AMI (Advanced Metering Infrastructure) enables real-time two-way communication between your utility and smart meters, allowing for precise monitoring and management of energy usage. AMR (Automated Meter Reading) automates data collection from meters but typically supports only one-way communication, limiting timely insights into consumption patterns.
Table of Comparison
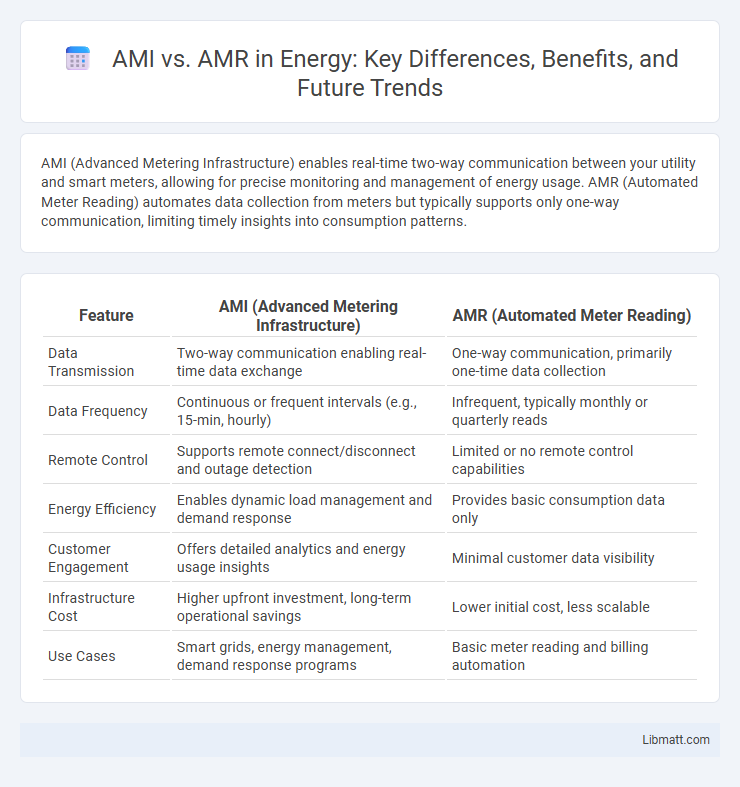
| Feature | AMI (Advanced Metering Infrastructure) | AMR (Automated Meter Reading) |
|---|---|---|
| Data Transmission | Two-way communication enabling real-time data exchange | One-way communication, primarily one-time data collection |
| Data Frequency | Continuous or frequent intervals (e.g., 15-min, hourly) | Infrequent, typically monthly or quarterly reads |
| Remote Control | Supports remote connect/disconnect and outage detection | Limited or no remote control capabilities |
| Energy Efficiency | Enables dynamic load management and demand response | Provides basic consumption data only |
| Customer Engagement | Offers detailed analytics and energy usage insights | Minimal customer data visibility |
| Infrastructure Cost | Higher upfront investment, long-term operational savings | Lower initial cost, less scalable |
| Use Cases | Smart grids, energy management, demand response programs | Basic meter reading and billing automation |
Introduction to AMI and AMR
Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) enables two-way communication between smart meters and utility providers, facilitating real-time data collection, remote monitoring, and improved energy management. Automated Meter Reading (AMR) primarily supports one-way data transmission, allowing utilities to collect meter readings remotely without manual intervention. Both technologies enhance efficiency but differ significantly in communication capabilities and data utilization.
Defining Automated Meter Infrastructure (AMI)
Automated Meter Infrastructure (AMI) refers to an integrated system of smart meters, communication networks, and data management software that enables two-way communication between utility providers and consumers. AMI facilitates real-time monitoring, remote meter readings, and enhanced energy usage analytics, significantly improving operational efficiency and customer service. Understanding AMI's capabilities helps you optimize energy management and reduce operational costs in comparison to Automated Meter Reading (AMR), which primarily focuses on one-way data collection.
Understanding Automatic Meter Reading (AMR)
Automatic Meter Reading (AMR) technology enables remote data collection from utility meters, reducing manual efforts and improving billing accuracy. By transmitting consumption data directly to utilities, AMR systems provide real-time monitoring and detect anomalies such as meter tampering or leaks. Understanding AMR can help you optimize energy management and ensure timely, precise billing.
Key Differences Between AMI and AMR
AMI (Advanced Metering Infrastructure) integrates smart meters, communication networks, and data management systems to enable two-way communication between utilities and consumers. AMR (Automated Meter Reading) primarily automates the collection of meter data using one-way communication, typically via drive-by or fixed network technologies. The key differences lie in AMI's comprehensive, real-time data exchange capabilities and advanced analytics support, whereas AMR focuses on periodic data collection with limited interaction and fewer operational benefits.
Advantages of Implementing AMI
Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) offers real-time two-way communication between meters and utility providers, enabling faster outage detection and efficient demand response management. AMI provides enhanced data accuracy and remote monitoring, reducing manual meter reading costs and improving billing precision. Implementing AMI allows your utility to optimize energy consumption, increase operational efficiency, and support advanced analytics for better decision-making.
Benefits and Limitations of AMR
Advanced Meter Reading (AMR) offers improved efficiency by automating data collection, reducing manual labor, and minimizing human error compared to Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI). AMR's key benefits include quicker data retrieval and lower operational costs, but it lacks two-way communication capabilities essential for real-time energy management and demand response. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize cost-effective meter reading or comprehensive, interactive energy monitoring provided by AMI.
Technology Components in AMI vs AMR
Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) integrates smart meters, communication networks, and data management systems, enabling two-way communication between utilities and consumers for real-time data collection and remote management. Automated Meter Reading (AMR) primarily involves smart meters and one-way communication technologies such as radio frequency or power line communication to collect meter readings without manual intervention. AMI's use of advanced communication protocols like cellular, mesh networks, and cloud-based analytics distinguishes it from AMR's simpler, one-directional data transmission framework.
Impact on Utility Operations and Efficiency
Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) enhances utility operations by providing real-time, two-way communication between meters and the utility, enabling faster detection of outages, improved load management, and accurate demand forecasting. Automated Meter Reading (AMR) offers basic remote data collection but lacks the interactive capabilities of AMI, limiting utility responsiveness and operational efficiency. Investing in AMI empowers your utility to optimize resource allocation, reduce operational costs, and improve service reliability through continuous monitoring and rapid data-driven decision-making.
Challenges in Transitioning from AMR to AMI
Transitioning from Advanced Meter Reading (AMR) to Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) presents challenges including integration complexity with existing utility systems and ensuring cybersecurity across connected devices. Utilities face significant costs related to upgrading infrastructure, training personnel, and managing data storage and analytics required for AMI's real-time capabilities. Addressing interoperability issues and maintaining customer engagement during the migration process are critical to achieving operational efficiency and enhanced grid management.
Future Trends in Metering Technology
Future trends in metering technology highlight the shift from Automated Meter Reading (AMR) to Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) systems, driven by the need for real-time data and enhanced grid management. AMI enables two-way communication between meters and utilities, supporting demand response, outage detection, and integration of distributed energy resources. Your utility can leverage AMI to improve operational efficiency, reduce costs, and empower consumers with detailed consumption insights.
AMI vs AMR Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com