Rigid conduit offers superior protection and durability for electrical wiring in harsh environments, ensuring long-term safety and compliance with building codes. Flexible conduit provides ease of installation and maneuverability around obstacles, making it ideal for areas requiring frequent adjustments or complex routing.
Table of Comparison
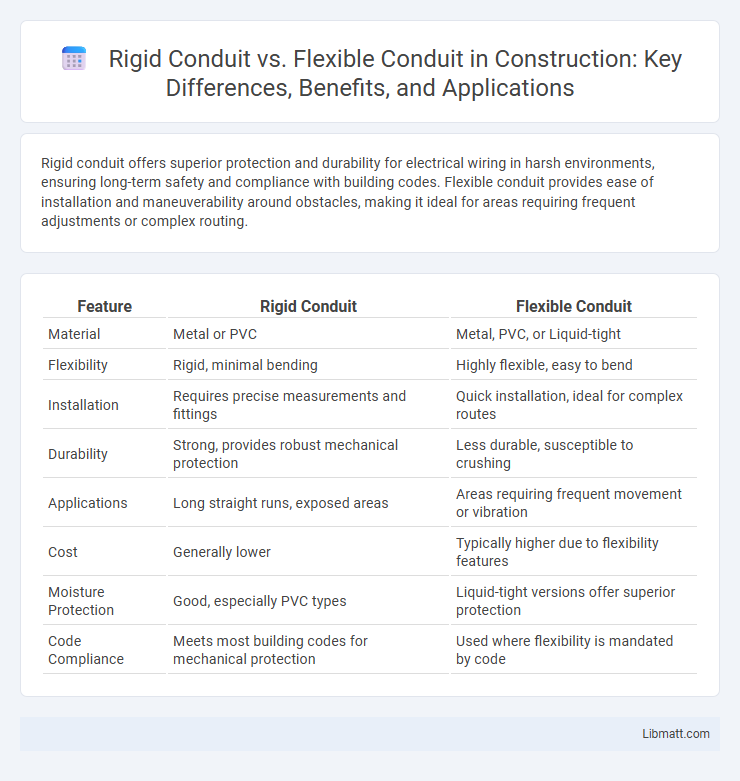
| Feature | Rigid Conduit | Flexible Conduit |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Metal or PVC | Metal, PVC, or Liquid-tight |
| Flexibility | Rigid, minimal bending | Highly flexible, easy to bend |
| Installation | Requires precise measurements and fittings | Quick installation, ideal for complex routes |
| Durability | Strong, provides robust mechanical protection | Less durable, susceptible to crushing |
| Applications | Long straight runs, exposed areas | Areas requiring frequent movement or vibration |
| Cost | Generally lower | Typically higher due to flexibility features |
| Moisture Protection | Good, especially PVC types | Liquid-tight versions offer superior protection |
| Code Compliance | Meets most building codes for mechanical protection | Used where flexibility is mandated by code |
Introduction to Rigid and Flexible Conduit
Rigid conduit provides durable, protective tubing for electrical wiring, commonly made from metal or plastic materials that resist crushing and environmental damage. Flexible conduit offers versatility with its bendable design, accommodating complex wiring paths and ease of installation in confined or irregular spaces. Your choice between rigid and flexible conduit will depend on the specific installation requirements for protection, flexibility, and durability.
Key Differences Between Rigid and Flexible Conduit
Rigid conduit, typically made from materials such as steel or PVC, offers superior protection against physical damage and environmental factors due to its solid, inflexible structure. Flexible conduit, often composed of metal or plastic, provides ease of installation in complex or tight spaces thanks to its bendable design, making it ideal for areas requiring frequent adjustments or movement. The key differences lie in their application suitability: rigid conduit is preferred for permanent, heavy-duty installations, while flexible conduit excels in scenarios demanding flexibility and quick routing.
Material Composition of Rigid and Flexible Conduit
Rigid conduit is typically made from materials like galvanized steel, aluminum, or PVC, providing strong protection against physical damage and corrosion for electrical wiring. Flexible conduit often consists of a metal core, such as steel, wrapped with a plastic or rubber outer jacket that allows for easier bending and installation in tight spaces. Your choice between these conduits depends on the durability required and the flexibility needed for the specific electrical application.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Rigid conduit offers superior strength and durability due to its thick metal or PVC construction, making it ideal for protecting electrical wiring in harsh environments and heavy-duty applications. Flexible conduit, while less robust, provides adequate durability for indoor or light-duty installations where flexibility and ease of routing are required. Steel rigid conduit (GRC) resists impact, corrosion, and crushing forces better than flexible metal conduit (FMC), ensuring long-term protection and structural integrity.
Installation Considerations: Rigid vs Flexible Conduit
Rigid conduit installation requires precise measurements and secure mounting with appropriate connectors to ensure durability and protection, making it ideal for permanent, exposed runs in industrial or commercial settings. Flexible conduit offers easier handling and adaptability around obstacles, reducing installation time and labor costs in complex or tight spaces, but may require additional support to maintain safety standards. Your choice between rigid and flexible conduit should factor in the installation environment, accessibility needs, and long-term maintenance requirements.
Applications and Suitability
Rigid conduit is ideal for permanent installations requiring high durability and protection in commercial and industrial settings, such as electrical wiring in buildings and outdoor environments. Flexible conduit excels in applications demanding adaptability to movement or vibration, like machinery, equipment, and tight or complex routing spaces in residential and commercial buildings. Selecting the appropriate conduit depends on the specific installation environment, mechanical stress, and ease of access needed for maintenance.
Cost Analysis: Rigid vs Flexible Conduit
Rigid conduit typically incurs higher initial material and installation costs compared to flexible conduit due to its heavy gauge metal composition and labor-intensive fitting process. Flexible conduit offers cost savings in labor and time, especially in complex or curved installations, as it requires fewer fittings and less precise measurements. Long-term maintenance costs favor rigid conduit for its durability and resistance to physical damage, potentially reducing replacement expenses over time.
Safety and Code Compliance
Rigid conduit offers superior protection against physical damage and is often mandated by electrical codes in commercial and industrial installations for enhanced safety. Flexible conduit provides easier installation around obstacles and vibration isolation but must meet specific code requirements, such as using liquid-tight flexible conduit in wet or corrosive environments. Adhering to the National Electrical Code (NEC) ensures both conduit types comply with grounding, bonding, and fire resistance standards critical for preventing electrical hazards.
Maintenance and Longevity
Rigid conduit offers superior durability and protection, resulting in lower maintenance requirements and extended longevity compared to flexible conduit. Flexible conduit provides easier installation in tight or complex spaces but may require more frequent inspections and repairs due to its susceptibility to wear and damage. Your choice should consider the maintenance intervals and lifespan expectations for your specific electrical system.
Choosing the Right Conduit for Your Project
Rigid conduit offers superior protection and durability for electrical wiring, making it ideal for outdoor or industrial environments where mechanical damage is a concern. Flexible conduit provides ease of installation around corners and in tight spaces, suitable for projects requiring adaptability and frequent adjustments. Evaluating the specific environmental conditions and mechanical stresses of your project ensures you choose the conduit that balances safety, flexibility, and compliance with electrical codes.
Rigid conduit vs Flexible conduit Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com