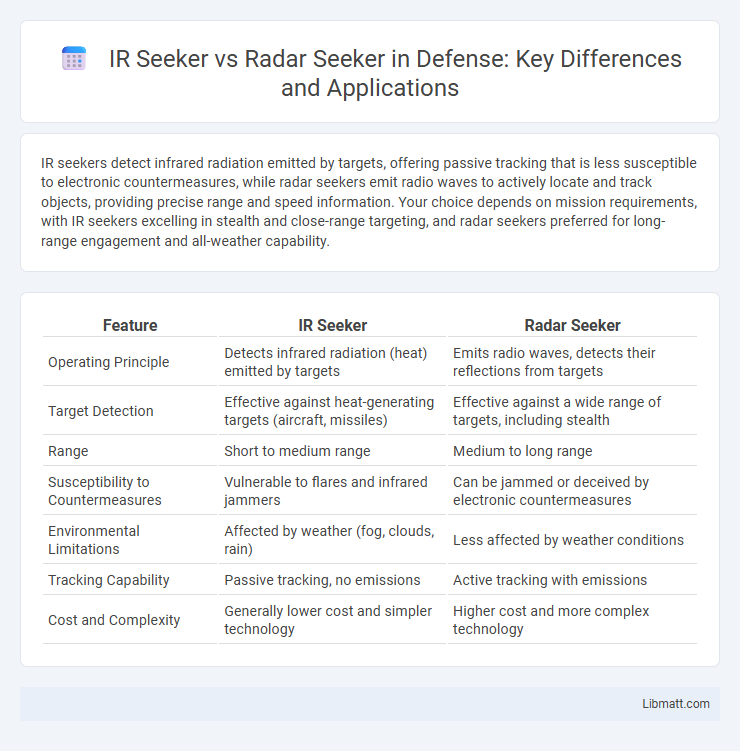
IR seekers detect infrared radiation emitted by targets, offering passive tracking that is less susceptible to electronic countermeasures, while radar seekers emit radio waves to actively locate and track objects, providing precise range and speed information. Your choice depends on mission requirements, with IR seekers excelling in stealth and close-range targeting, and radar seekers preferred for long-range engagement and all-weather capability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | IR Seeker | Radar Seeker |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Principle | Detects infrared radiation (heat) emitted by targets | Emits radio waves, detects their reflections from targets |
| Target Detection | Effective against heat-generating targets (aircraft, missiles) | Effective against a wide range of targets, including stealth |
| Range | Short to medium range | Medium to long range |
| Susceptibility to Countermeasures | Vulnerable to flares and infrared jammers | Can be jammed or deceived by electronic countermeasures |
| Environmental Limitations | Affected by weather (fog, clouds, rain) | Less affected by weather conditions |
| Tracking Capability | Passive tracking, no emissions | Active tracking with emissions |
| Cost and Complexity | Generally lower cost and simpler technology | Higher cost and more complex technology |
Introduction to IR and Radar Seekers
Infrared (IR) seekers detect the heat signatures emitted by targets, enabling precise tracking in environments where thermal contrast is significant, especially against aerial or ground threats. Radar seekers utilize radio waves to actively or passively detect and track objects by measuring the reflected signals, offering longer range detection and the ability to operate in diverse weather conditions. Both seeker types are integral to modern missile guidance systems, each optimized for specific operational scenarios based on target characteristics and environmental factors.
How IR Seekers Work
IR seekers detect infrared radiation emitted by heat sources such as aircraft engines, providing passive target tracking without revealing your position. They use sensors to capture the thermal signature, converting it into electronic signals to guide missiles accurately, especially in low-visibility conditions. Unlike radar seekers that emit signals and detect reflections, IR seekers rely solely on detecting emitted heat, offering stealth advantages during targeting.
How Radar Seekers Operate
Radar seekers operate by emitting radio frequency signals that bounce off targets and return to the receiver, enabling precise tracking based on the reflected signal's time delay and Doppler shift. These seekers continuously update the missile's guidance system with target position data, improving accuracy in various weather conditions and against countermeasures. Unlike IR seekers, radar seekers can detect targets beyond visual range and through smoke, fog, or darkness.
Key Differences Between IR and Radar Seekers
IR seekers detect infrared radiation emitted by targets, providing passive tracking without revealing the interceptor's position, ideal for stealth attacks. Radar seekers emit radio waves and analyze their reflections, enabling all-weather, long-range detection and tracking of moving objects. Unlike radar seekers, IR seekers are less effective in adverse weather conditions but offer higher resistance to electronic countermeasures.
Advantages of IR Seeker Technology
IR seeker technology offers distinct advantages over traditional radar seekers by providing enhanced target discrimination through infrared signature detection, which allows your systems to effectively track heat-emitting objects even in cluttered environments. IR seekers operate passively, reducing the risk of detection by enemy electronic countermeasures and improving stealth capabilities. Their ability to perform well in electronic warfare environments and maintain target lock in low-visibility conditions like smoke or fog makes IR seekers a critical component in modern missile guidance systems.
Benefits of Radar Seeker Systems
Radar seeker systems offer superior target detection and tracking capabilities in various weather conditions, including fog, rain, and smoke, where IR seekers may struggle. They provide longer range engagement and better resistance to countermeasures such as flares, enhancing Your missile's accuracy and reliability. The active radar seeker allows real-time target updates, improving hit probability against fast-moving or maneuvering threats.
Limitations and Vulnerabilities of IR Seekers
IR seekers face limitations such as susceptibility to environmental factors like fog, smoke, and cloud cover, which can degrade target detection and tracking accuracy. They are vulnerable to countermeasures including flares and infrared jamming that can mislead or confuse the sensor, reducing the effectiveness of the missile or targeting system. Your reliance on IR seekers requires understanding these constraints to optimize use in environments where thermal contrast is reliable and adversarial countermeasures are minimal.
Limitations and Countermeasures Against Radar Seekers
Radar seekers face limitations such as susceptibility to electronic countermeasures (ECM) including jamming, chaff, and deceptive signals that can confuse or mislead the radar tracking system. Their effectiveness decreases in environments with heavy electronic interference or with targets employing advanced stealth technology that reduces radar cross-section. You can counter radar seekers by deploying ECM pods, utilizing radar-absorbent materials, or executing evasive maneuvers to disrupt radar locking and targeting accuracy.
Real-World Applications: IR vs Radar Seeker
IR seekers excel in stealth targeting by detecting heat signatures of vehicles and aircraft, making them ideal for short-range missile guidance in complex environments. Radar seekers offer superior long-range tracking and all-weather capability, commonly used in air-to-air and surface-to-air missile systems for reliable detection through smoke, fog, and bad weather. Your choice between IR and radar seekers depends on mission requirements such as range, environmental conditions, and target type.
Future Trends in Seeker Technology
Future trends in seeker technology emphasize advancements in AI-driven data processing and multi-sensor integration, enhancing both IR seekers and radar seekers. IR seekers are evolving to offer improved spectral resolution and resistance to countermeasures, while radar seekers focus on higher frequency bands and adaptive beam steering for greater precision. Your defense systems will benefit from these innovations, achieving superior target detection and tracking capabilities in complex environments.
IR seeker vs radar seeker Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com