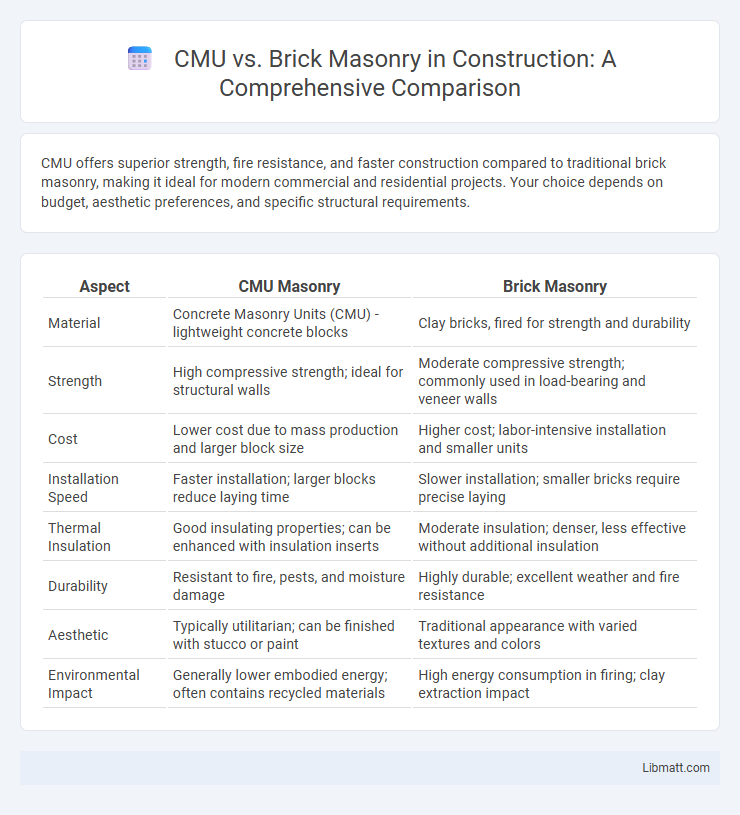
CMU offers superior strength, fire resistance, and faster construction compared to traditional brick masonry, making it ideal for modern commercial and residential projects. Your choice depends on budget, aesthetic preferences, and specific structural requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | CMU Masonry | Brick Masonry |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Concrete Masonry Units (CMU) - lightweight concrete blocks | Clay bricks, fired for strength and durability |
| Strength | High compressive strength; ideal for structural walls | Moderate compressive strength; commonly used in load-bearing and veneer walls |
| Cost | Lower cost due to mass production and larger block size | Higher cost; labor-intensive installation and smaller units |
| Installation Speed | Faster installation; larger blocks reduce laying time | Slower installation; smaller bricks require precise laying |
| Thermal Insulation | Good insulating properties; can be enhanced with insulation inserts | Moderate insulation; denser, less effective without additional insulation |
| Durability | Resistant to fire, pests, and moisture damage | Highly durable; excellent weather and fire resistance |
| Aesthetic | Typically utilitarian; can be finished with stucco or paint | Traditional appearance with varied textures and colors |
| Environmental Impact | Generally lower embodied energy; often contains recycled materials | High energy consumption in firing; clay extraction impact |
Overview of CMU and Brick Masonry
Concrete Masonry Units (CMU) are modular, hollow or solid concrete blocks known for their strength, durability, and cost-effectiveness in construction. Brick masonry involves the use of uniform, fired clay bricks that offer aesthetic appeal, thermal insulation, and traditional structural reliability. Your choice between CMU and brick masonry depends on factors such as project budget, desired appearance, and structural requirements.
Material Composition and Properties
CMU (Concrete Masonry Units) consist primarily of cement, aggregates, and water, providing high compressive strength, durability, and fire resistance. Brick masonry is made from clay or shale, fired at high temperatures, resulting in excellent thermal insulation, aesthetic appeal, and moderate compressive strength. Both materials offer distinct advantages: CMU excels in structural load-bearing applications, while brick masonry is preferred for its weather resistance and decorative versatility.
Structural Strength and Durability
CMU (Concrete Masonry Units) typically offer higher structural strength due to their uniform composition and ability to be reinforced with steel and grout, making them ideal for load-bearing walls. Brick masonry, while durable and resistant to weathering, generally has lower compressive strength compared to CMU and relies heavily on the quality of mortar joints for stability. The durability of CMU is enhanced by its resistance to fire, pests, and moisture, whereas brick masonry provides excellent thermal mass and long-term weather resistance, but may require more maintenance to address mortar degradation.
Construction Techniques and Methods
CMU (Concrete Masonry Unit) construction involves stacking interlocking concrete blocks, often reinforced with steel rods and filled with grout for enhanced structural integrity. Brick masonry employs traditional clay bricks laid in mortar joints, requiring precise alignment and skilled labor to ensure uniform bonding patterns and durability. CMU techniques enable faster construction and improved load-bearing capacity, while brick masonry emphasizes aesthetic finish and thermal insulation properties.
Cost Comparison: CMU vs Brick Masonry
CMU (Concrete Masonry Unit) typically offers a lower initial cost compared to brick masonry due to faster installation times and reduced labor expenses. Brick masonry involves higher material and labor costs but provides superior aesthetic appeal and durability, which may increase long-term value. Assessing Your project budget and design preferences helps determine whether the cost savings of CMU outweigh the premium finish of brick masonry.
Insulation and Energy Efficiency
Concrete masonry units (CMU) typically offer lower insulation values compared to brick masonry due to their denser, more porous structure, often requiring added insulation layers to meet energy-efficient standards. Brick masonry naturally provides better thermal mass, helping regulate indoor temperatures by absorbing and slowly releasing heat, which can reduce heating and cooling costs. Enhancing CMU walls with rigid foam or insulated cores significantly improves energy efficiency, making it competitive with brick masonry in sustainable building applications.
Design Flexibility and Aesthetic Options
CMU (Concrete Masonry Unit) offers greater design flexibility with its modular sizes, allowing for varied wall thicknesses, shapes, and structural configurations. Brick masonry provides rich aesthetic options through diverse colors, textures, and bonding patterns, enhancing architectural character. Combining CMU's structural adaptability with brick's visual appeal optimizes both function and design versatility in construction projects.
Maintenance Requirements and Lifespan
CMU (concrete masonry units) typically require less maintenance than brick masonry due to their uniformity and resistance to cracking, reducing repair frequency. Brick masonry offers a longer lifespan, often exceeding 100 years, thanks to its natural durability and weather resistance, whereas CMU may have a lifespan around 50-70 years with proper upkeep. Your choice between CMU and brick masonry should consider maintenance capabilities and desired longevity for optimal performance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
CMU (Concrete Masonry Units) typically have a higher embodied energy compared to brick masonry due to the cement content and energy-intensive manufacturing processes. Brick masonry often utilizes natural clay and can incorporate recycled materials, resulting in lower carbon emissions and better biodegradability. Sustainable construction favors bricks for their thermal efficiency and longer lifespan, reducing the overall environmental footprint.
Common Applications and Best Uses
CMU masonry is commonly used in commercial and industrial buildings, retaining walls, and load-bearing structures due to its high compressive strength and affordability. Brick masonry excels in residential homes, decorative facades, and historical restorations because of its aesthetic appeal and durability against weather conditions. Both materials are chosen based on structural requirements, cost considerations, and desired architectural style.
CMU vs brick masonry Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com