Hollow core planks offer lightweight, high-strength flooring solutions with excellent load-bearing capacity and faster installation, making them ideal for large spans and industrial buildings. Solid slabs provide superior durability and sound insulation, suitable for structures requiring high impact resistance and minimal deflection; your choice depends on the specific structural and acoustic needs of your project.
Table of Comparison
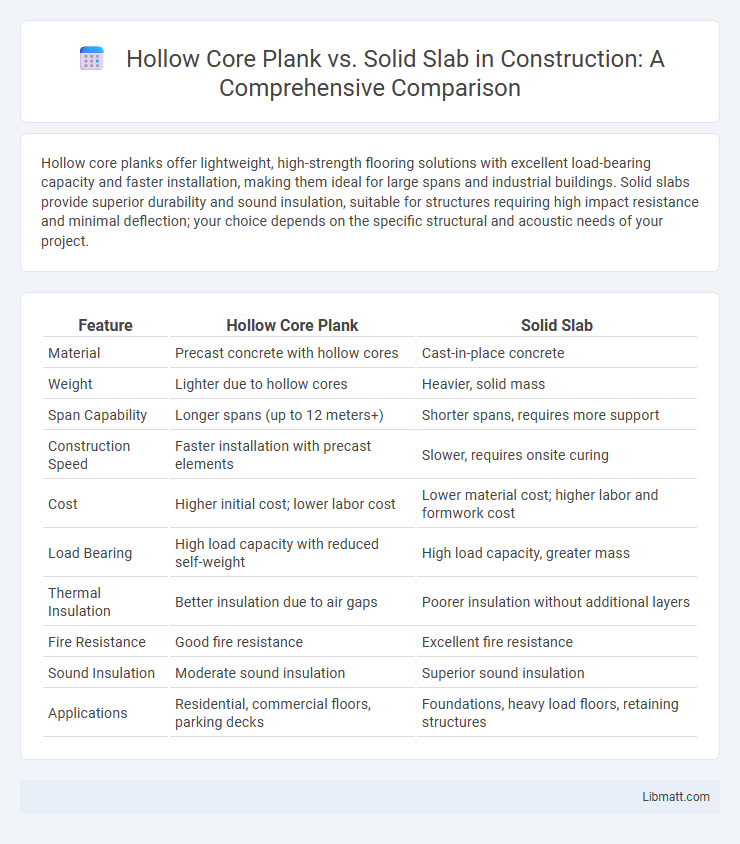
| Feature | Hollow Core Plank | Solid Slab |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Precast concrete with hollow cores | Cast-in-place concrete |
| Weight | Lighter due to hollow cores | Heavier, solid mass |
| Span Capability | Longer spans (up to 12 meters+) | Shorter spans, requires more support |
| Construction Speed | Faster installation with precast elements | Slower, requires onsite curing |
| Cost | Higher initial cost; lower labor cost | Lower material cost; higher labor and formwork cost |
| Load Bearing | High load capacity with reduced self-weight | High load capacity, greater mass |
| Thermal Insulation | Better insulation due to air gaps | Poorer insulation without additional layers |
| Fire Resistance | Good fire resistance | Excellent fire resistance |
| Sound Insulation | Moderate sound insulation | Superior sound insulation |
| Applications | Residential, commercial floors, parking decks | Foundations, heavy load floors, retaining structures |
Introduction to Hollow Core Plank and Solid Slab
Hollow core planks are precast concrete elements with continuous voids that reduce weight and material while maintaining structural strength, making them ideal for long-span flooring and roofing systems. Solid slabs are uniform, solid concrete slabs known for their high load-bearing capacity and versatility in various construction projects. Choosing between hollow core plank and solid slab depends on your project's structural requirements, span length, and budget considerations.
Structural Composition and Manufacturing Methods
Hollow core planks consist of pre-stressed concrete with continuous hollow voids running through their length, reducing weight while maintaining strength, and are manufactured using automated extrusion processes. Solid slabs are cast-in-place or precast concrete elements with a fully solid structure that provides uniform load distribution and higher mass for damping but involve longer curing times and more formwork. The manufacturing of hollow core planks emphasizes efficiency and repetitive precision through factory-controlled environments, whereas solid slabs require extensive on-site labor and formwork setup.
Weight and Load-Bearing Capacity Comparison
Hollow core planks offer a significantly lighter weight compared to solid slabs, reducing the overall dead load on the structure while maintaining efficient load-bearing capacity due to their pre-stressed concrete design. Solid slabs provide higher load-bearing capacity and greater resistance to point loads, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications where strength is critical. Understanding these differences helps you select the appropriate material based on structural weight constraints and load requirements.
Installation Process and Construction Speed
Hollow core planks offer a faster installation process due to their prefabricated nature, allowing large sections to be quickly placed and reducing on-site labor time when compared to solid slabs. Solid slabs require extensive formwork, reinforcement, and curing time, which can significantly extend the overall construction schedule. Choosing hollow core planks can streamline your project timeline, especially in fast-track construction, by minimizing on-site work and accelerating concrete setting.
Cost Analysis: Hollow Core vs Solid Slab
Hollow core planks generally offer a cost advantage over solid slabs due to reduced material usage and faster installation times, which lower labor expenses. Solid slabs, while often more expensive upfront, provide greater load-bearing capacity and durability, potentially reducing long-term maintenance costs. Project-specific factors such as span length, design requirements, and site accessibility significantly influence the overall cost-effectiveness between hollow core planks and solid slabs.
Insulation Properties: Thermal and Acoustic Performance
Hollow core planks offer superior thermal insulation due to their air-filled voids, which reduce heat transfer and improve energy efficiency in buildings. Their design also provides enhanced acoustic performance by dampening sound transmission compared to solid slabs, making them ideal for both residential and commercial applications. Solid slabs, while structurally robust, generally exhibit lower insulation properties, resulting in higher thermal conductivity and less effective soundproofing.
Durability and Lifespan Considerations
Hollow core planks offer enhanced durability through pre-stressed concrete technology, reducing the risk of cracking and providing a lifespan of up to 75 years under proper maintenance. Solid slabs, known for their uniform density and structural integrity, can last over 50 years but may be more susceptible to environmental wear and require additional reinforcement to prevent deterioration. Your choice between these options should consider the specific environmental conditions and load requirements to maximize longevity and performance.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Hollow core planks offer superior sustainability compared to solid slabs by using less concrete and reducing material waste through their lightweight, pre-stressed design. This results in a lower carbon footprint during production and transportation, promoting environmentally friendly construction practices. Choosing hollow core planks can significantly enhance your project's environmental impact by minimizing resource consumption and energy use.
Best Use Cases and Applications
Hollow core planks excel in long-span structures like parking garages and office buildings due to their lightweight design and efficient load distribution, reducing the need for extensive formwork. Solid slabs are best suited for residential buildings and areas requiring high fire resistance and sound insulation, offering robust strength and simpler installation for shorter spans. Both systems optimize construction speed and structural integrity, but selection depends on specific load requirements, span lengths, and architectural priorities.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Hollow Core Plank and Solid Slab
Hollow core planks offer lightweight construction with pre-stressed concrete benefits that reduce material use and speed up installation, making them ideal for large spans and repetitive floor systems. Solid slabs provide superior rigidity and load-bearing capacity, suitable for complex structural demands and heavy load scenarios. Your choice depends on project requirements for weight, load, span, installation speed, and budget constraints.
Hollow core plank vs solid slab Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com