Sheet membrane waterproofing offers a factory-made barrier that provides consistent thickness and durability, ideal for large surface areas, while liquid applied waterproofing conforms seamlessly to complex shapes and joints, creating a monolithic, fully adhered layer. Your choice depends on project specifics like substrate type, application conditions, and desired flexibility, ensuring optimal protection against moisture intrusion.
Table of Comparison
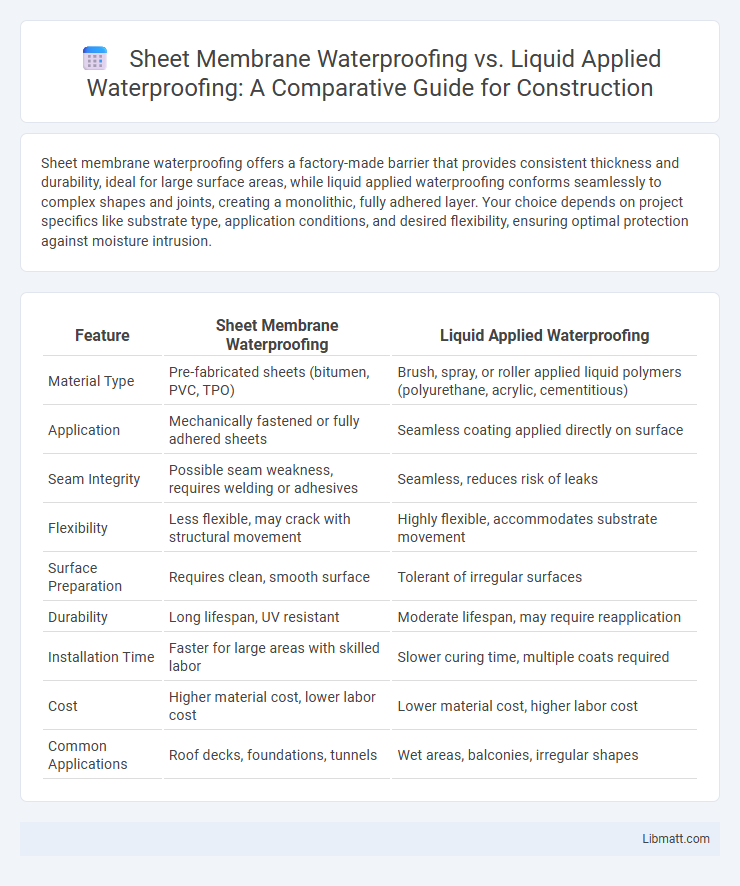
| Feature | Sheet Membrane Waterproofing | Liquid Applied Waterproofing |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Pre-fabricated sheets (bitumen, PVC, TPO) | Brush, spray, or roller applied liquid polymers (polyurethane, acrylic, cementitious) |
| Application | Mechanically fastened or fully adhered sheets | Seamless coating applied directly on surface |
| Seam Integrity | Possible seam weakness, requires welding or adhesives | Seamless, reduces risk of leaks |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, may crack with structural movement | Highly flexible, accommodates substrate movement |
| Surface Preparation | Requires clean, smooth surface | Tolerant of irregular surfaces |
| Durability | Long lifespan, UV resistant | Moderate lifespan, may require reapplication |
| Installation Time | Faster for large areas with skilled labor | Slower curing time, multiple coats required |
| Cost | Higher material cost, lower labor cost | Lower material cost, higher labor cost |
| Common Applications | Roof decks, foundations, tunnels | Wet areas, balconies, irregular shapes |
Introduction to Waterproofing Methods
Sheet membrane waterproofing involves the application of prefabricated sheets made from materials like bitumen, PVC, or TPO, offering a consistent barrier against water infiltration. Liquid applied waterproofing uses coatings such as polyurethane or acrylic that cure to form a seamless, flexible membrane, adapting well to complex surfaces. Your choice depends on factors like substrate type, area size, and environmental exposure to ensure optimal durability and protection.
Overview of Sheet Membrane Waterproofing
Sheet membrane waterproofing involves the use of pre-formed, flexible sheets made from materials such as bitumen, rubber, or PVC, applied to surfaces to create a durable, impermeable barrier against water infiltration. These membranes are typically heat-welded or mechanically fastened to ensure seamless coverage, providing high resistance to punctures and environmental damage. Commonly used in foundation walls, roofs, and below-grade structures, sheet membranes offer consistent thickness and reliable protection in a variety of construction applications.
Overview of Liquid Applied Waterproofing
Liquid applied waterproofing provides a seamless, flexible barrier that adapts to complex surfaces and structural movements, making it ideal for areas prone to cracks or irregular shapes. This method involves applying a fluid coating that cures to form a durable, monolithic membrane, enhancing adhesion to substrates and reducing the risk of leaks. Common materials include polyurethane, acrylics, and bituminous emulsions, which offer excellent resistance to water ingress, UV exposure, and weathering.
Key Material Differences
Sheet membrane waterproofing uses pre-formed rolls of synthetic materials like polyethylene or rubberized asphalt that provide a consistent thickness and stronger physical barrier against water intrusion. Liquid applied waterproofing involves spray or brush-on polymers, such as polyurethane or acrylics, which cure into a seamless, flexible coating that adapts to complex shapes and cracks. Understanding these key material differences helps you select the best solution for your project's surface type and waterproofing requirements.
Installation Process Comparison
Sheet membrane waterproofing involves rolling pre-fabricated sheets onto the substrate, requiring precise surface preparation and careful alignment to avoid seams and bubbles, ensuring a continuous barrier. Liquid applied waterproofing is applied as a fluid coating that cures to form a seamless membrane, allowing it to conform easily to complex shapes and details without joints. The installation of liquid membranes generally offers faster application times and greater adaptability to irregular surfaces compared to the more labor-intensive, rigid handling of sheet membranes.
Performance and Durability
Sheet membrane waterproofing offers consistent thickness and reliable barrier protection, ensuring superior resistance to punctures and UV degradation over time. Liquid applied waterproofing creates a seamless, monolithic membrane that adapts to complex shapes and cracks, enhancing flexibility and reducing the risk of leaks. Performance longevity in sheet membranes typically exceeds 20 years with proper installation, while liquid applied systems provide excellent durability but may require more frequent maintenance depending on environmental exposure.
Cost Analysis: Sheet vs Liquid Applied
Sheet membrane waterproofing generally has higher upfront material costs due to factory-produced rolls, but offers consistent thickness and faster installation, potentially reducing labor expenses. Liquid applied waterproofing tends to be more cost-effective initially with lower material prices and flexible application on complex surfaces, though it may require more preparation and curing time, influencing overall project duration and cost. Evaluating your project size and substrate complexity helps determine the most economical method for your waterproofing needs.
Ideal Applications for Each Method
Sheet membrane waterproofing is ideal for large, flat surfaces such as basements, tunnels, and foundations, providing a consistent barrier with uniform thickness and high durability. Liquid applied waterproofing suits complex shapes, vertical surfaces, and areas with intricate details, allowing seamless coverage and easy customization to irregular structures. Your choice depends on the project's surface type and complexity, optimizing protection against water infiltration in specific construction scenarios.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Sheet membrane waterproofing commonly faces challenges such as seam failures and improper adhesion, which can lead to water infiltration; these issues are mitigated by thorough substrate preparation and careful installation of overlapping sheets with compatible adhesives. Liquid applied waterproofing often encounters problems like uneven application and curing defects, resolved through the use of skilled applicators and strict adherence to manufacturer guidelines to ensure uniform thickness and complete coverage. Both methods require routine inspection and maintenance to detect early signs of damage and prolong the waterproofing system's service life.
Choosing the Right Waterproofing System
Selecting the right waterproofing system depends on project requirements, substrate type, and environmental conditions. Sheet membrane waterproofing offers consistent thickness and rapid installation suitable for large, flat surfaces, while liquid applied waterproofing provides superior adaptability to complex shapes and seamless coverage. Consider factors such as durability, flexibility, ease of application, and cost-effectiveness to ensure optimal protection against water intrusion.
Sheet membrane waterproofing vs liquid applied waterproofing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com