Stick framing uses individual dimensional lumber pieces nailed together on-site for flexible, cost-effective construction, while timber framing employs large, heavy wooden beams joined with intricate joinery, offering exceptional strength and aesthetic appeal. Your choice depends on budget, design preferences, and desired structural characteristics.
Table of Comparison
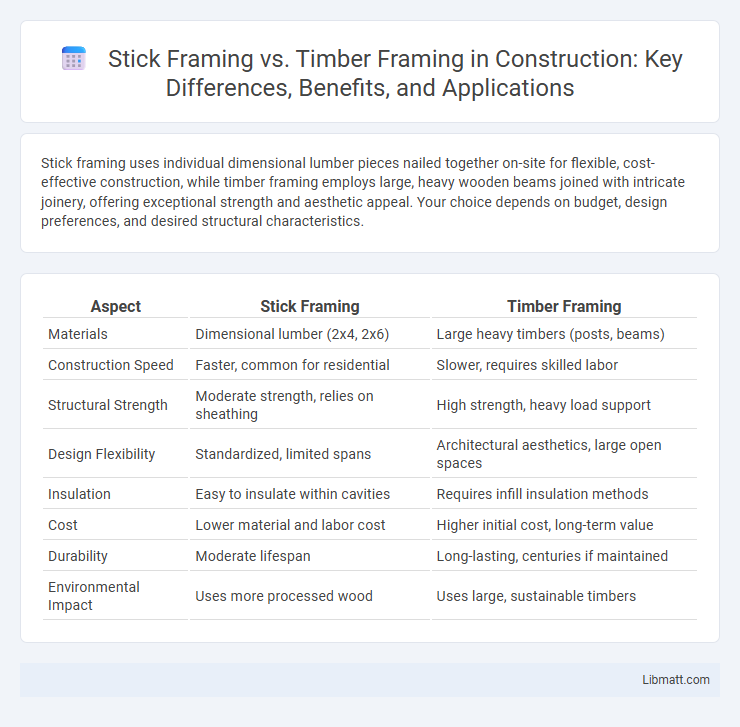
| Aspect | Stick Framing | Timber Framing |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | Dimensional lumber (2x4, 2x6) | Large heavy timbers (posts, beams) |
| Construction Speed | Faster, common for residential | Slower, requires skilled labor |
| Structural Strength | Moderate strength, relies on sheathing | High strength, heavy load support |
| Design Flexibility | Standardized, limited spans | Architectural aesthetics, large open spaces |
| Insulation | Easy to insulate within cavities | Requires infill insulation methods |
| Cost | Lower material and labor cost | Higher initial cost, long-term value |
| Durability | Moderate lifespan | Long-lasting, centuries if maintained |
| Environmental Impact | Uses more processed wood | Uses large, sustainable timbers |
Introduction to Stick Framing and Timber Framing
Stick framing utilizes standardized dimensional lumber such as 2x4s or 2x6s, creating a lightweight, flexible framework commonly used in modern residential construction for its cost-effectiveness and ease of assembly. Timber framing relies on large, heavy timbers joined by complex mortise and tenon connections, offering superior durability, aesthetic appeal, and historical craftsmanship associated with traditional and high-end custom homes. Both methods provide structural support, but stick framing emphasizes speed and affordability while timber framing prioritizes strength and architectural character.
Historical Background of Framing Methods
Stick framing emerged in the 19th century as a response to the need for faster, more cost-effective construction using standardized dimensional lumber, revolutionizing residential building in North America. Timber framing, with origins dating back thousands of years, relies on large, carefully joined wooden beams, showcasing traditional craftsmanship prevalent in medieval Europe and early American settlements. Your choice between stick framing and timber framing impacts not only the aesthetic but also reflects a deep historical evolution in building techniques.
Key Differences Between Stick Framing and Timber Framing
Stick framing uses smaller, standardized dimensional lumber such as 2x4s or 2x6s assembled on-site for quick, cost-effective construction, while timber framing relies on large, heavy timber beams connected with intricate joinery and wooden pegs, emphasizing strength and durability. Stick framing is common in residential construction due to its affordability and speed, whereas timber framing offers aesthetic appeal and structural robustness, often seen in custom homes or historic restorations. The choice between stick framing and timber framing impacts project cost, construction time, and architectural style significantly.
Construction Techniques: Step-by-Step Comparison
Stick framing involves assembling individual dimensional lumber pieces, typically 2x4s or 2x6s, to create walls, floors, and roofs, using nails and metal fasteners for quick, modular construction. Timber framing relies on large, heavy timbers connected through precise joinery techniques such as mortise-and-tenon, often secured with wooden pegs, emphasizing structural strength and aesthetic appeal. Your choice between stick framing and timber framing impacts construction speed, material costs, and architectural style, requiring careful consideration of project requirements and long-term durability.
Material Requirements and Sustainability
Stick framing primarily uses dimensional lumber such as 2x4s and 2x6s, which are widely available and require less raw material per structure, making it cost-effective but often less durable. Timber framing employs larger, solid wood beams, typically sourced from old-growth or sustainably managed forests, offering superior durability and natural insulation but higher material use per square foot. Timber framing's inherent longevity and potential for reuse enhance its sustainability profile compared to the more disposable nature of stick framing materials.
Structural Strength and Durability
Timber framing offers superior structural strength and durability due to its large, solid wood beams capable of withstanding heavy loads and resisting environmental stresses over time. Stick framing relies on smaller, closely spaced studs that provide flexibility and ease of construction but generally lack the long-term resilience of timber framing. Your choice between these methods will impact the building's ability to endure harsh conditions and maintain structural integrity for decades.
Cost Analysis: Stick Framing vs Timber Framing
Stick framing generally offers a lower initial cost due to the widespread availability of materials like dimensional lumber and faster construction times. Timber framing incurs higher upfront expenses because of the specialized craftsmanship and larger timber beams required, but it can add long-term value through durability and aesthetic appeal. Evaluating your budget should consider both immediate costs and potential resale benefits associated with each framing method.
Design Flexibility and Aesthetics
Stick framing offers greater design flexibility due to its use of smaller, standardized lumber pieces that can be easily cut and assembled into complex shapes and varied architectural styles. Timber framing emphasizes large, exposed wooden beams that create a rustic, traditional aesthetic, often showcasing intricate joinery and craftsmanship. This method prioritizes visual appeal and structural expression, while stick framing allows for more adaptability in layout and finishes.
Energy Efficiency and Insulation
Timber framing provides superior thermal mass, which helps regulate indoor temperatures and reduces energy consumption by maintaining consistent heat levels. Stick framing, with its closely spaced studs, allows for easier installation of modern insulation materials, improving overall energy efficiency in colder climates. Proper air sealing and insulation in both framing types are crucial for maximizing energy performance in residential construction.
Choosing the Right Framing Method for Your Project
Stick framing offers versatility and cost-efficiency, making it ideal for residential construction and projects with complex architectural designs. Timber framing provides superior durability and aesthetic appeal, best suited for large, open spaces and structures emphasizing natural wood elements. Selecting the right framing method depends on budget, design preferences, structural requirements, and the desired balance between speed and craftsmanship.
Stick framing vs Timber framing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com