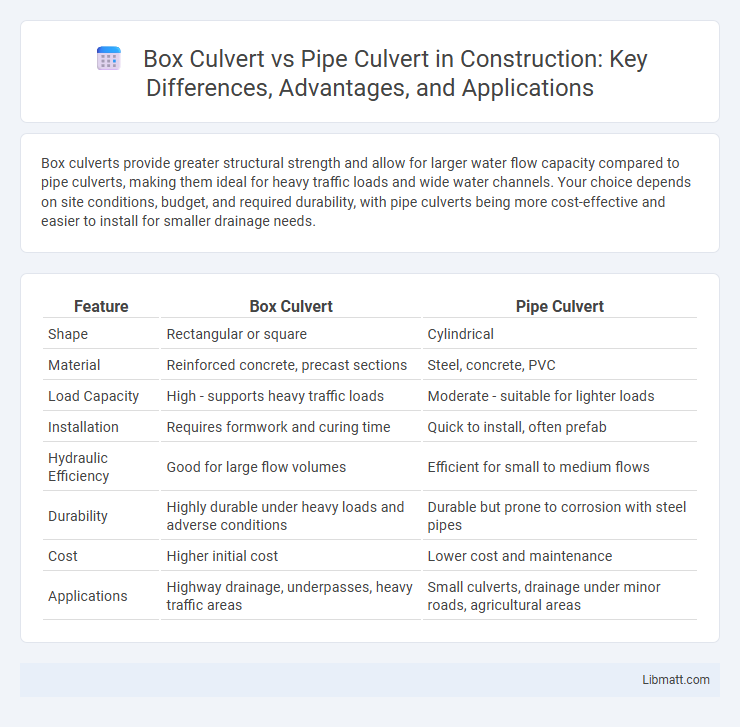
Box culverts provide greater structural strength and allow for larger water flow capacity compared to pipe culverts, making them ideal for heavy traffic loads and wide water channels. Your choice depends on site conditions, budget, and required durability, with pipe culverts being more cost-effective and easier to install for smaller drainage needs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Box Culvert | Pipe Culvert |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | Rectangular or square | Cylindrical |
| Material | Reinforced concrete, precast sections | Steel, concrete, PVC |
| Load Capacity | High - supports heavy traffic loads | Moderate - suitable for lighter loads |
| Installation | Requires formwork and curing time | Quick to install, often prefab |
| Hydraulic Efficiency | Good for large flow volumes | Efficient for small to medium flows |
| Durability | Highly durable under heavy loads and adverse conditions | Durable but prone to corrosion with steel pipes |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower cost and maintenance |
| Applications | Highway drainage, underpasses, heavy traffic areas | Small culverts, drainage under minor roads, agricultural areas |
Introduction to Box Culverts and Pipe Culverts
Box culverts are rectangular or square-shaped structures made from reinforced concrete, commonly used for drainage and roadway underpasses due to their high load-bearing capacity and ease of installation. Pipe culverts consist of circular pipes, typically made from materials like concrete, steel, or plastic, favored for efficient water flow and cost-effective solutions in smaller spans. Both culvert types play crucial roles in managing water flow and supporting infrastructure, with choice depending on site conditions, load requirements, and hydraulic performance.
Structural Design Differences
Box culverts feature a rectangular cross-section designed to support heavy loads with flat slabs and beams, offering superior load distribution and resistance to bending. Pipe culverts typically use circular sections, optimized for soil cover and hydraulic capacity, relying on the surrounding backfill for structural support rather than inherent rigidity. The structural design of box culverts allows for higher load-bearing capacity and easier integration with roadways, while pipe culverts prioritize ease of installation and cost-effectiveness under less demanding load conditions.
Material Selection and Durability
Box culverts are typically constructed from reinforced concrete, offering high compressive strength and excellent durability against heavy loads and harsh environmental conditions. Pipe culverts are commonly made from materials like corrugated steel, HDPE, or concrete, each providing varying resistance to corrosion, abrasion, and chemical exposure depending on the site requirements. Material selection for both culvert types should prioritize soil conditions, load-bearing capacity, and expected lifespan to ensure structural integrity and minimize maintenance costs.
Hydraulic Performance Comparison
Box culverts often provide superior hydraulic performance compared to pipe culverts due to their larger cross-sectional area and smoother flow transition, reducing velocity and minimizing head loss. Pipe culverts may experience higher friction losses and are more prone to sediment buildup, affecting flow capacity and increasing maintenance. The rectangular shape of box culverts allows better accommodation of varying flow conditions, enhancing overall stormwater management efficiency.
Installation Process and Time Requirements
Box culverts typically require extensive excavation and formwork, leading to longer installation times compared to pipe culverts, which can be quickly laid using trenching methods. Pipe culverts, often made of precast concrete or corrugated metal, offer faster installation with minimal surface disruption, making them ideal for projects with tight schedules. Your choice between these options should consider site conditions and project timelines to optimize construction efficiency.
Cost Analysis: Box vs Pipe Culverts
Box culverts generally have higher initial costs due to their larger size, complex formwork, and increased material requirements compared to pipe culverts. Pipe culverts, made from materials like reinforced concrete, steel, or plastic, often provide a cost-effective solution for small to medium spans because of easier installation and lower material usage. Life-cycle cost considerations favor pipe culverts in scenarios with simpler load conditions, while box culverts may offer better long-term value for larger spans and heavy traffic due to superior structural capacity.
Maintenance and Inspection Needs
Box culverts require more frequent inspection due to their larger surface area and potential for debris accumulation, which can lead to blockages or structural damage. Pipe culverts generally have lower maintenance needs because of their smoother interior surfaces, which facilitate better flow and reduce sediment build-up. Both types demand regular monitoring for cracks, joint integrity, and signs of corrosion or erosion to ensure long-term functionality and safety.
Suitability for Various Site Conditions
Box culverts, made from reinforced concrete, are ideal for sites requiring large clear openings and heavy load support, commonly used in urban areas with constrained space and shallow cover. Pipe culverts, typically constructed from steel, concrete, or plastic, suit locations with limited hydraulic requirement and are preferred for ease of installation in less restrictive environments or rural settings. Site soil conditions, water flow volume, and load demands influence the choice between box and pipe culvert designs for optimal performance and longevity.
Lifespan and Long-Term Performance
Box culverts typically offer a longer lifespan and superior long-term performance due to their reinforced concrete construction, which provides greater structural strength and durability against heavy loads and environmental stress. Pipe culverts, often made from materials like corrugated metal or plastic, may have shorter lifespans and require more frequent maintenance or replacement, especially in areas prone to corrosion or mechanical damage. Choosing the right culvert for your project depends on expected load conditions, environmental factors, and long-term maintenance considerations.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Box culverts typically have a larger footprint and require more concrete, which can increase environmental impact through higher carbon emissions during production. Pipe culverts generally use less material and promote better water flow, reducing habitat disruption and sediment buildup, making them more sustainable options for stormwater management. Choosing the appropriate culvert type can enhance Your project's environmental sustainability by minimizing ecological disturbance and supporting natural water ecosystems.
Box culvert vs pipe culvert Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com