes, providing efficient storage and easy dispensing. You can optimize product handling and reduce contamination risks by selecting the appropriate packaging solution suited to your specific food and beverage application.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
Bag-in-box offers a cost-effective, lightweight option ideal for beverages and liquid products requiring extended shelf life with airtight sealing, while bag-in-tank provides a more robust, reusable solution suitable for industrial applications with larger volumes and frequent dispensing needs. Evaluating factors such as product type, volume requirements, environmental impact, and dispensing frequency is essential to determine the optimal packaging system. Selecting the right solution ensures product integrity, reduces waste, and improves operational efficiency.
Bag-in-box vs bag-in-tank Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com