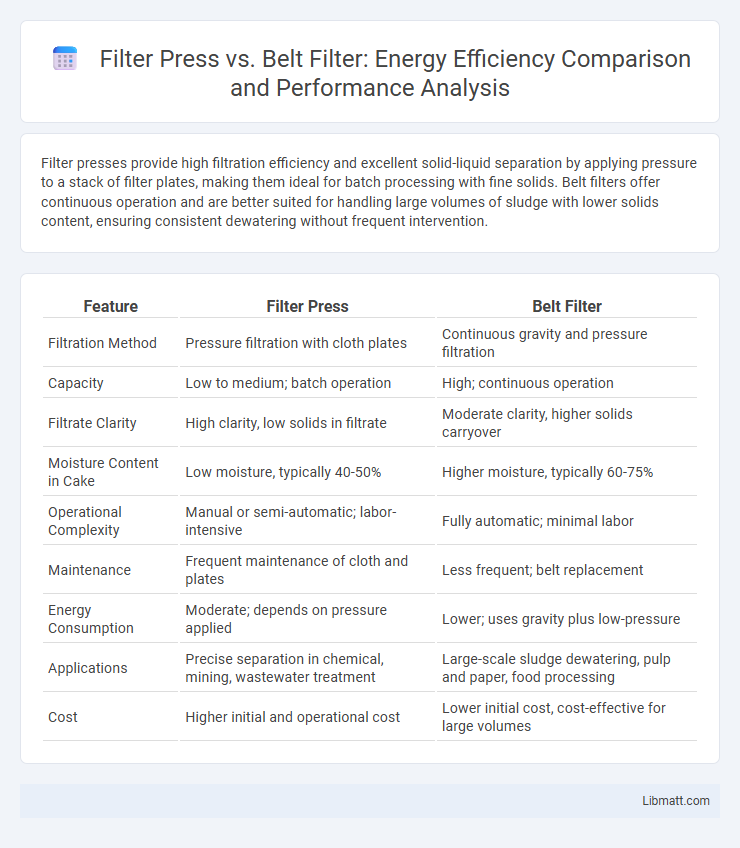
Filter presses provide high filtration efficiency and excellent solid-liquid separation by applying pressure to a stack of filter plates, making them ideal for batch processing with fine solids. Belt filters offer continuous operation and are better suited for handling large volumes of sludge with lower solids content, ensuring consistent dewatering without frequent intervention.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Filter Press | Belt Filter |
|---|---|---|
| Filtration Method | Pressure filtration with cloth plates | Continuous gravity and pressure filtration |
| Capacity | Low to medium; batch operation | High; continuous operation |
| Filtrate Clarity | High clarity, low solids in filtrate | Moderate clarity, higher solids carryover |
| Moisture Content in Cake | Low moisture, typically 40-50% | Higher moisture, typically 60-75% |
| Operational Complexity | Manual or semi-automatic; labor-intensive | Fully automatic; minimal labor |
| Maintenance | Frequent maintenance of cloth and plates | Less frequent; belt replacement |
| Energy Consumption | Moderate; depends on pressure applied | Lower; uses gravity plus low-pressure |
| Applications | Precise separation in chemical, mining, wastewater treatment | Large-scale sludge dewatering, pulp and paper, food processing |
| Cost | Higher initial and operational cost | Lower initial cost, cost-effective for large volumes |
Introduction to Solid-Liquid Separation Technologies
Solid-liquid separation technologies like filter presses and belt filters play crucial roles in efficiently extracting liquids from slurries, widely used in industries such as mining, wastewater treatment, and chemical processing. Filter presses offer precise filtration with high solids capture and dry cake discharge, ideal for applications needing superior dewatering and clear filtrate. Belt filters provide continuous operation with moderate cake dryness, designed to handle large volumes and deliver consistent throughput, making them suitable for processes requiring steady, high-capacity separation.
What is a Filter Press?
A filter press is an industrial filtration device that separates solids and liquids through pressure filtration, using multiple filter plates covered with filter cloths to capture solid particles. It operates by pumping slurry into the press, where the liquid passes through the filter media while the solids form a filter cake on the plates. Filter presses are widely used in wastewater treatment, chemical manufacturing, and mining for their high-efficiency dewatering and ability to handle diverse slurry types.
Understanding Belt Filter Systems
Belt filter systems utilize a continuous belt to dewater sludge by applying mechanical pressure and gravity, making them efficient for treating large volumes of wastewater sludge. These systems offer advantages such as lower energy consumption, simpler operation, and consistent filtration compared to filter press technology. Understanding the mechanics and operational parameters of belt filter presses is crucial for optimizing sludge dehydration in municipal and industrial applications.
Working Principles: Filter Press vs Belt Filter
A filter press operates by applying high pressure to separate solids from liquids through a series of filter plates, creating a cake-like residue that is periodically removed. In contrast, a belt filter uses continuous gravity drainage followed by mechanical compression on a moving belt to dewater sludge or slurry. Understanding these working principles helps you select the most efficient filtration method for your specific industrial or wastewater treatment needs.
Key Components and Design Differences
Filter press systems consist of multiple plates with filter cloths that form chambers to separate solids from liquids through pressure, while belt filters use continuous belts to filter slurry by gravity and pressure. Key components of filter presses include the frame, hydraulic system, and filter plates, designed for batch operation and high-pressure filtration, whereas belt filters feature a series of belts, rollers, and gravity drainage zones, optimized for continuous processing. Your choice depends on the required filtration capacity, operational mode, and maintenance preferences related to these distinct design elements.
Performance and Efficiency Comparison
Filter presses exhibit higher solid capture efficiency, achieving moisture content as low as 15-20%, making them ideal for applications requiring thorough dewatering. Belt filters offer continuous operation with lower energy consumption but typically yield higher moisture content around 30-50%, balancing throughput and operational costs. Performance differences are influenced by sludge characteristics, with filter presses favored for high solids concentration and belt filters suited for large volume, lower solids waste streams.
Filtration Quality: Cake Moisture and Clarity
Filter presses typically deliver superior filtration quality with lower cake moisture content, producing drier cakes compared to belt filters. Belt filters often provide higher clarity in the filtrate due to continuous operation but may result in wetter cakes with higher moisture levels. Your choice between these two should consider the trade-off between cake dryness and filtrate clarity based on process requirements.
Operating Costs and Maintenance Requirements
Filter presses generally have higher initial investment and maintenance costs due to their complex plates and cloth replacement needs, but they offer lower operating costs in long-term dewatering efficiency. Belt filters typically incur lower upfront expenses and simpler maintenance, involving periodic belt replacement and tension adjustments, yet may demand more energy during continuous operation. Both systems require tailored maintenance schedules to optimize filtration performance and manage operational costs effectively.
Applications and Industry Suitability
Filter presses excel in industries requiring high-efficiency solid-liquid separation such as chemical manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, and mining due to their ability to handle high solids content and produce dry filter cakes. Belt filters are better suited for wastewater treatment and food processing where continuous, low-maintenance operation and handling of large volumes of sludge with lower solids concentration is essential. Your choice depends on the specific application demands and industry standards, balancing factors like dryness of output, throughput, and process continuity.
Choosing the Right Filter: Factors to Consider
Selecting the right filtration system between a filter press and a belt filter depends on factors such as sludge type, moisture content requirements, and processing capacity. Filter presses offer higher solid capture and drier output, ideal for industrial applications with thick, high solids sludge, while belt filters provide continuous operation and lower energy consumption for large volumes of low to medium solids. Your choice should balance operational efficiency, space constraints, and maintenance needs to optimize filtration performance.
Filter Press vs Belt Filter Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com