EPS insulation offers excellent thermal performance with high vapor permeability, making it suitable for applications requiring breathability, while XPS insulation provides superior moisture resistance and compressive strength, ideal for below-grade or high-load areas. Choosing between EPS and XPS depends on your specific project needs, such as exposure to moisture, load-bearing requirements, and budget considerations.
Table of Comparison
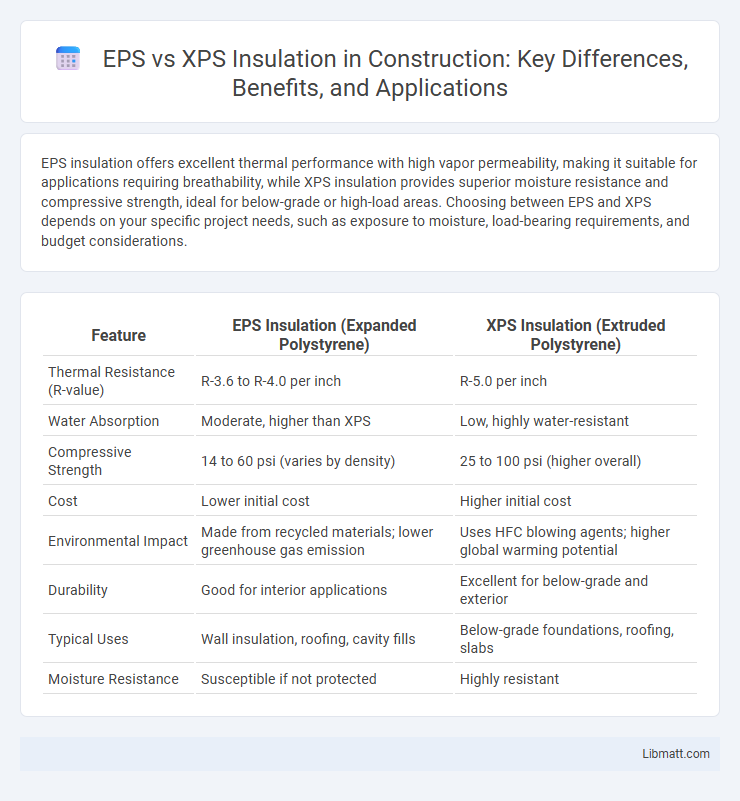
| Feature | EPS Insulation (Expanded Polystyrene) | XPS Insulation (Extruded Polystyrene) |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Resistance (R-value) | R-3.6 to R-4.0 per inch | R-5.0 per inch |
| Water Absorption | Moderate, higher than XPS | Low, highly water-resistant |
| Compressive Strength | 14 to 60 psi (varies by density) | 25 to 100 psi (higher overall) |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost |
| Environmental Impact | Made from recycled materials; lower greenhouse gas emission | Uses HFC blowing agents; higher global warming potential |
| Durability | Good for interior applications | Excellent for below-grade and exterior |
| Typical Uses | Wall insulation, roofing, cavity fills | Below-grade foundations, roofing, slabs |
| Moisture Resistance | Susceptible if not protected | Highly resistant |
Introduction to EPS and XPS Insulation
EPS insulation consists of expanded polystyrene beads fused together, offering a lightweight, cost-effective thermal barrier with moderate moisture resistance. XPS insulation is made from extruded polystyrene foam sheets, providing higher compressive strength and superior water resistance, ideal for below-grade and high-moisture environments. Your choice between EPS and XPS depends on specific project needs such as durability, insulation R-value, and moisture exposure.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
EPS (Expanded Polystyrene) insulation is made from expandable polystyrene beads that are molded and expanded using steam, resulting in a lightweight, closed-cell foam with good thermal resistance. XPS (Extruded Polystyrene) insulation is produced by melting polystyrene crystals and extruding them through a die to form rigid, dense foam panels with a uniform closed-cell structure and higher compressive strength. The manufacturing process of EPS involves bead expansion and molding, while XPS uses an extrusion method that provides enhanced moisture resistance and mechanical durability.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
EPS insulation features a lower density and higher vapor permeability compared to XPS, making it more breathable but less resistant to moisture absorption. XPS insulation demonstrates superior compressive strength and water resistance due to its closed-cell structure, ideal for applications requiring durability under load and moisture exposure. When choosing between EPS and XPS for your project, consider factors like thermal performance, moisture resistance, and mechanical strength to match your insulation needs effectively.
Thermal Performance: EPS vs XPS
EPS insulation offers a thermal conductivity ranging from 0.032 to 0.038 W/m*K, while XPS insulation typically provides a lower thermal conductivity of about 0.029 to 0.035 W/m*K, making XPS slightly more efficient in thermal performance. Your choice between EPS and XPS will depend on the insulation's intended application, with XPS being preferable for areas requiring higher moisture resistance and consistent R-values over time. Both materials deliver reliable thermal performance, but XPS generally maintains its insulating properties better in wet conditions.
Moisture Resistance of EPS and XPS
EPS insulation offers moderate moisture resistance due to its closed-cell structure but can absorb water over time if exposed continuously, potentially reducing its thermal performance. XPS insulation exhibits superior moisture resistance with higher water repellency and lower water absorption rates, making it ideal for environments prone to moisture exposure. When choosing insulation for your project, understanding the moisture resistance differences between EPS and XPS ensures long-lasting thermal efficiency and durability.
Compressive Strength and Durability
EPS insulation offers moderate compressive strength, typically ranging from 10 to 45 psi, making it suitable for applications with lighter load requirements. XPS insulation provides higher compressive strength, often between 25 and 100 psi, which enhances its durability under heavy loads and long-term structural stress. The closed-cell structure of XPS also contributes to superior moisture resistance and dimensional stability compared to the more open-cell EPS, resulting in enhanced durability in harsh environments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
EPS insulation has a lower environmental impact due to its lower embodied energy and recyclability compared to XPS, which contains blowing agents with higher global warming potential. You can enhance your building's sustainability by choosing EPS, as it generates less greenhouse gas emissions during production and disposal. However, XPS offers superior moisture resistance, which may influence sustainability outcomes depending on application conditions.
Typical Applications and Use Cases
EPS insulation excels in applications requiring lightweight, cost-effective thermal insulation, commonly used in walls, roofs, and under concrete slabs for residential and commercial buildings. XPS insulation is preferred for high-moisture environments and load-bearing applications such as foundation walls, basements, and exterior insulation due to its superior moisture resistance and compressive strength. Your choice between EPS and XPS depends on the specific thermal, moisture, and structural demands of your project.
Cost Differences: EPS vs XPS
EPS insulation typically costs less per square foot compared to XPS, making it a more budget-friendly option for projects with tight cost constraints. The lower manufacturing costs of EPS contribute to its affordability, while XPS insulation offers higher compressive strength and moisture resistance at a premium price. You can optimize your insulation investment by balancing initial costs with long-term performance needs in your specific application.
Choosing the Right Insulation for Your Project
EPS insulation offers excellent thermal resistance and moisture permeability, making it ideal for applications requiring breathability and cost-efficiency. XPS insulation provides superior compressive strength and water resistance, suitable for high-load environments like foundations and below-grade walls. Evaluating project-specific factors such as moisture exposure, load requirements, and budget ensures optimal performance and durability with the right insulation choice.
EPS insulation vs XPS insulation Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com