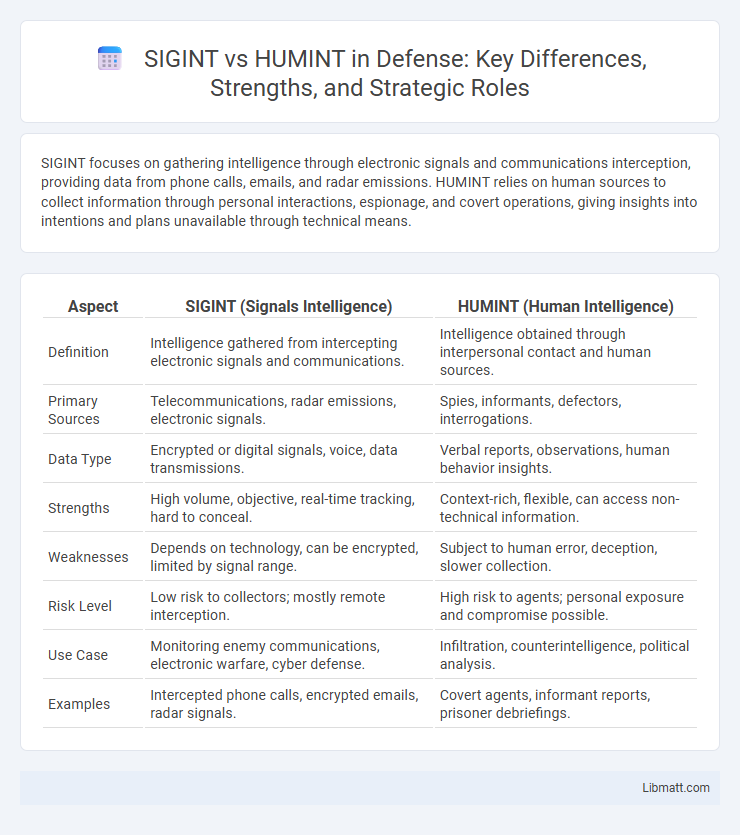
SIGINT focuses on gathering intelligence through electronic signals and communications interception, providing data from phone calls, emails, and radar emissions. HUMINT relies on human sources to collect information through personal interactions, espionage, and covert operations, giving insights into intentions and plans unavailable through technical means.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | SIGINT (Signals Intelligence) | HUMINT (Human Intelligence) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Intelligence gathered from intercepting electronic signals and communications. | Intelligence obtained through interpersonal contact and human sources. |
| Primary Sources | Telecommunications, radar emissions, electronic signals. | Spies, informants, defectors, interrogations. |
| Data Type | Encrypted or digital signals, voice, data transmissions. | Verbal reports, observations, human behavior insights. |
| Strengths | High volume, objective, real-time tracking, hard to conceal. | Context-rich, flexible, can access non-technical information. |
| Weaknesses | Depends on technology, can be encrypted, limited by signal range. | Subject to human error, deception, slower collection. |
| Risk Level | Low risk to collectors; mostly remote interception. | High risk to agents; personal exposure and compromise possible. |
| Use Case | Monitoring enemy communications, electronic warfare, cyber defense. | Infiltration, counterintelligence, political analysis. |
| Examples | Intercepted phone calls, encrypted emails, radar signals. | Covert agents, informant reports, prisoner debriefings. |
Introduction to SIGINT and HUMINT
SIGINT (Signals Intelligence) involves the interception and analysis of electronic communications, such as phone calls, emails, and radar signals, to gather valuable information. HUMINT (Human Intelligence) relies on information collected directly from human sources through espionage, interviews, or undercover operations, providing context and insight that electronic means cannot capture. Your understanding of intelligence gathering improves significantly by distinguishing the technical scope of SIGINT from the interpersonal nature of HUMINT.
Defining SIGINT: Signals Intelligence Explained
Signals Intelligence (SIGINT) involves the interception and analysis of electronic signals, including communications between individuals (COMINT) and electronic emissions from radar or weapon systems (ELINT). SIGINT plays a crucial role in gathering real-time information without direct human contact, providing strategic insights on enemy capabilities and intentions. Unlike Human Intelligence (HUMINT), which relies on interpersonal sources, SIGINT focuses on technological means to capture data transmitted through various communication channels.
Defining HUMINT: Human Intelligence Explained
Human Intelligence (HUMINT) involves collecting information through direct human interaction, such as interviews, interrogations, and espionage activities. It provides context and insights that signals intelligence (SIGINT), which gathers data from electronic communications and signals interception, may miss. HUMINT is essential for understanding intentions, motivations, and nuanced cultural or social dynamics that technical means cannot easily capture.
Key Differences Between SIGINT and HUMINT
SIGINT, or Signals Intelligence, involves intercepting electronic communications and signals for intelligence gathering, while HUMINT, or Human Intelligence, relies on information collected from human sources through direct interaction. SIGINT provides real-time, technical data, often from electronic devices, whereas HUMINT offers nuanced, contextual insights based on personal observations and interpersonal relationships. The key differences lie in the methods of collection, the type of intelligence acquired, and the operational environments suitable for each method.
Advantages of SIGINT in Modern Intelligence
SIGINT (Signals Intelligence) offers unparalleled advantages in modern intelligence through its ability to intercept and analyze electronic communications and signals at a global scale with high speed and accuracy. This method enables the collection of vast amounts of data from telecommunications, radar, and satellite transmissions, providing real-time insights critical for national security and counterterrorism. The automated processing and encryption-breaking capabilities of SIGINT enhance surveillance effectiveness while minimizing human risk compared to HUMINT (Human Intelligence).
Strengths of HUMINT in Intelligence Gathering
HUMINT excels in providing nuanced, context-rich intelligence through direct human sources, enabling insights into intentions, motivations, and plans that electronic signals cannot reveal. Your ability to access emotions, cultural subtleties, and interpersonal dynamics offers a distinct advantage in complex environments where SIGINT may be limited or encrypted. The adaptability and real-time feedback from human agents ensure HUMINT remains indispensable for comprehensive intelligence gathering.
Challenges and Limitations of SIGINT
SIGINT (Signals Intelligence) faces significant challenges including encryption and secure communication technologies that limit data interception and decryption capabilities. The vast volume of signals data requires advanced filtering and analysis tools to extract actionable intelligence, often hindered by signal jamming and electronic countermeasures. Your reliance on SIGINT can also be constrained by legal and ethical considerations surrounding privacy and international regulations.
Limitations and Risks Associated with HUMINT
Human Intelligence (HUMINT) faces significant limitations including the reliance on human sources, which can lead to issues such as misinformation, bias, and deception. Operational risks involve exposure of agents, compromising missions, and diplomatic consequences if sources are uncovered. Unlike Signals Intelligence (SIGINT), HUMINT requires extensive training, cultural understanding, and interpersonal skills, increasing resource intensity and potential for human error.
Integrating SIGINT and HUMINT for Comprehensive Intelligence
Integrating SIGINT (Signals Intelligence) and HUMINT (Human Intelligence) creates a comprehensive intelligence framework by combining electronic data collection with firsthand human insights, enhancing threat detection and decision-making accuracy. This fusion allows your intelligence analysts to cross-verify information, uncover hidden patterns, and fill gaps that single-source methods might miss. Leveraging both SIGINT and HUMINT optimizes operational effectiveness and strategic planning across military, security, and intelligence domains.
Future Trends: The Evolving Roles of SIGINT and HUMINT
Future trends reveal SIGINT's growing reliance on artificial intelligence and machine learning to process vast data streams and enhance predictive analytics. HUMINT continues to evolve with increased emphasis on cultural intelligence and human-machine collaboration for nuanced insights in complex environments. Both disciplines integrate advanced technologies to improve real-time decision-making and operational effectiveness in intelligence gathering.
SIGINT vs HUMINT Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com