Peak load refers to the highest demand for electricity during a specific period, requiring fast-response power sources to manage sudden surges. Base load is the consistent minimum level of demand on the power grid, typically supplied by reliable, continuous energy sources like coal or nuclear plants to ensure steady electricity availability.
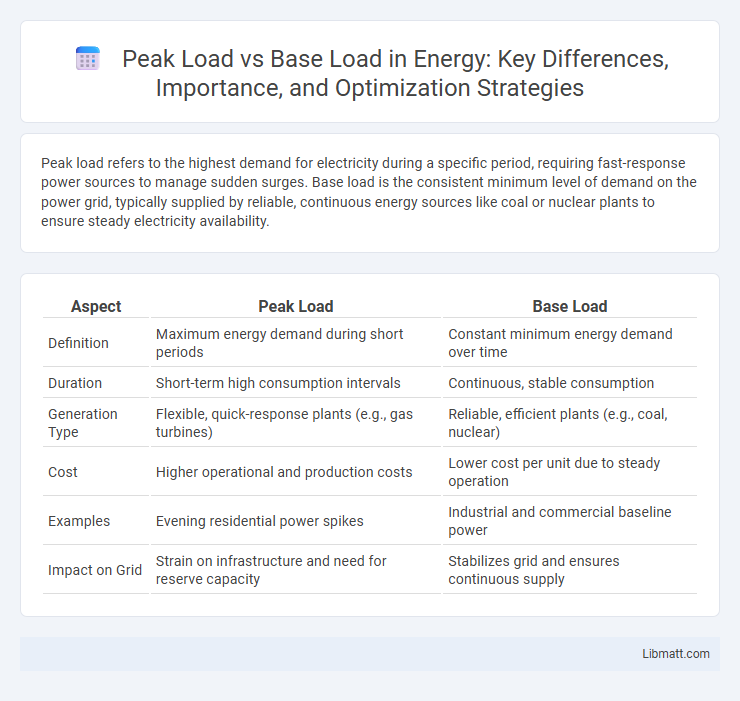
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Peak Load | Base Load |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Maximum energy demand during short periods | Constant minimum energy demand over time |
| Duration | Short-term high consumption intervals | Continuous, stable consumption |
| Generation Type | Flexible, quick-response plants (e.g., gas turbines) | Reliable, efficient plants (e.g., coal, nuclear) |
| Cost | Higher operational and production costs | Lower cost per unit due to steady operation |
| Examples | Evening residential power spikes | Industrial and commercial baseline power |
| Impact on Grid | Strain on infrastructure and need for reserve capacity | Stabilizes grid and ensures continuous supply |
Understanding Peak Load and Base Load
Peak load refers to the highest electricity demand recorded during a specific period, typically driven by activities such as extreme weather conditions or industrial operations. Base load represents the minimum continuous power supply required to meet essential demand, usually provided by reliable and consistent energy sources like nuclear or coal plants. Understanding the distinction between peak load and base load is crucial for efficient energy management and grid stability.
Key Differences Between Peak Load and Base Load
Peak load refers to the maximum electrical power demand observed during specific periods, often fluctuating based on consumer activity, while base load represents the constant minimum power demand sustained over time. Peak load requires flexible power plants capable of rapid ramp-up, such as gas turbines, whereas base load is typically supplied by stable, continuous energy sources like coal, nuclear, or hydroelectric plants. Managing the balance between peak and base loads is crucial for grid stability, cost efficiency, and optimized energy resource utilization.
Importance of Peak Load in Power Systems
Peak load represents the highest electrical demand within a specific period, critical for maintaining grid stability and preventing outages. Managing peak load requires efficient resource allocation and infrastructure capable of rapid response, ensuring your power system remains reliable during usage spikes. Optimizing peak load handling minimizes costs and improves overall energy efficiency in power systems.
Role of Base Load in Energy Supply
Base load power plants provide a continuous and reliable supply of electricity, meeting the minimum demand on the grid 24/7. These plants, often fueled by coal, nuclear, or hydro, operate at high efficiency and lower operational costs compared to peak load plants. Their stability ensures grid reliability, supporting energy security and minimizing fluctuations in power supply.
Peak Load vs Base Load: Energy Sources Comparison
Peak load energy is typically supplied by fast-ramping sources such as natural gas turbines, diesel generators, and hydroelectric power plants, which can quickly meet sudden increases in electricity demand. Base load energy relies on steady, continuous sources like coal, nuclear, and large-scale hydroelectric plants that provide consistent power output with high capacity factors. Renewable sources like solar and wind contribute variably to both loads but require storage or backup to reliably support peak or base load demands.
Challenges of Managing Peak Load
Managing peak load presents significant challenges due to sudden surges in electricity demand requiring rapid activation of additional power plants, often relying on costly and less efficient peaking units. Grid operators must balance supply and demand in real-time, preventing blackouts while minimizing operational costs and emissions. Integration of renewable energy sources complicates peak load management further by introducing variability and uncertainty in power availability.
Base Load Reliability and Stability
Base load power plants provide consistent and reliable energy output, ensuring grid stability by meeting the minimum electricity demand around the clock. Their continuous operation prevents frequency fluctuations and voltage instability, which are critical for maintaining a stable power system. High capacity factor and robust infrastructure contribute to the dependable supply of base load power during peak and off-peak hours.
Impact of Renewable Energy on Peak and Base Load
Renewable energy sources like solar and wind significantly reduce base load demand by supplying consistent power during daylight and windy periods, shifting traditional energy consumption patterns. However, their intermittent nature increases reliance on flexible peak load power plants or energy storage systems to maintain grid stability during low renewable output periods. Integration of renewables requires advanced grid management and demand response strategies to optimize peak and base load balance effectively.
Strategies for Optimizing Peak and Base Load
Optimizing peak and base load involves deploying demand response programs that shift electricity usage from peak to off-peak hours, enhancing grid stability and reducing costs. Incorporating energy storage systems like batteries allows excess energy generated during low demand to be stored and utilized during peak periods, smoothing load fluctuations. Implementing smart grid technologies and real-time data analytics enables precise load forecasting and adaptive energy distribution tailored to consumption patterns.
Future Trends in Load Management
Future trends in load management emphasize the integration of advanced energy storage systems and demand response technologies to balance peak load and base load efficiently. Smart grid innovations enable real-time data analytics and automated adjustments, reducing peak demand stress while optimizing base load stability. Increased adoption of renewable energy sources further necessitates dynamic load management strategies to accommodate their variable output.
Peak load vs Base load Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com