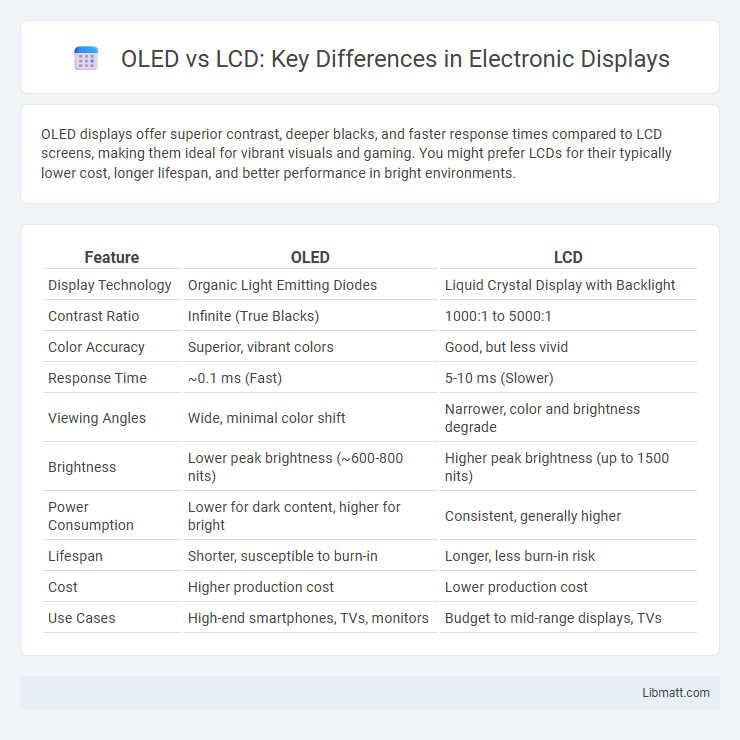
OLED displays offer superior contrast, deeper blacks, and faster response times compared to LCD screens, making them ideal for vibrant visuals and gaming. You might prefer LCDs for their typically lower cost, longer lifespan, and better performance in bright environments.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | OLED | LCD |
|---|---|---|
| Display Technology | Organic Light Emitting Diodes | Liquid Crystal Display with Backlight |
| Contrast Ratio | Infinite (True Blacks) | 1000:1 to 5000:1 |
| Color Accuracy | Superior, vibrant colors | Good, but less vivid |
| Response Time | ~0.1 ms (Fast) | 5-10 ms (Slower) |
| Viewing Angles | Wide, minimal color shift | Narrower, color and brightness degrade |
| Brightness | Lower peak brightness (~600-800 nits) | Higher peak brightness (up to 1500 nits) |
| Power Consumption | Lower for dark content, higher for bright | Consistent, generally higher |
| Lifespan | Shorter, susceptible to burn-in | Longer, less burn-in risk |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Lower production cost |
| Use Cases | High-end smartphones, TVs, monitors | Budget to mid-range displays, TVs |
Introduction to OLED and LCD Technologies
OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology uses organic compounds that emit light when an electric current passes through, enabling self-emissive displays with deep blacks and high contrast ratios. LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) technology relies on a backlight shining through liquid crystals to produce images, often resulting in less vibrant colors and lower contrast compared to OLED. The fundamental difference lies in OLED's ability to turn individual pixels on or off, whereas LCD pixels depend on consistent backlighting for image formation.
How OLED Works: Core Principles
OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) technology functions by passing an electric current through organic compounds that emit light when energized, eliminating the need for a backlight. Each pixel in an OLED display produces its own light, enabling true blacks and higher contrast ratios compared to LCDs, which rely on a backlit panel. The self-emissive nature of OLEDs allows for thinner displays and more vibrant color reproduction, making them superior in image quality and energy efficiency for dynamic content.
How LCD Works: Structure and Function
LCDs use a backlight that shines through multiple layers, including polarizers, a liquid crystal layer, and color filters, to produce images. The liquid crystals twist and align in response to electrical currents, controlling the light passage and thus creating varying brightness and color on the screen. Understanding this structure helps you appreciate how LCD technology balances energy efficiency with vibrant display quality.
Display Quality Comparison: OLED vs LCD
OLED displays offer superior contrast ratios and deeper blacks by individually lighting each pixel, resulting in vibrant colors and improved viewing angles compared to LCD screens, which rely on backlighting that can cause light bleed and less uniform color accuracy. LCD panels, while generally more affordable and energy-efficient for static images, typically struggle to match the true blacks and dynamic range visible on OLED displays. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize exceptional display quality and rich visual depth or prefer a budget-friendly option with reliable brightness in well-lit environments.
Brightness and Contrast Differences
OLED displays offer superior contrast ratios due to their ability to turn off individual pixels completely, resulting in true blacks and vibrant colors, whereas LCD screens rely on backlighting that limits black levels and reduces overall contrast. Brightness levels typically favor LCD panels, which can achieve higher peak brightness suitable for well-lit environments, while OLEDs may struggle with peak luminance but excel in presenting deep, rich visual detail in darker scenes. The difference in brightness and contrast significantly impacts image quality, with OLEDs providing more immersive viewing experiences through enhanced contrast, despite LCDs' advantage in brightness intensity.
Color Accuracy and Reproduction
OLED displays offer superior color accuracy and reproduction due to their self-emissive pixels, enabling true blacks and vibrant colors with a wider color gamut compared to LCD panels. LCD technology relies on backlighting and color filters, which can cause color shifts and reduce precision, especially in darker scenes. High-end OLED models consistently outperform LCDs in delivering more lifelike images and better HDR performance.
Energy Efficiency: Which Is Better?
OLED displays consume less power than LCDs when displaying dark or black content due to their ability to turn off individual pixels, leading to higher energy efficiency in low-light scenes. In contrast, LCDs require a constant backlight, which results in steady energy consumption regardless of the image displayed. For bright or white-dominated visuals, LCDs may be more energy-efficient as OLED pixels use more power to produce bright colors.
Durability and Lifespan Considerations
OLED displays offer superior contrast and vibrant colors but generally have shorter lifespans due to organic material degradation, especially when exposed to static images that cause burn-in. LCD panels use longer-lasting backlight technology and are more resistant to screen burn-in, making them more durable for prolonged use. Your choice depends on balancing OLED's rich visuals against LCD's longevity and robustness in various lighting conditions.
Price and Availability Factors
OLED displays generally cost more than LCDs due to advanced manufacturing processes and expensive organic materials, impacting availability especially in budget devices. LCD panels benefit from mass production economies, resulting in lower prices and wider availability across various electronics and screen sizes. Your choice may depend on balancing OLED's premium pricing with superior image quality against the affordability and accessibility of LCD technology.
Choosing the Right Display: OLED or LCD?
OLED displays offer superior contrast ratios, deeper blacks, and faster response times compared to LCDs, making them ideal for high-quality visuals and gaming. LCD panels typically provide better brightness levels and are more cost-effective, making them suitable for budget-conscious users and well-lit environments. Choosing between OLED and LCD depends on prioritizing image quality, power efficiency, and price based on specific use cases.
OLED vs LCD Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com