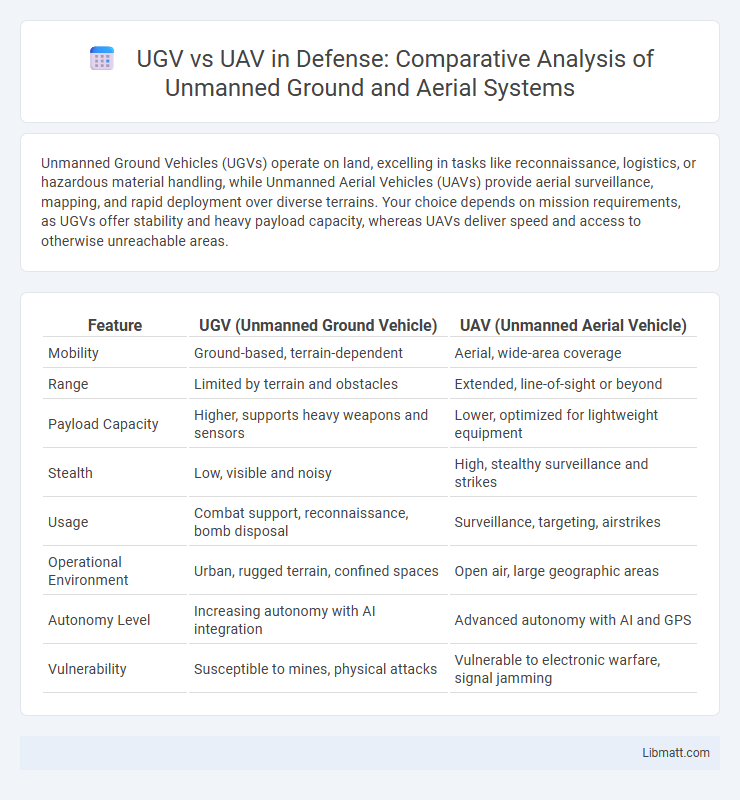
Unmanned Ground Vehicles (UGVs) operate on land, excelling in tasks like reconnaissance, logistics, or hazardous material handling, while Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) provide aerial surveillance, mapping, and rapid deployment over diverse terrains. Your choice depends on mission requirements, as UGVs offer stability and heavy payload capacity, whereas UAVs deliver speed and access to otherwise unreachable areas.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | UGV (Unmanned Ground Vehicle) | UAV (Unmanned Aerial Vehicle) |
|---|---|---|
| Mobility | Ground-based, terrain-dependent | Aerial, wide-area coverage |
| Range | Limited by terrain and obstacles | Extended, line-of-sight or beyond |
| Payload Capacity | Higher, supports heavy weapons and sensors | Lower, optimized for lightweight equipment |
| Stealth | Low, visible and noisy | High, stealthy surveillance and strikes |
| Usage | Combat support, reconnaissance, bomb disposal | Surveillance, targeting, airstrikes |
| Operational Environment | Urban, rugged terrain, confined spaces | Open air, large geographic areas |
| Autonomy Level | Increasing autonomy with AI integration | Advanced autonomy with AI and GPS |
| Vulnerability | Susceptible to mines, physical attacks | Vulnerable to electronic warfare, signal jamming |
Introduction to UGVs and UAVs
Unmanned Ground Vehicles (UGVs) and Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) represent advanced robotic systems designed for remote or autonomous operations in diverse environments. UGVs operate on terrains ranging from urban streets to rugged landscapes, enabling tasks like surveillance, logistics, and hazardous material handling. UAVs, commonly known as drones, navigate airspace for applications including aerial photography, agriculture monitoring, and reconnaissance, leveraging their ability to cover large areas quickly and access difficult-to-reach locations.
Key Differences Between UGVs and UAVs
UGVs (Unmanned Ground Vehicles) operate on terrain and are equipped with wheels or tracks for mobility, while UAVs (Unmanned Aerial Vehicles) fly using rotors or fixed wings. UGVs typically excel in tasks requiring ground interaction, such as bomb disposal or reconnaissance in hazardous environments, whereas UAVs provide aerial surveillance, mapping, and real-time data collection over large areas. You should consider factors like terrain accessibility, mission requirements, and payload capacity when choosing between UGVs and UAVs for your specific application.
Core Technologies Powering UGVs and UAVs
UGVs rely on advanced robotics technologies including autonomous navigation systems, LIDAR, and sensor fusion for precise terrain mapping and obstacle detection, enabling robust ground operations. UAVs utilize cutting-edge aerodynamics, GPS-based flight control, and real-time data transmission technologies to achieve agile flight performance and comprehensive aerial surveillance. Both platforms integrate machine learning algorithms and AI-driven decision-making processes to enhance autonomy and operational efficiency in diverse environments.
Use Cases and Applications of UGVs
Unmanned Ground Vehicles (UGVs) excel in applications like military reconnaissance, hazardous environment inspection, and agricultural automation where terrain interaction is critical. They perform tasks such as bomb disposal, remote surveillance, and precision farming with enhanced stability and payload capacity compared to UAVs. Industries benefit from UGVs in logistics and mining by automating material transport and conducting ground-level exploration in inaccessible or dangerous areas.
Use Cases and Applications of UAVs
UAVs excel in applications such as aerial surveillance, agriculture monitoring, and disaster response due to their ability to access challenging terrains and provide real-time data. They are widely used in precision farming to optimize crop yields through detailed imaging and in infrastructure inspections to enhance safety without risking human lives. Your operations can benefit significantly from UAVs' efficiency in tasks requiring rapid deployment and extensive area coverage.
Advantages of UGVs Over UAVs
Unmanned Ground Vehicles (UGVs) offer superior operational endurance and payload capacity compared to Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), allowing longer missions with heavier equipment. UGVs provide enhanced stability and precise ground-level maneuvering, crucial for tasks in confined or hazardous environments where UAVs may struggle. Your choice of UGV over UAV ensures dependable performance in conditions such as rough terrain, poor weather, or limited airspace.
Advantages of UAVs Over UGVs
UAVs offer unparalleled aerial mobility, enabling rapid access to remote or hazardous areas that UGVs cannot reach due to terrain limitations. Their ability to capture high-resolution aerial imagery and real-time data enhances surveillance, mapping, and reconnaissance missions with greater efficiency. You benefit from UAVs' extended operational range and flexibility, making them ideal for dynamic environments and time-sensitive tasks.
Challenges Facing UGV and UAV Deployment
Unmanned Ground Vehicles (UGVs) face challenges such as terrain navigation, obstacle avoidance, and limited battery life, impacting mission duration and effectiveness in complex environments. Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) confront issues including regulatory restrictions, weather sensitivity, and airspace management, affecting operational reliability and safety. Both UGVs and UAVs require advancements in autonomous control systems, sensor integration, and communication networks to overcome deployment limitations.
Future Trends in UGV and UAV Development
Future trends in UGV and UAV development emphasize increased autonomy through advanced artificial intelligence and machine learning integration, enhancing operational efficiency and decision-making capabilities. Enhanced sensor fusion and real-time data processing enable more precise navigation and obstacle avoidance in complex environments. Your choice between UGV or UAV will increasingly depend on specific mission requirements, with hybrid platforms merging ground and aerial capabilities gaining traction.
Choosing Between UGVs and UAVs: Factors to Consider
Choosing between Unmanned Ground Vehicles (UGVs) and Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) involves evaluating terrain accessibility, mission objectives, and payload capacity. UGVs excel in navigating complex ground environments with heavy payloads and extended operational times, while UAVs offer superior speed, aerial surveillance capabilities, and access to hard-to-reach areas. Cost considerations, communication range, and environmental conditions also play critical roles in determining the optimal platform for specific applications.
UGV vs UAV Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com