Conventional drilling extracts oil and gas by tapping reservoirs with natural pressure or pumping, relying on vertical wells that access permeable rock formations. Hydraulic fracturing enhances extraction by injecting high-pressure fluid to create fractures in impermeable rock, significantly boosting Your ability to recover trapped hydrocarbons from shale and tight sandstone formations.
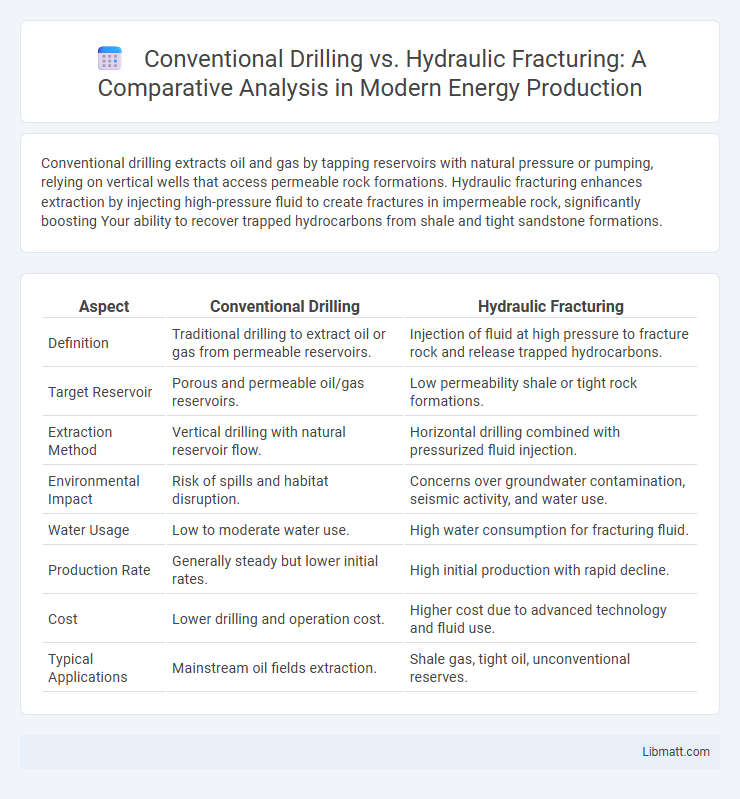
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Conventional Drilling | Hydraulic Fracturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Traditional drilling to extract oil or gas from permeable reservoirs. | Injection of fluid at high pressure to fracture rock and release trapped hydrocarbons. |
| Target Reservoir | Porous and permeable oil/gas reservoirs. | Low permeability shale or tight rock formations. |
| Extraction Method | Vertical drilling with natural reservoir flow. | Horizontal drilling combined with pressurized fluid injection. |
| Environmental Impact | Risk of spills and habitat disruption. | Concerns over groundwater contamination, seismic activity, and water use. |
| Water Usage | Low to moderate water use. | High water consumption for fracturing fluid. |
| Production Rate | Generally steady but lower initial rates. | High initial production with rapid decline. |
| Cost | Lower drilling and operation cost. | Higher cost due to advanced technology and fluid use. |
| Typical Applications | Mainstream oil fields extraction. | Shale gas, tight oil, unconventional reserves. |
Introduction: Understanding Oil and Gas Extraction
Conventional drilling involves accessing oil and gas reserves trapped in porous rock formations through vertical wells, relying on natural reservoir pressure for extraction. Hydraulic fracturing, or fracking, enhances extraction by injecting high-pressure fluid to create fractures in impermeable shale formations, releasing trapped hydrocarbons. Both methods are fundamental in the energy industry, with hydraulic fracturing significantly boosting production from previously inaccessible resources.
What Is Conventional Drilling?
Conventional drilling involves extracting oil and gas from porous rock formations using vertical wells that access naturally occurring reservoirs where hydrocarbons flow freely. This method relies on natural pressure or pumps to bring resources to the surface without fracturing the rock. Understanding conventional drilling helps you evaluate traditional energy extraction methods versus more complex techniques like hydraulic fracturing.
The Process of Hydraulic Fracturing
Hydraulic fracturing involves injecting a high-pressure fluid mixture, typically water, sand, and chemical additives, into rock formations to create fractures that release trapped oil and natural gas. The sand acts as a proppant, keeping the fractures open to enable continuous extraction of hydrocarbons. This process significantly enhances well productivity compared to conventional drilling, which relies on natural reservoir pressure to bring fluids to the surface.
Key Differences Between Conventional Drilling and Fracking
Conventional drilling involves extracting oil or gas from porous rock formations using vertical wells, relying on natural reservoir pressure or pumps to bring hydrocarbons to the surface. Hydraulic fracturing, or fracking, employs high-pressure fluid injections to create fractures in shale or tight rock formations, significantly enhancing hydrocarbon flow. The key differences include the geological formations targeted, extraction techniques, environmental impact, and production efficiency, with fracking enabling access to otherwise inaccessible reserves.
Resource Types: Reservoirs and Accessibility
Conventional drilling targets permeable reservoirs where hydrocarbons naturally flow to wellbores, typically found in large, easily accessible sandstone or limestone formations. Hydraulic fracturing accesses unconventional reservoirs such as shale or tight sandstone, where hydrocarbons are trapped in low-permeability rock, requiring the injection of high-pressure fluid to create fractures and release resources. Your choice between these methods depends on the geology and accessibility of the resource formations, influencing extraction efficiency and production costs.
Environmental Impacts: Comparing Methods
Conventional drilling typically results in surface disturbance, habitat disruption, and risks of groundwater contamination due to drilling fluid spills and waste. Hydraulic fracturing, or fracking, involves high water usage and chemical additives, leading to concerns about groundwater pollution, induced seismic activity, and long-term aquifer contamination. Both methods contribute to greenhouse gas emissions, but fracking's potential methane leaks pose heightened climate change risks compared to conventional drilling.
Economic Considerations and Production Efficiency
Conventional drilling offers lower upfront costs and simpler operational logistics, making it economically favorable for sites with easily accessible resources. Hydraulic fracturing significantly boosts production efficiency by enabling access to tight shale formations, driving higher output but at increased capital and environmental costs. Your choice between these methods should weigh immediate economic considerations against potential long-term production gains and market volatility.
Technological Innovations in Extraction Techniques
Conventional drilling relies on vertical wells to access oil and gas reservoirs, utilizing rotary drilling technology that has evolved with improved drill bits and directional drilling capabilities. Hydraulic fracturing, or fracking, employs high-pressure fluid injections to create fractures in rock formations, enhancing hydrocarbon flow and unlocking previously inaccessible resources, driven by advancements in pump technology and proppant materials. Your choice between these extraction techniques depends on resource characteristics, where hydraulic fracturing offers greater efficiency in tight shale formations compared to traditional methods.
Regulatory and Safety Challenges
Conventional drilling faces regulatory challenges centered on groundwater protection and air quality standards, with strict permitting processes ensuring minimal environmental impact. Hydraulic fracturing involves additional safety concerns such as chemical handling, wastewater management, and induced seismicity, leading to more complex regulations and monitoring requirements. Your compliance with evolving federal and state regulations is crucial to mitigate risks and ensure operational safety in both extraction methods.
The Future of Energy: Balancing Conventional and Unconventional Methods
Conventional drilling methods have long been the backbone of global energy production, providing steady access to oil and gas reserves through established techniques that minimize initial costs and infrastructure needs. Hydraulic fracturing, or fracking, unlocks previously inaccessible shale formations, significantly boosting supply and extending the lifespan of fossil fuel resources while raising environmental concerns such as water usage and seismic risks. Your energy strategy should balance these technologies by integrating conventional drilling's reliability with fracking's resource expansion potential, promoting a transitional pathway toward cleaner, more sustainable energy solutions.
Conventional Drilling vs Hydraulic Fracturing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com