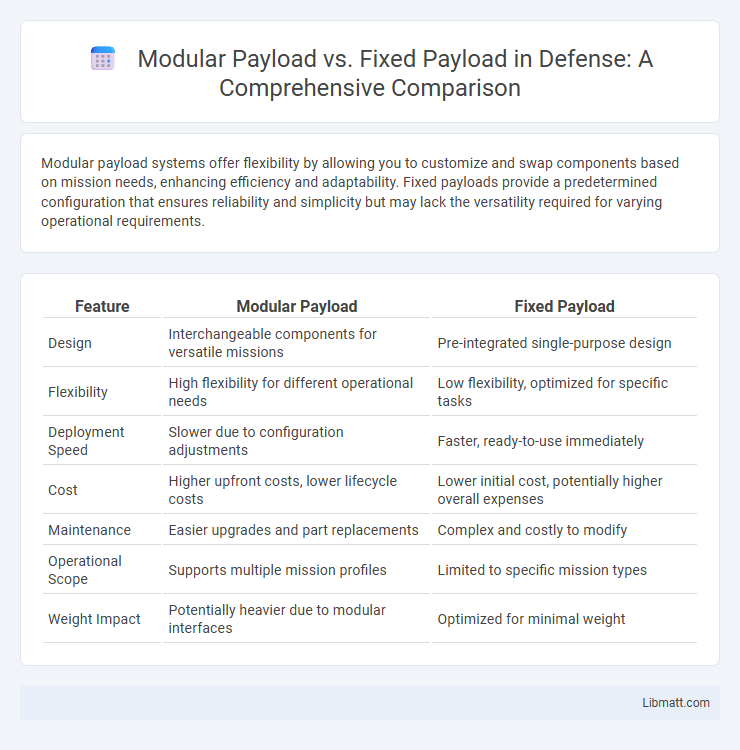
Modular payload systems offer flexibility by allowing you to customize and swap components based on mission needs, enhancing efficiency and adaptability. Fixed payloads provide a predetermined configuration that ensures reliability and simplicity but may lack the versatility required for varying operational requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Modular Payload | Fixed Payload |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Interchangeable components for versatile missions | Pre-integrated single-purpose design |
| Flexibility | High flexibility for different operational needs | Low flexibility, optimized for specific tasks |
| Deployment Speed | Slower due to configuration adjustments | Faster, ready-to-use immediately |
| Cost | Higher upfront costs, lower lifecycle costs | Lower initial cost, potentially higher overall expenses |
| Maintenance | Easier upgrades and part replacements | Complex and costly to modify |
| Operational Scope | Supports multiple mission profiles | Limited to specific mission types |
| Weight Impact | Potentially heavier due to modular interfaces | Optimized for minimal weight |
Introduction to Payload Systems
Payload systems in aerospace and robotics are categorized into modular and fixed types, each offering distinct operational advantages. Modular payloads provide flexibility through interchangeable components that can be easily reconfigured for various missions, enhancing adaptability and reducing turnaround time. Fixed payloads are designed for specific, unchanging tasks, delivering optimized performance and reliability tailored to a single objective.
Defining Modular Payloads
Modular payloads refer to interchangeable components designed to be easily installed, removed, or reconfigured on a platform, enhancing operational flexibility compared to fixed payloads, which are permanently integrated and limited in adaptability. These payloads enable rapid mission customization across various applications such as military, aerospace, and robotics by accommodating diverse sensors, equipment, or tools without major structural modifications. The modular approach reduces downtime, lowers costs, and improves system versatility, making it ideal for evolving mission requirements and technological advancements.
Understanding Fixed Payloads
Fixed payloads refer to pre-designed, non-adjustable modules integrated into systems or vehicles, offering consistent performance and simplified installation. They provide optimized functionality for specific tasks but lack flexibility for diverse mission requirements. Understanding your fixed payload's limitations helps in planning for maintenance, upgrades, or adopting complementary modular solutions to enhance operational efficiency.
Key Advantages of Modular Payloads
Modular payloads offer significant flexibility by allowing quick adaptation and reconfiguration for various mission requirements, reducing downtime and increasing operational efficiency. Their scalable design enables easy upgrades and maintenance, extending the payload's lifespan compared to fixed payloads. You benefit from improved cost-effectiveness and enhanced mission customization, making modular systems ideal for evolving technological environments.
Benefits of Fixed Payload Designs
Fixed payload designs offer enhanced reliability and optimal performance through their specialized engineering tailored to a single mission profile. By eliminating the need for interchangeable components, fixed payloads reduce complexity and potential failure points, ensuring consistent operational efficiency. Your choice of a fixed payload can lead to lower overall costs and streamlined maintenance, making it ideal for applications requiring stability and precision.
Flexibility and Adaptability Comparison
Modular payload systems offer superior flexibility by allowing quick reconfiguration for diverse mission requirements, enhancing adaptability across various operational scenarios. Fixed payloads, while often optimized for specific tasks, lack the versatility to accommodate rapid changes or multi-mission roles, limiting their operational scope. The modular approach supports scalable upgrades and integration of new technologies, providing long-term adaptability in dynamic environments.
Cost Implications: Modular vs Fixed Payloads
Modular payload systems typically incur higher initial costs due to design complexity and the need for interchangeable components, but they offer long-term savings through flexibility and reusability across multiple missions. Fixed payloads have lower upfront expenses since they are purpose-built for specific tasks, yet they can lead to increased costs over time because of limited adaptability and the need for frequent redesigns or replacements. Evaluating mission requirements and lifecycle expenses is essential to optimize cost-efficiency between modular and fixed payload options.
Maintenance and Upgrade Considerations
Modular payload systems simplify maintenance and upgrades by allowing individual components to be replaced or enhanced without overhauling the entire system, reducing downtime and costs. Fixed payload designs often require more extensive disassembly and can lead to longer service interruptions due to their integrated construction. Your choice between modular and fixed payloads directly impacts the ease and efficiency of future maintenance and technological updates.
Industry Use Cases and Applications
Modular payload systems enable industries such as aerospace, defense, and unmanned vehicles to quickly adapt equipment for varied missions, enhancing operational flexibility and cost efficiency. Fixed payloads, commonly used in commercial aviation and satellite communications, offer optimized performance for specific, consistent applications but lack adaptability. The choice between modular and fixed payloads directly impacts the deployment speed, maintenance complexity, and scalability in sectors like surveillance, scientific research, and logistics.
Choosing the Right Payload System
Selecting the right payload system depends on your mission requirements and operational flexibility. Modular payloads offer adaptability by allowing quick swaps and customized configurations, ideal for diverse tasks and evolving needs. Fixed payloads provide optimized performance for specific applications, ensuring reliability and streamlined integration in consistent use cases.
Modular payload vs Fixed payload Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com