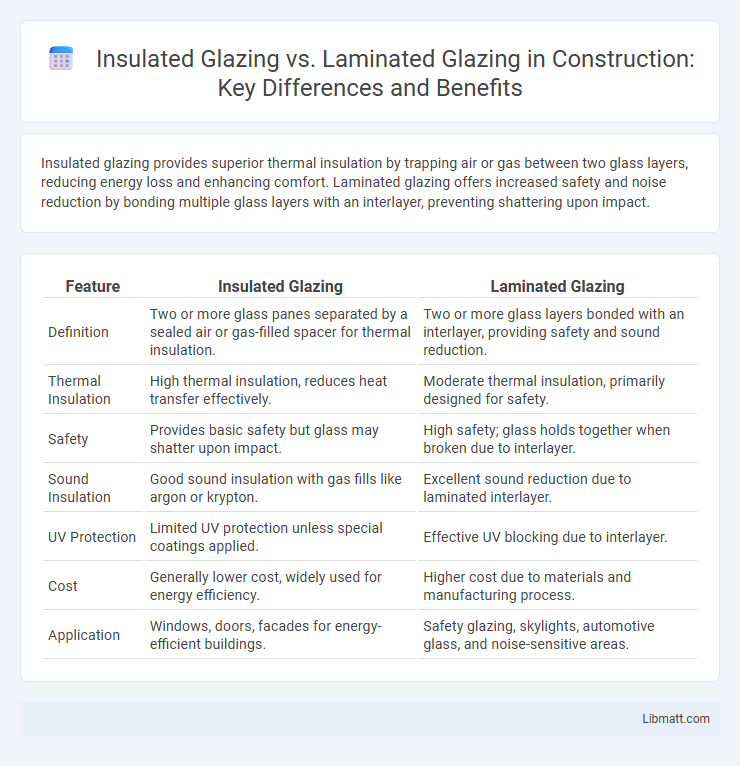
Insulated glazing provides superior thermal insulation by trapping air or gas between two glass layers, reducing energy loss and enhancing comfort. Laminated glazing offers increased safety and noise reduction by bonding multiple glass layers with an interlayer, preventing shattering upon impact.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Insulated Glazing | Laminated Glazing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Two or more glass panes separated by a sealed air or gas-filled spacer for thermal insulation. | Two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer, providing safety and sound reduction. |
| Thermal Insulation | High thermal insulation, reduces heat transfer effectively. | Moderate thermal insulation, primarily designed for safety. |
| Safety | Provides basic safety but glass may shatter upon impact. | High safety; glass holds together when broken due to interlayer. |
| Sound Insulation | Good sound insulation with gas fills like argon or krypton. | Excellent sound reduction due to laminated interlayer. |
| UV Protection | Limited UV protection unless special coatings applied. | Effective UV blocking due to interlayer. |
| Cost | Generally lower cost, widely used for energy efficiency. | Higher cost due to materials and manufacturing process. |
| Application | Windows, doors, facades for energy-efficient buildings. | Safety glazing, skylights, automotive glass, and noise-sensitive areas. |
Introduction to Insulated and Laminated Glazing
Insulated glazing consists of two or more glass panes separated by an air or gas-filled space, enhancing thermal insulation and reducing energy loss in buildings. Laminated glazing uses multiple layers of glass bonded with an interlayer, providing superior safety, sound reduction, and UV protection. These technologies serve distinct purposes, with insulated glazing optimizing energy efficiency and laminated glazing offering enhanced security and durability.
Definition and Composition of Insulated Glazing
Insulated glazing, also known as double or triple glazing, consists of two or more glass panes separated by a spacer filled with inert gas such as argon or krypton to enhance thermal insulation. The sealed air gap between the panes reduces heat transfer and improves energy efficiency compared to single glazing. This composition significantly lowers U-values, minimizing heat loss and condensation while contributing to soundproofing in building applications.
Definition and Composition of Laminated Glazing
Laminated glazing consists of two or more glass layers bonded together by an interlayer, typically made of polyvinyl butyral (PVB) or ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), offering enhanced safety and sound insulation. Unlike insulated glazing, which uses multiple glass panes separated by a gas-filled spacer for thermal efficiency, laminated glazing focuses on impact resistance and preventing glass shatter. Your choice between laminated and insulated glazing should consider factors like security, noise reduction, and energy performance based on specific needs.
Key Differences Between Insulated and Laminated Glazing
Insulated glazing consists of two or more glass panes separated by a spacer filled with air or gas, enhancing thermal insulation and reducing energy costs. Laminated glazing features a plastic interlayer between glass sheets, improving safety and soundproofing by preventing shattering upon impact. Your choice between insulated and laminated glazing depends on whether energy efficiency or security and noise reduction are the primary concerns.
Thermal Performance: Insulated vs Laminated Glazing
Insulated glazing offers superior thermal performance by incorporating multiple glass panes separated by a spacer filled with inert gas, significantly reducing heat transfer and improving energy efficiency. Laminated glazing, while primarily designed for safety and sound insulation, consists of two or more glass layers bonded with a plastic interlayer, providing moderate thermal resistance but less effective than insulated units. You should choose insulated glazing for maximum thermal efficiency in your building, whereas laminated glazing is better suited for enhanced security and noise reduction with some thermal benefits.
Sound Insulation Capabilities
Insulated glazing significantly reduces external noise by trapping air or inert gas between two or more glass panes, creating a barrier that dampens sound transmission. Laminated glazing enhances sound insulation through an interlayer of polyvinyl butyral (PVB) or ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), which absorbs sound waves and prevents them from passing through the glass. Your choice between insulated and laminated glazing depends on whether you prioritize thermal efficiency with sound reduction or enhanced acoustic performance with additional safety features.
Safety and Security Features Comparison
Insulated glazing enhances safety by reducing heat transfer and minimizing condensation, which helps maintain structural integrity, while laminated glazing offers superior security with its tough, shatter-resistant interlayer that holds glass fragments in place upon impact. Laminated glazing is particularly effective in preventing forced entry and protecting against impact hazards, making it ideal for high-security environments. Your choice depends on whether thermal performance or impact resistance is the primary concern for safety and security.
Energy Efficiency Assessment
Insulated glazing offers superior energy efficiency by reducing heat transfer through multiple glass layers separated by a gas-filled space, significantly lowering heating and cooling costs. Laminated glazing, while primarily designed for safety and sound insulation, provides limited thermal insulation compared to insulated glazing. Your energy efficiency assessment should favor insulated glazing when minimization of energy loss and enhanced thermal performance are priorities.
Cost Analysis and Value Considerations
Insulated glazing typically costs more upfront than laminated glazing due to its multiple glass panes and gas-filled spaces designed for superior thermal insulation, resulting in energy savings that enhance long-term value. Laminated glazing offers additional safety benefits by holding shards together upon impact, often at a lower initial price, but may not provide the same level of energy efficiency. Evaluating Your specific needs for energy performance versus safety and budget constraints will determine which glazing option delivers the best overall cost-effectiveness.
Choosing the Right Glazing Solution for Your Needs
Insulated glazing offers superior thermal performance by combining two or more glass panes separated by an air or gas-filled space, reducing heat transfer and enhancing energy efficiency. Laminated glazing features a layer of plastic interlayer between glass sheets, providing improved safety, sound insulation, and UV protection. Selecting the right glazing solution depends on priorities such as energy savings, impact resistance, noise reduction, and budget considerations.
Insulated glazing vs laminated glazing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com