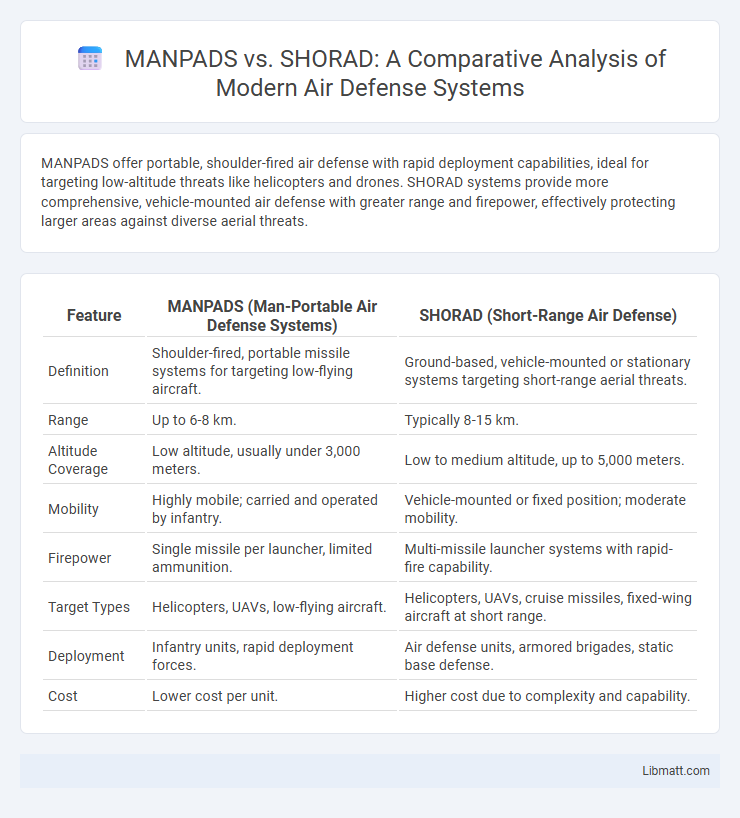
MANPADS offer portable, shoulder-fired air defense with rapid deployment capabilities, ideal for targeting low-altitude threats like helicopters and drones. SHORAD systems provide more comprehensive, vehicle-mounted air defense with greater range and firepower, effectively protecting larger areas against diverse aerial threats.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | MANPADS (Man-Portable Air Defense Systems) | SHORAD (Short-Range Air Defense) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Shoulder-fired, portable missile systems for targeting low-flying aircraft. | Ground-based, vehicle-mounted or stationary systems targeting short-range aerial threats. |
| Range | Up to 6-8 km. | Typically 8-15 km. |
| Altitude Coverage | Low altitude, usually under 3,000 meters. | Low to medium altitude, up to 5,000 meters. |
| Mobility | Highly mobile; carried and operated by infantry. | Vehicle-mounted or fixed position; moderate mobility. |
| Firepower | Single missile per launcher, limited ammunition. | Multi-missile launcher systems with rapid-fire capability. |
| Target Types | Helicopters, UAVs, low-flying aircraft. | Helicopters, UAVs, cruise missiles, fixed-wing aircraft at short range. |
| Deployment | Infantry units, rapid deployment forces. | Air defense units, armored brigades, static base defense. |
| Cost | Lower cost per unit. | Higher cost due to complexity and capability. |
Introduction to MANPADS and SHORAD
MANPADS (Man-Portable Air-Defense Systems) are shoulder-fired surface-to-air missiles designed for short-range air defense against low-flying aircraft and helicopters, offering portability and rapid response capabilities. SHORAD (Short-Range Air Defense) encompasses a broader category of ground-based systems, including radar-guided missile launchers and anti-aircraft guns, aimed at protecting critical assets within a limited radius from aerial threats. Understanding the capabilities and deployment of MANPADS and SHORAD is essential for enhancing your tactical air defense strategies.
Core Differences Between MANPADS and SHORAD
MANPADS (Man-Portable Air-Defense Systems) are lightweight, shoulder-fired missile systems designed for individual soldiers to target low-flying aircraft and helicopters at short ranges, typically up to 5 kilometers. SHORAD (Short Range Air Defense) encompasses a broader category of ground-based air defense systems, including missile launchers, radar, and anti-aircraft guns, capable of engaging aerial threats within a range of up to 15 kilometers. Core differences lie in their deployment: MANPADS offer high mobility and rapid reaction due to their portable nature, while SHORAD provides integrated, multi-layered defense with enhanced situational awareness and firepower.
Historical Development of MANPADS
MANPADS (Man-Portable Air-Defense Systems) originated during the Cold War as lightweight, shoulder-fired missile systems designed for infantry use against low-flying aircraft. The 1960s marked the introduction of the iconic Soviet SA-7 Strela, revolutionizing short-range air defense by providing ground forces with portable, heat-seeking capabilities. These developments led to the evolution of SHORAD (Short-Range Air Defense) systems that integrated MANPADS with radar and vehicle-mounted platforms, enhancing battlefield air defense versatility and response time.
Evolution and Role of SHORAD Systems
SHORAD (Short-Range Air Defense) systems have evolved to address the growing threat posed by MANPADS (Man-Portable Air-Defense Systems) through enhanced radar capabilities, multi-layered missile engagement, and integration with networked command and control systems. Modern SHORAD platforms incorporate advanced fire-and-forget missiles, electro-optical sensors, and rapid-response launchers to neutralize low-flying aircraft, drones, and cruise missiles effectively. Their role has expanded from point defense to area defense, providing mobile, flexible, and layered protection crucial for countering the increasing proliferation and sophistication of MANPADS on the battlefield.
Operational Applications: MANPADS vs SHORAD
MANPADS (Man-Portable Air Defense Systems) are designed for highly mobile, short-range engagements, offering ground troops rapid, flexible protection against low-flying aircraft and helicopters. SHORAD (Short-Range Air Defense) systems provide more robust, multi-layered defenses with integrated radar and targeting capabilities, ideal for protecting key installations and larger force concentrations. Your choice between MANPADS and SHORAD depends on operational needs, whether prioritizing individual soldier mobility or comprehensive area air defense coverage.
Range, Portability, and Deployment
MANPADS (Man-Portable Air Defense Systems) offer a compact, shoulder-fired solution with an effective range typically between 4 to 8 kilometers, enabling rapid deployment by individual infantry. SHORAD (Short-Range Air Defense) systems cover a broader range, often up to 15-20 kilometers, with vehicle-mounted platforms providing enhanced mobility but reduced portability compared to MANPADS. MANPADS excel in stealth and flexibility, whereas SHORAD units deliver layered defense with integrated radar and tracking but require more logistical support for deployment.
Effectiveness Against Modern Aerial Threats
MANPADS (Man-Portable Air-Defense Systems) provide highly mobile and flexible short-range defense against low-flying aircraft, targeting drones, helicopters, and slow-moving jets with infrared homing missiles. SHORAD (Short-Range Air Defense) systems integrate radar-guided surface-to-air missiles, autocannons, and electro-optical sensors to engage a wider spectrum of modern aerial threats, including fast jets, cruise missiles, and UAV swarms at varying altitudes. The combination of MANPADS' portability and SHORAD's multi-layered sensor and weapon capabilities enhances overall effectiveness by addressing diverse and evolving aerial attack profiles in modern combat environments.
Integration with Modern Battlefield Networks
MANPADS provide highly mobile, short-range air defense with rapid targeting capabilities but often operate independently with limited network integration. SHORAD systems increasingly feature advanced sensors and communication links, facilitating seamless integration into modern battlefield networks for real-time data sharing and coordinated defense. Enhanced interoperability between SHORAD and broader air defense architectures maximizes situational awareness, threat tracking, and response efficiency.
Case Studies: MANPADS and SHORAD in Recent Conflicts
Recent conflicts in Ukraine and Syria highlight the effectiveness of MANPADS in providing infantry units with portable, short-range air defense capabilities, disrupting enemy drone operations and low-flying aircraft. SHORAD systems, such as the German Ozelot and American Avenger, demonstrated superior radar-guided targeting and integration with broader air defense networks, successfully neutralizing a wider range of aerial threats. Your understanding of these case studies reveals the complementary roles of MANPADS for mobility and SHORAD for comprehensive airspace control in modern warfare.
Future Trends in Short-Range Air Defense
Future trends in short-range air defense (SHORAD) emphasize integrating advanced MANPADS with network-centric systems to enhance target detection and interception capabilities against evolving aerial threats. Innovations include artificial intelligence-driven fire control and multi-sensor fusion for rapid response to low-altitude drones, helicopters, and cruise missiles. Enhanced mobility and modular platforms ensure SHORAD units maintain versatility and resilience on dynamic battlefields.
MANPADS vs SHORAD Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com