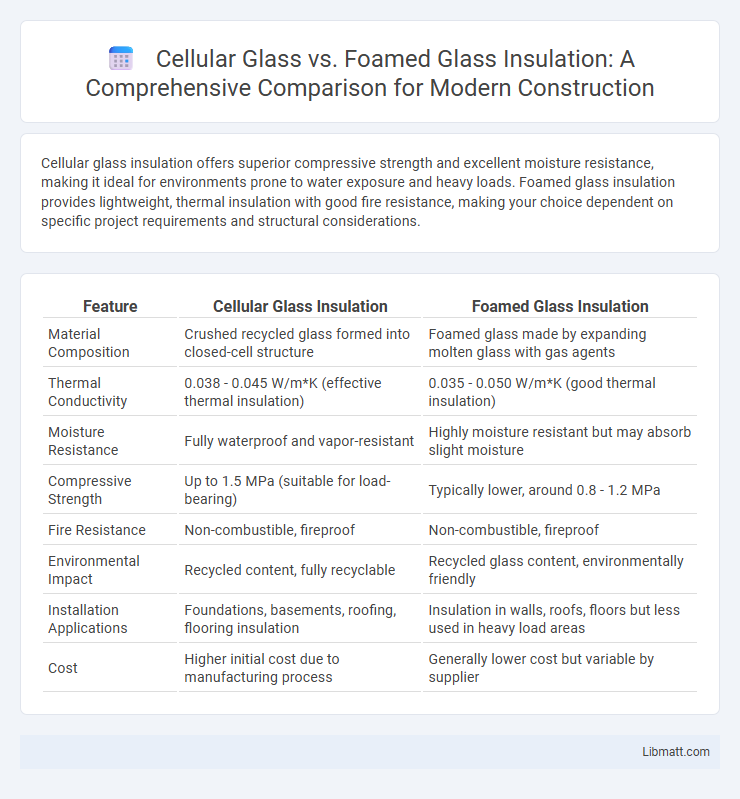
Cellular glass insulation offers superior compressive strength and excellent moisture resistance, making it ideal for environments prone to water exposure and heavy loads. Foamed glass insulation provides lightweight, thermal insulation with good fire resistance, making your choice dependent on specific project requirements and structural considerations.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cellular Glass Insulation | Foamed Glass Insulation |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Crushed recycled glass formed into closed-cell structure | Foamed glass made by expanding molten glass with gas agents |
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.038 - 0.045 W/m*K (effective thermal insulation) | 0.035 - 0.050 W/m*K (good thermal insulation) |
| Moisture Resistance | Fully waterproof and vapor-resistant | Highly moisture resistant but may absorb slight moisture |
| Compressive Strength | Up to 1.5 MPa (suitable for load-bearing) | Typically lower, around 0.8 - 1.2 MPa |
| Fire Resistance | Non-combustible, fireproof | Non-combustible, fireproof |
| Environmental Impact | Recycled content, fully recyclable | Recycled glass content, environmentally friendly |
| Installation Applications | Foundations, basements, roofing, flooring insulation | Insulation in walls, roofs, floors but less used in heavy load areas |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to manufacturing process | Generally lower cost but variable by supplier |
Introduction to Cellular Glass and Foamed Glass Insulation
Cellular glass insulation, made from crushed glass fused into a rigid, impermeable structure, offers exceptional moisture resistance and high compressive strength, making it ideal for waterproofing and thermal insulation in industrial applications. Foamed glass insulation, created by heating glass with foaming agents to produce a lightweight, porous material, provides excellent thermal performance combined with fire resistance and durability. Your choice between these materials depends on specific project requirements such as load-bearing capacity, moisture exposure, and thermal efficiency.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Cellular glass insulation is made from crushed glass that is heated and foamed with a gas to create a rigid, closed-cell structure, providing exceptional moisture and fire resistance. Foamed glass insulation undergoes a similar process but typically involves adding foaming agents or gases during manufacturing to produce varied cell sizes and densities; this results in lightweight, durable materials ideal for thermal insulation. Understanding these differences in composition and manufacturing helps you select the best insulation solution for thermal efficiency and durability needs.
Physical and Mechanical Properties
Cellular glass insulation features a closed-cell structure providing superior compressive strength, high moisture resistance, and excellent dimensional stability, making it ideal for load-bearing and waterproof applications. Foamed glass insulation, while also lightweight and moisture-resistant, generally exhibits lower compressive strength and is better suited for thermal insulation where less mechanical load is involved. Your choice between cellular glass and foamed glass insulation should consider the specific physical demands, including durability and structural stress, to ensure optimal performance.
Thermal Performance and Insulation Capabilities
Cellular glass insulation offers superior thermal performance due to its closed-cell structure, providing excellent resistance to heat transfer and moisture infiltration, which enhances energy efficiency in buildings. Foamed glass insulation, while also featuring a closed-cell composition, tends to have slightly lower insulation capabilities but excels in lightweight applications and impact resistance. Your choice between cellular glass and foamed glass should consider specific thermal conductivity values and the required insulation effectiveness for your project.
Moisture Resistance and Water Absorption
Cellular glass insulation offers superior moisture resistance and zero water absorption due to its closed-cell structure, making it ideal for environments prone to humidity or water exposure. Foamed glass insulation, while also resistant to moisture, may absorb minimal water over time because of its slightly more porous composition. For your project, choosing cellular glass ensures long-term durability and protection against moisture-related damage.
Fire Resistance and Safety Ratings
Cellular glass insulation offers superior fire resistance, classified as non-combustible with a high safety rating due to its closed-cell structure that prevents flame spread and smoke generation. Foamed glass insulation, while also non-combustible, may vary in fire performance depending on density and binder materials, often achieving fire ratings suitable for building codes but generally lower than cellular glass. Both materials contribute to passive fire protection, but cellular glass is preferred in applications demanding the highest fire safety standards.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Cellular glass insulation stands out for its recyclability and non-toxic composition, making it an environmentally sustainable choice with zero off-gassing and long lifespan. Foamed glass insulation also offers strong sustainability benefits by utilizing recycled glass content and providing excellent thermal efficiency that reduces energy consumption over time. Your choice between the two should consider the specific environmental requirements of your project, as both materials contribute to reducing carbon footprints through durability and reuse potential.
Installation Methods and Application Areas
Cellular glass insulation is typically installed using rigid panels or blocks that are glued or mechanically fastened to surfaces, making it ideal for below-grade applications, piping, and industrial settings due to its moisture resistance and compressive strength. Foamed glass insulation, often applied as loose-fill or molded shapes, offers versatility for void filling, cavity insulation, and lightweight structural support in roofing and flooring systems, benefiting from its thermal insulation and fire-resistant properties. Both materials excel in environments requiring durability and environmental protection, but cellular glass's rigid form suits precise installations, while foamed glass's adaptability accommodates irregular spaces.
Cost Comparison and Long-Term Value
Cellular glass insulation typically has a higher upfront cost compared to foamed glass due to its dense, closed-cell structure and superior durability. Foamed glass offers a more budget-friendly initial investment, but cellular glass provides greater long-term value by resisting moisture, fire, and chemical damage, reducing maintenance and replacement expenses. Your choice should weigh immediate budget constraints against the extended lifespan and reliability of cellular glass for optimal cost efficiency.
Choosing the Right Insulation: Cellular Glass vs Foamed Glass
Cellular glass insulation offers superior compressive strength, moisture resistance, and fireproof properties, making it ideal for industrial and underground applications requiring durability and long-term performance. Foamed glass insulation provides excellent thermal insulation with a lightweight, flexible structure suitable for residential or commercial projects where ease of installation and cost efficiency are priorities. Selecting between cellular glass and foamed glass depends on specific application demands such as environmental exposure, mechanical stress, and budget constraints.
Cellular glass vs foamed glass insulation Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com