Demand Charges are fees based on the highest level of electricity usage during a specific period, encouraging you to reduce peak power consumption, while Time-of-Use Tariffs vary electricity rates depending on the time of day to promote energy use during off-peak hours. Understanding these billing methods can help optimize your energy costs by managing consumption patterns effectively.
Table of Comparison
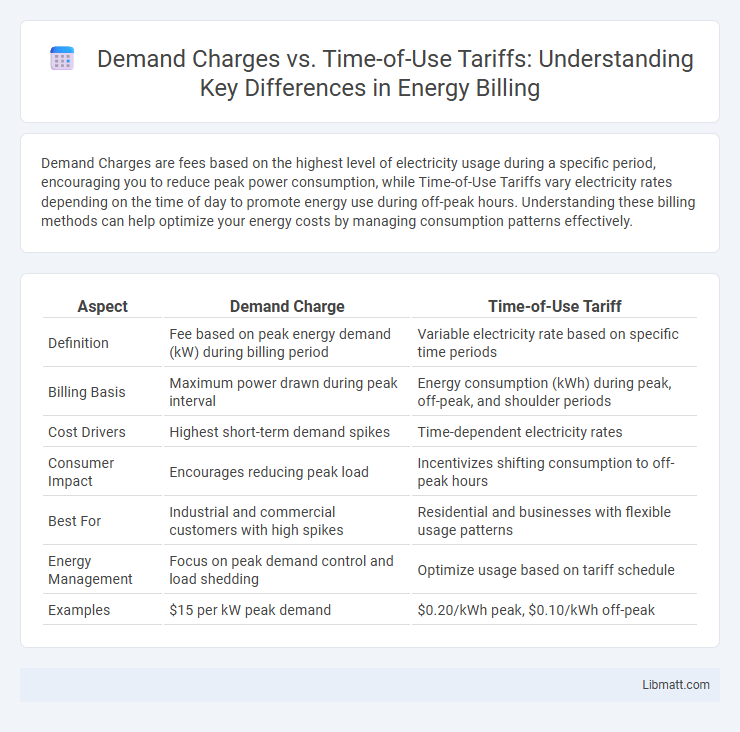
| Aspect | Demand Charge | Time-of-Use Tariff |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fee based on peak energy demand (kW) during billing period | Variable electricity rate based on specific time periods |
| Billing Basis | Maximum power drawn during peak interval | Energy consumption (kWh) during peak, off-peak, and shoulder periods |
| Cost Drivers | Highest short-term demand spikes | Time-dependent electricity rates |
| Consumer Impact | Encourages reducing peak load | Incentivizes shifting consumption to off-peak hours |
| Best For | Industrial and commercial customers with high spikes | Residential and businesses with flexible usage patterns |
| Energy Management | Focus on peak demand control and load shedding | Optimize usage based on tariff schedule |
| Examples | $15 per kW peak demand | $0.20/kWh peak, $0.10/kWh off-peak |
Understanding Demand Charges: Definition and Purpose
Demand charges are fees based on the highest level of power your facility consumes during a specific period, typically measured in kilowatts (kW). These charges aim to recover the cost utilities incur to meet peak energy demand, incentivizing businesses to manage and reduce peak consumption. Understanding demand charges enables you to optimize energy usage patterns and avoid unexpected spikes in your electricity bills.
What Are Time-of-Use (TOU) Tariffs?
Time-of-Use (TOU) tariffs are electricity pricing structures that vary rates based on the time of day, reflecting changes in demand and supply conditions. These tariffs encourage consumers to shift their energy usage to off-peak periods when electricity costs less, helping to reduce grid congestion and lower overall energy expenses. Unlike demand charges that focus on peak power consumption during short intervals, TOU tariffs promote consistent load management by incentivizing energy use during designated low-rate hours.
Key Differences Between Demand Charges and TOU Tariffs
Demand charges are based on the highest peak power demand within a billing cycle, measured in kilowatts (kW), while Time-of-Use (TOU) tariffs charge customers based on electricity consumption during specific time periods with varying rates. Demand charges incentivize reducing peak demand to lower bills, whereas TOU tariffs encourage shifting energy use to off-peak hours for cost savings. Utilities implement demand charges primarily for managing infrastructure stress, while TOU tariffs aim to balance grid load and integrate renewable energy sources more effectively.
How Demand Charges Impact Your Electricity Bill
Demand charges are based on the highest level of power demand you place on the electrical grid during a billing period, often measured in kilowatts (kW), significantly influencing your overall electricity costs. Unlike time-of-use tariffs that vary rates by the time electricity is consumed, demand charges focus on peak demand spikes regardless of the time, which can cause sharp increases in your bills if your usage peaks are not managed effectively. Understanding how demand charges impact your electricity bill enables you to implement strategies like load shifting or peak shaving to reduce peak demand and lower costs.
Evaluating Peak Hours in TOU Tariffs
Time-of-Use (TOU) tariffs segment electricity pricing based on predefined peak hours, encouraging consumers to reduce usage during high-demand periods. Evaluating peak hours involves analyzing consumption patterns and grid demand data to identify when electricity costs are highest, enabling you to shift your energy use for cost savings. Understanding these peak intervals is essential for optimizing energy efficiency and minimizing charges compared to Demand Charge structures.
Pros and Cons of Demand Charges
Demand charges provide businesses with a pricing model based on their peak electricity usage, encouraging efficient energy management and potential cost savings by reducing maximum demand. These charges can lead to higher bills during short periods of intense consumption, posing challenges for industries with fluctuating energy needs. Your ability to monitor and control peak demand directly affects how advantageous demand charges are compared to time-of-use tariffs.
Advantages and Disadvantages of TOU Tariffs
Time-of-Use (TOU) tariffs incentivize energy usage during off-peak periods by offering lower rates, helping reduce overall electricity costs and ease grid demand. Your ability to shift consumption to cheaper hours maximizes savings but may require lifestyle adjustments and smart energy management systems. However, TOU tariffs can lead to higher bills if peak usage is not controlled effectively, posing a challenge for consumers lacking flexible energy habits.
Choosing the Right Tariff: Factors to Consider
Selecting the right tariff between Demand Charge and Time-of-Use Tariff depends on energy consumption patterns and peak demand periods. Businesses with high peak usage may benefit from Demand Charge tariffs by managing their maximum demand to reduce costs, while Time-of-Use tariffs favor users who can shift energy use to off-peak hours to take advantage of lower rates. Evaluating historical consumption data, load flexibility, and the ability to implement energy management strategies is crucial for optimizing savings under either tariff structure.
Case Studies: Demand Charge vs. TOU Tariff Savings
Case studies reveal that businesses implementing Demand Charge management strategies can achieve up to 25% reduction in peak electricity costs by optimizing equipment usage during high-demand periods. In contrast, Time-of-Use (TOU) tariff savings depend heavily on shifting energy consumption to off-peak hours, with some commercial clients reporting up to 15% lower energy bills through smart scheduling. Your choice between Demand Charge and TOU tariffs should factor in your load profile and flexibility to adjust consumption patterns for maximum cost efficiency.
Future Trends in Utility Pricing Models
Future trends in utility pricing models indicate a shift towards integrating Demand Charge structures with Time-of-Use Tariffs to better reflect grid stress and consumer usage patterns. Advanced metering infrastructure enables utilities to implement dynamic pricing that incentivizes load shifting and peak demand reduction, improving grid efficiency and reducing operational costs. Emerging technologies such as smart grids and energy storage systems will further optimize these pricing strategies, promoting sustainability and cost savings for both utilities and consumers.
Demand Charge vs Time-of-Use Tariff Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com