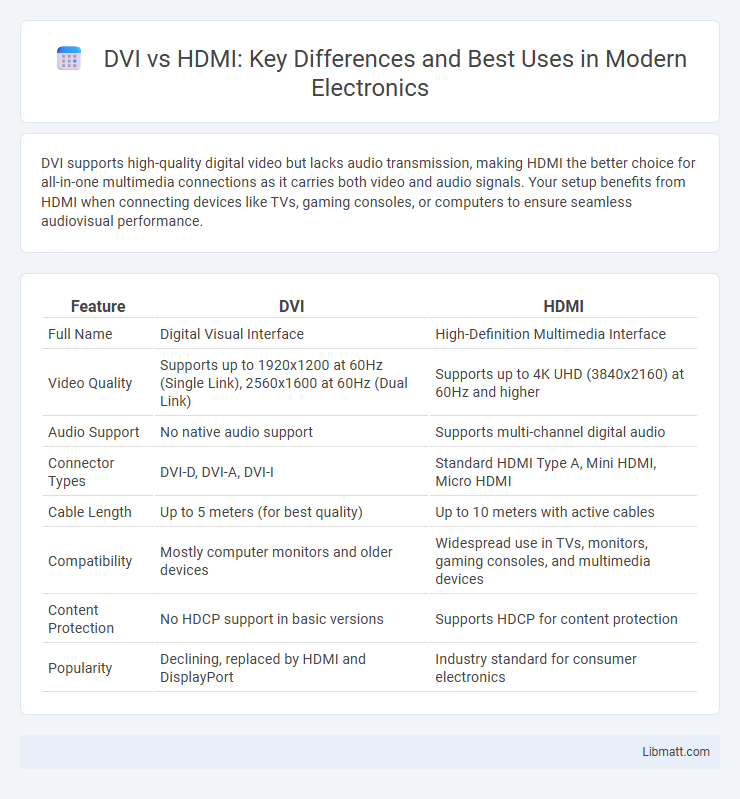
DVI supports high-quality digital video but lacks audio transmission, making HDMI the better choice for all-in-one multimedia connections as it carries both video and audio signals. Your setup benefits from HDMI when connecting devices like TVs, gaming consoles, or computers to ensure seamless audiovisual performance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | DVI | HDMI |
|---|---|---|
| Full Name | Digital Visual Interface | High-Definition Multimedia Interface |
| Video Quality | Supports up to 1920x1200 at 60Hz (Single Link), 2560x1600 at 60Hz (Dual Link) | Supports up to 4K UHD (3840x2160) at 60Hz and higher |
| Audio Support | No native audio support | Supports multi-channel digital audio |
| Connector Types | DVI-D, DVI-A, DVI-I | Standard HDMI Type A, Mini HDMI, Micro HDMI |
| Cable Length | Up to 5 meters (for best quality) | Up to 10 meters with active cables |
| Compatibility | Mostly computer monitors and older devices | Widespread use in TVs, monitors, gaming consoles, and multimedia devices |
| Content Protection | No HDCP support in basic versions | Supports HDCP for content protection |
| Popularity | Declining, replaced by HDMI and DisplayPort | Industry standard for consumer electronics |
Introduction to DVI and HDMI
DVI (Digital Visual Interface) and HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface) are two common video interface standards used to connect devices like monitors, TVs, and computers. DVI primarily supports digital video signals and was widely adopted for computer displays, while HDMI transmits both high-definition video and audio, becoming the standard for modern multimedia devices. Understanding the differences between these interfaces helps you choose the right connection for your display and audio needs.
DVI: Overview and Key Features
DVI (Digital Visual Interface) is a video display interface primarily used to connect a video source to a display device such as a monitor. It supports high-quality digital video signals but does not carry audio, making it suitable for pure video transmission in computer systems and professional displays. Your choice of DVI ensures compatibility with older monitors and offers a reliable, uncompressed video output ideal for gaming and graphic design.
HDMI: Overview and Key Features
HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface) supports high-definition video and audio through a single cable, providing a streamlined connection for modern devices like TVs, gaming consoles, and computers. It carries uncompressed digital signals, ensuring superior image and sound quality compared to older standards like DVI, which only transmits video. Your home entertainment setup benefits from HDMI's compatibility with HDCP copy protection, Ethernet data channel, and support for 3D and 4K resolutions.
Signal Types: Digital vs Analog
DVI primarily supports both digital and analog signals, making it versatile for older monitors that require analog input through DVI-A or DVI-I connectors. HDMI exclusively transmits digital signals, ensuring higher fidelity and supporting advanced features like HDCP for content protection and audio transmission. Understanding these signal differences helps you choose the right interface for your display needs, especially when balancing compatibility with image and sound quality.
Video Quality Comparison
HDMI supports higher resolutions and refresh rates compared to DVI, making it ideal for modern 4K and even 8K displays. DVI typically maxes out at 1920x1200 resolution and lacks audio support, limiting its use for full multimedia experiences. HDMI's ability to carry both video and audio signals enhances overall video quality and simplifies connectivity for advanced devices.
Audio Transmission Capabilities
HDMI supports both high-definition video and multi-channel audio transmission through a single cable, making it ideal for seamless audio-video integration in home theater systems and modern devices. DVI primarily transmits video signals without native audio support, requiring separate audio cables for sound transmission. This limitation makes HDMI the preferred choice for users seeking simplified connectivity and enriched multimedia experiences.
Connector Types and Compatibility
DVI connectors come in three main types: DVI-D (digital only), DVI-A (analog only), and DVI-I (integrated digital and analog), designed primarily for computer monitors and older devices. HDMI connectors offer a single, compact interface supporting both audio and video signals, widely compatible with modern TVs, gaming consoles, and streaming devices. Choosing between DVI and HDMI depends on your device's compatibility needs, with HDMI providing broader support for high-definition multimedia content.
Common Use Cases: DVI vs HDMI
DVI is commonly used for older computer monitors and legacy video equipment, delivering high-quality video without audio support, making it ideal for desktop PCs and workstations. HDMI is prevalent in modern consumer electronics, including TVs, gaming consoles, and home theater systems, offering both high-definition video and audio through a single cable for seamless multimedia experiences. Your choice between DVI and HDMI depends on the device compatibility and whether integrated audio transmission is essential for your setup.
Pros and Cons of DVI and HDMI
DVI supports high-quality digital video signals but lacks audio transmission, making it suitable for monitors where sound is handled separately; it is also compatible with older hardware but bulkier and less versatile than HDMI. HDMI carries both high-definition video and audio through a single cable, supporting modern features like Ethernet and ARC, making it ideal for home entertainment systems, yet it can be more expensive and less robust for legacy equipment compatibility. Your choice should consider device compatibility, audio requirements, and cable length needs when comparing DVI and HDMI connections.
Which Should You Choose: DVI or HDMI?
HDMI supports both high-definition video and audio signals in a single cable, making it ideal for modern home entertainment systems and gaming setups where convenience and compatibility with devices like TVs, monitors, and soundbars are essential. DVI, primarily designed for video-only transmission, remains suitable for legacy computer monitors or scenarios where audio transfer is unnecessary, offering comparable video quality up to 1920x1200 resolution but lacking support for 4K at 60Hz without dual-link cables. If seamless audio-video integration and future-proofing with support for 4K UHD and HDR content are priorities, HDMI is the recommended choice over DVI.
DVI vs HDMI Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com