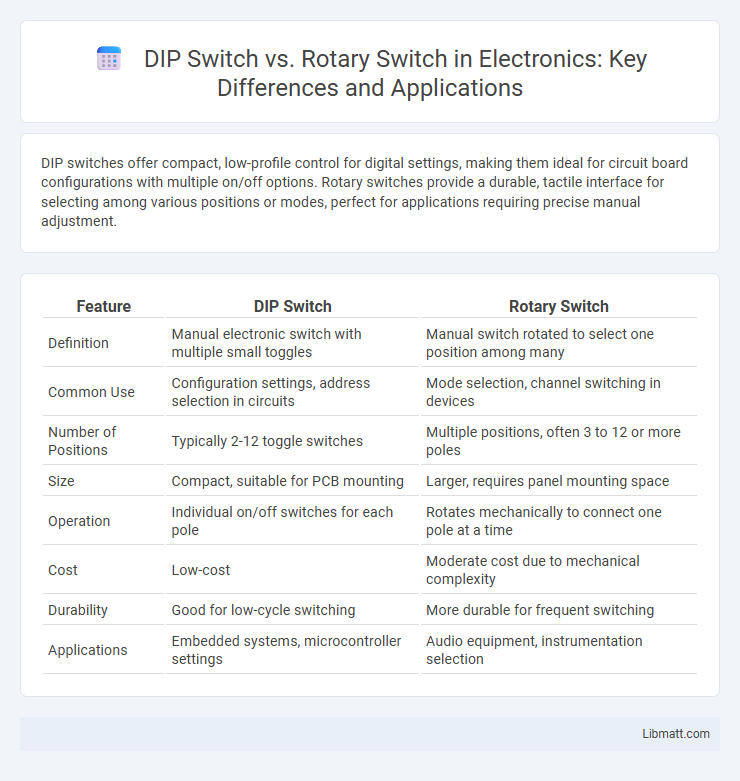
DIP switches offer compact, low-profile control for digital settings, making them ideal for circuit board configurations with multiple on/off options. Rotary switches provide a durable, tactile interface for selecting among various positions or modes, perfect for applications requiring precise manual adjustment.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | DIP Switch | Rotary Switch |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Manual electronic switch with multiple small toggles | Manual switch rotated to select one position among many |
| Common Use | Configuration settings, address selection in circuits | Mode selection, channel switching in devices |
| Number of Positions | Typically 2-12 toggle switches | Multiple positions, often 3 to 12 or more poles |
| Size | Compact, suitable for PCB mounting | Larger, requires panel mounting space |
| Operation | Individual on/off switches for each pole | Rotates mechanically to connect one pole at a time |
| Cost | Low-cost | Moderate cost due to mechanical complexity |
| Durability | Good for low-cycle switching | More durable for frequent switching |
| Applications | Embedded systems, microcontroller settings | Audio equipment, instrumentation selection |
Overview of DIP Switches and Rotary Switches
DIP switches consist of a series of small, manual toggle switches mounted on a dual in-line package, allowing users to configure electronic settings efficiently and compactly. Rotary switches offer multiple positions that rotate around a central axis, enabling selection between various circuits or functions within a device. Your choice between DIP switches and rotary switches depends on factors like required configuration options, space constraints, and ease of use.
How DIP Switches Work
DIP switches operate by toggling individual small switches embedded within a dual in-line package, allowing precise binary control for electronic circuits and configurations. Each switch on the DIP package can be set to an ON or OFF position, representing distinct logical states that enable or disable specific functions or settings. Your device's customization relies on the DIP switch's ability to provide compact, reliable, and easy-to-configure binary inputs.
How Rotary Switches Function
Rotary switches function by rotating a spindle or shaft to connect different contacts, enabling the selection of multiple electrical circuits within a single switch. Each position corresponds to a unique output, allowing users to easily change settings or channels with a simple turn. This mechanism provides reliable, precise multi-position switching ideal for applications requiring various circuit configurations.
Key Differences Between DIP and Rotary Switches
DIP switches feature multiple small, individual switches in a single package for binary on/off control, while rotary switches use a rotating spindle to select one of many positions or circuits. DIP switches are commonly used for setting configurations on PCBs and allow for compact, precise on/off combinations, whereas rotary switches enable multi-position selection ideal for mode or channel switching in devices. The key difference lies in their operation method--DIP switches offer discrete toggles for binary control, and rotary switches provide a single selector for multiple options.
Applications of DIP Switches
DIP switches are commonly used in electronic devices for setting configurations such as device IDs, address selection in networking equipment, and enabling or disabling features in industrial machinery. They provide a reliable and compact solution for configuring printed circuit boards (PCBs) in consumer electronics, telecommunications, and automotive applications. Their ease of use and stability make them ideal for embedded system settings where physical access is required.
Common Uses for Rotary Switches
Rotary switches are commonly used in applications requiring multiple circuit selections, such as in audio equipment, industrial machinery, and communication devices. Their design allows for easy switching between several positions or modes, making them ideal for controlling complex functions with a single control knob. You can find rotary switches in settings where precise, tactile selection of different electrical pathways is necessary for efficient operation.
Advantages of DIP Switches
DIP switches offer compact size and ease of use, making them ideal for configuring settings in electronic devices without requiring specialized tools. They provide reliable, manual control over circuits, allowing you to quickly change options or addresses in embedded systems with minimal risk of accidental modification. Their low cost and straightforward design contribute to enhanced durability and long-term performance in various applications.
Benefits of Rotary Switches
Rotary switches provide precise multi-position control, allowing you to select various circuit options with ease in a compact form factor. Their durable construction ensures long-lasting performance in industrial and electronic applications where reliability is critical. This type of switch also reduces wiring complexity by combining multiple switching functions into a single device, enhancing system efficiency.
Selecting the Right Switch for Your Project
Selecting the right switch for your project depends on factors such as space constraints, required functionality, and ease of configuration. DIP switches offer compact, reliable binary settings ideal for circuit boards and low-profile applications, while rotary switches provide multiple positions with clear tactile feedback suitable for varied user input in larger devices. Evaluating your project's electrical needs, user interface complexity, and installation environment ensures optimal switch performance and longevity.
DIP Switch vs Rotary Switch: Comparison Table
The DIP switch offers compact, multiple-position settings ideal for circuit configuration with up to 12 individual switches in a small form factor, while the rotary switch provides a single selector mechanism with multiple positions, commonly ranging from 2 to 12, for selecting one output among several. DIP switches are favored in applications requiring low-cost, manual binary options such as device addressing, whereas rotary switches are preferred for applications needing straightforward, tactile position selection, such as mode or channel switching. Key comparison factors include size, number of selectable positions, durability, ease of use, and electrical isolation, with DIP switches excelling in multi-switch configurations and rotary switches offering clearer, singular position feedback.
DIP Switch vs Rotary Switch Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com