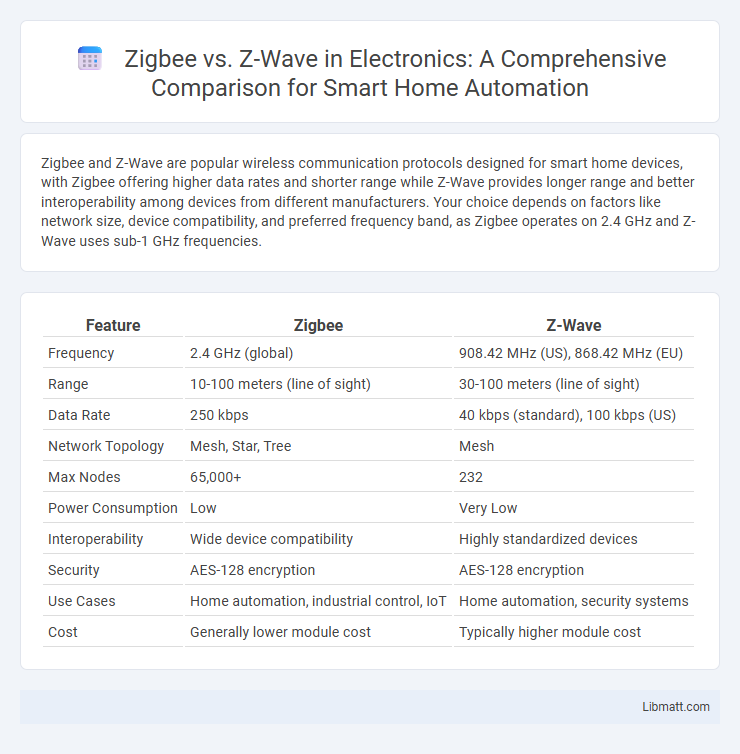
Zigbee and Z-Wave are popular wireless communication protocols designed for smart home devices, with Zigbee offering higher data rates and shorter range while Z-Wave provides longer range and better interoperability among devices from different manufacturers. Your choice depends on factors like network size, device compatibility, and preferred frequency band, as Zigbee operates on 2.4 GHz and Z-Wave uses sub-1 GHz frequencies.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Zigbee | Z-Wave |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency | 2.4 GHz (global) | 908.42 MHz (US), 868.42 MHz (EU) |
| Range | 10-100 meters (line of sight) | 30-100 meters (line of sight) |
| Data Rate | 250 kbps | 40 kbps (standard), 100 kbps (US) |
| Network Topology | Mesh, Star, Tree | Mesh |
| Max Nodes | 65,000+ | 232 |
| Power Consumption | Low | Very Low |
| Interoperability | Wide device compatibility | Highly standardized devices |
| Security | AES-128 encryption | AES-128 encryption |
| Use Cases | Home automation, industrial control, IoT | Home automation, security systems |
| Cost | Generally lower module cost | Typically higher module cost |
Introduction to Zigbee and Z-Wave
Zigbee and Z-Wave are two prominent wireless communication protocols designed for smart home automation, enabling devices to connect and communicate efficiently. Zigbee operates on the IEEE 802.15.4 standard at 2.4 GHz frequency, supporting mesh networking for low-power, short-range device interactions. Z-Wave uses a proprietary protocol at sub-1 GHz frequencies, offering interference resistance and optimized for reliability in home automation with a simpler device penetration range than Zigbee.
Core Technologies and Protocols
Zigbee operates on the IEEE 802.15.4 standard in the 2.4 GHz frequency band, utilizing a mesh network topology for robust device communication and low power consumption. Z-Wave functions on a proprietary protocol within the sub-1 GHz frequency range (around 908 MHz in the US), optimizing range and interference resistance with a simpler mesh network design. Your choice between Zigbee and Z-Wave may depend on the specific wireless frequency environment and device compatibility required for your smart home ecosystem.
Network Topology Comparison
Zigbee uses a mesh network topology that allows devices to communicate directly or through other nodes, enhancing range and reliability for smart home systems. Z-Wave also employs a mesh network but typically supports fewer nodes per network, optimizing interoperability with smart devices by minimizing interference in the 900 MHz band. Your choice between the two should consider the network size and device compatibility for efficient home automation.
Device Compatibility and Ecosystem
Zigbee offers broad device compatibility with support from over 3,000 products across numerous brands, forming a vast and diverse ecosystem ideal for scalable smart home solutions. Z-Wave features a more focused but highly interoperable ecosystem with more than 3,200 certified devices designed to work seamlessly together, prioritizing reliability and ease of integration within its mesh network. When choosing your smart home protocol, consider Zigbee for extensive brand variety and Z-Wave for assured device interoperability and consistent communication.
Range and Signal Strength
Zigbee typically offers a range of up to 10-20 meters indoors, with a maximum line-of-sight distance reaching around 100 meters, while Z-Wave provides a slightly longer indoor range of approximately 30 meters and an extended line-of-sight range up to 150 meters. Zigbee operates on the 2.4 GHz frequency, which can be prone to interference from Wi-Fi networks, potentially affecting signal strength and reliability in dense wireless environments. Z-Wave functions on sub-1 GHz frequencies (around 908 MHz in the US), resulting in better penetration through walls and obstacles, leading to more stable signal strength and longer effective range in typical home settings.
Power Consumption and Efficiency
Zigbee and Z-Wave both excel in low power consumption, but Zigbee typically operates at a lower power level, making it more efficient for battery-powered devices. Zigbee's mesh network allows devices to relay signals efficiently, reducing overall energy use compared to Z-Wave's primarily hub-and-spoke model. Optimizing your smart home system with Zigbee can lead to longer device battery life and more energy-efficient connectivity.
Security Features and Encryption
Zigbee employs AES-128 encryption at the network and application layers, ensuring secure communication through a trust center that manages device authentication and key distribution. Z-Wave also uses AES-128 encryption with a Security 2 (S2) framework, which enhances protection via device inclusion security and encrypted communication based on Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman key exchange. Both protocols prioritize secure data transmission and robust key management to safeguard smart home and IoT devices from unauthorized access and interference.
Installation and Setup Ease
Zigbee offers straightforward installation with widespread device compatibility and automatic mesh network formation, simplifying setup for smart home users. Z-Wave systems require inclusion mode for each device, which can be more time-consuming, but benefit from a more controlled frequency band reducing interference. Both protocols support user-friendly mobile apps and hubs, yet Zigbee's open-standard nature often results in broader device variety and faster integration.
Scalability and Flexibility
Zigbee offers superior scalability with support for thousands of devices on a single network, making it ideal for extensive smart home or commercial setups. Z-Wave networks are more limited, typically handling up to 232 devices, but provide strong interoperability due to strict device certification standards. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize the expansive, flexible device ecosystem of Zigbee or the reliable, straightforward device integration of Z-Wave.
Which Is Best for Your Smart Home?
Zigbee offers a wider range of device compatibility and faster data transfer rates, making it ideal for densely populated smart homes that require robust network performance. Z-Wave provides superior range and better interoperability with fewer devices, which can enhance reliability in larger spaces with fewer interference issues. Your smart home setup benefits most from Zigbee's extensive ecosystem and mesh networking if you prioritize device variety, while Z-Wave excels in stability and ease of integration for simpler configurations.
Zigbee vs Z-wave Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com