A barrage jammer emits a broad-spectrum signal that disrupts multiple frequencies simultaneously, while a spot jammer targets a specific frequency to interfere with a single communication channel. Your choice depends on whether you need to block wide-range signals or focus on a particular frequency for precise jamming.
Table of Comparison
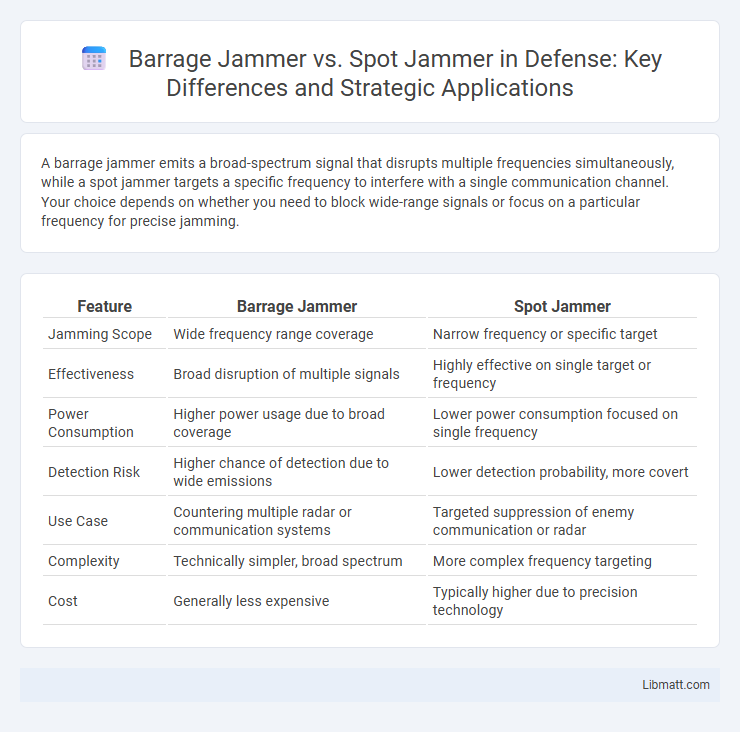
| Feature | Barrage Jammer | Spot Jammer |
|---|---|---|
| Jamming Scope | Wide frequency range coverage | Narrow frequency or specific target |
| Effectiveness | Broad disruption of multiple signals | Highly effective on single target or frequency |
| Power Consumption | Higher power usage due to broad coverage | Lower power consumption focused on single frequency |
| Detection Risk | Higher chance of detection due to wide emissions | Lower detection probability, more covert |
| Use Case | Countering multiple radar or communication systems | Targeted suppression of enemy communication or radar |
| Complexity | Technically simpler, broad spectrum | More complex frequency targeting |
| Cost | Generally less expensive | Typically higher due to precision technology |
Introduction to Jamming Techniques
Barrage jammers emit a broad spectrum of radio frequencies simultaneously to disrupt multiple communication channels at once, effectively overwhelming enemy signals over a wide area. Spot jammers target a specific frequency or narrowband signal, providing concentrated interference aimed at a single communication link or radar system. Both techniques are critical in electronic warfare, with barrage jammers offering wide coverage and spot jammers delivering precision disruption capabilities.
Understanding Barrage Jammers
Barrage jammers emit wideband signals to simultaneously disrupt multiple frequencies, effectively overwhelming enemy communications and radar systems. Spot jammers target a specific frequency or signal with high power, offering focused interference but limited bandwidth coverage. Understanding barrage jammers helps you choose the right electronic warfare tool for broad-spectrum signal denial scenarios.
Exploring Spot Jammers
Spot jammers target specific frequencies with high-intensity interference, effectively disrupting communications on narrow bandwidths. This precision allows spot jammers to conserve power and reduce collateral disruption compared to barrage jammers, which emit broad-spectrum signals across multiple frequencies simultaneously. Spot jammers are ideal for tactical scenarios requiring selective communication denial without compromising overall electronic spectrum usage.
Key Differences Between Barrage and Spot Jammers
Barrage jammers emit a broad spectrum of radio frequencies simultaneously, effectively disrupting multiple communication channels over a wide area, while spot jammers target a specific frequency or narrow band to neutralize a single transmission. The key difference lies in their operational scope: barrage jammers offer extensive coverage but with lower power per frequency, whereas spot jammers provide concentrated power for precise, high-level interference. Understanding these distinctions helps you select the appropriate jammer based on your required range and specificity of signal disruption.
Advantages of Barrage Jamming
Barrage jammers provide the advantage of simultaneously disrupting a wide range of frequencies, making them effective against multiple communication channels and radar systems. They deliver continuous noise over a broad spectrum without requiring precise target frequency information, increasing the likelihood of jamming success in dynamic or unknown environments. The broad coverage reduces the need for frequent retuning compared to spot jammers, enhancing operational efficiency in electronic warfare scenarios.
Benefits of Spot Jamming
Spot jamming targets specific frequencies, allowing precise disruption of enemy communications without collateral interference to other channels. This focused approach enhances operational stealth and conserves power by limiting the jamming signal to critical bands. Spot jammers improve electronic warfare effectiveness by minimizing detection risk and enabling continuous communication on non-targeted frequencies.
Tactical Applications of Barrage Jammers
Barrage jammers emit a wide spectrum of radio frequencies simultaneously to disrupt multiple enemy communication signals and radar systems, making them highly effective in suppressing wide-area threats. Their tactical applications include protecting troops from detection during maneuvers, securing critical assets from coordinated electronic attacks, and ensuring operational security in complex combat environments. These jammers provide continuous electronic warfare support by covering multiple frequency bands, unlike spot jammers, which target specific frequencies, offering broader defense in dynamic battlefield scenarios.
Strategic Uses of Spot Jammers
Spot jammers target specific frequencies, making them highly effective for disrupting precise enemy communications or radar signals without affecting broader bands. Their strategic use allows you to neutralize critical threats silently and with minimal collateral interference, ideal for covert operations or selective electronic warfare missions. Spot jamming supports tactical precision by concentrating power on key frequencies, ensuring efficient resource use and enhanced battlefield control.
Limitations and Vulnerabilities
Barrage jammers, while effective at disrupting a wide range of frequencies simultaneously, suffer from high power consumption and reduced efficiency in targeting specific threats, making them vulnerable to adaptive or frequency-hopping signals. Spot jammers offer precise interference at targeted frequencies but are limited by their narrow focus, allowing signals outside the jammed band to bypass and communicate successfully. Understanding these limitations helps optimize Your electronic warfare strategy by balancing broad coverage with focused disruption based on operational needs.
Choosing the Right Jamming Method
Choosing the right jamming method depends on your specific interference needs and target environment. Barrage jammers emit signals across a wide frequency range, effectively disrupting multiple channels simultaneously, making them ideal for broad-spectrum threats. Spot jammers concentrate power on a single frequency, offering precise disruption with lower power consumption, perfect for targeted interference where efficiency and focus are critical.
barrage jammer vs spot jammer Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com