An inverter changes direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC), which is essential for powering AC devices from batteries or solar panels. A converter, on the other hand, transforms AC to DC or adjusts voltage levels, ensuring your electronic devices receive the appropriate power type and voltage for optimal performance.
Table of Comparison
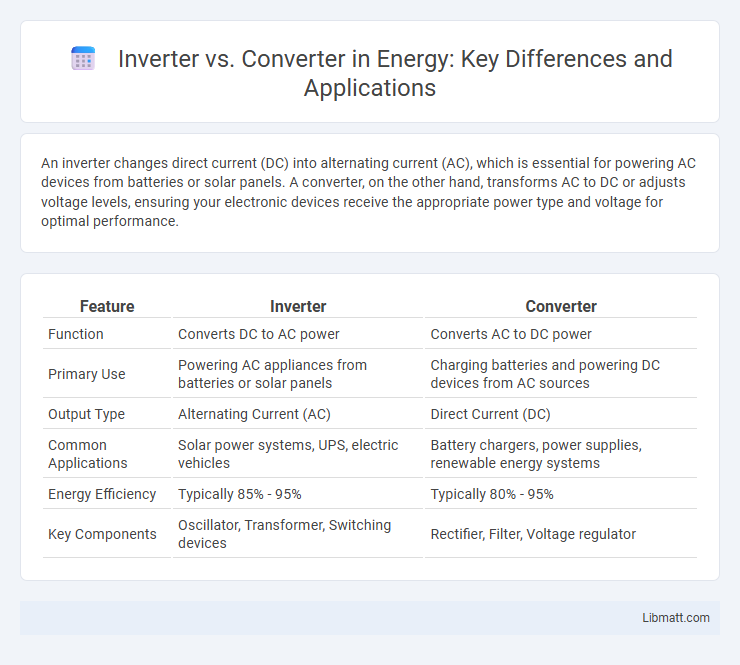
| Feature | Inverter | Converter |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Converts DC to AC power | Converts AC to DC power |
| Primary Use | Powering AC appliances from batteries or solar panels | Charging batteries and powering DC devices from AC sources |
| Output Type | Alternating Current (AC) | Direct Current (DC) |
| Common Applications | Solar power systems, UPS, electric vehicles | Battery chargers, power supplies, renewable energy systems |
| Energy Efficiency | Typically 85% - 95% | Typically 80% - 95% |
| Key Components | Oscillator, Transformer, Switching devices | Rectifier, Filter, Voltage regulator |
Introduction to Power Electronics
In power electronics, inverters and converters are essential devices that control and transform electrical energy for various applications. An inverter converts direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC), enabling the use of DC sources like batteries in AC-powered systems, while a converter changes voltage levels within DC or AC systems to match device requirements. Understanding the operational principles of inverters and converters is fundamental for designing efficient energy management systems and renewable energy integration.
What is an Inverter?
An inverter is an electronic device that converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC), enabling the use of DC power sources such as batteries and solar panels for AC appliances. It plays a crucial role in renewable energy systems, uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), and electric vehicles by providing stable and reliable AC output. Advanced inverters incorporate features like waveform shaping, voltage regulation, and frequency control to ensure efficient and safe power conversion.
What is a Converter?
A converter is an electrical device that changes the form of electrical energy from one type to another, typically converting AC (alternating current) to DC (direct current) or vice versa. It plays a crucial role in power supply systems, enabling compatibility between devices that operate on different electrical standards. Common applications include battery charging, power adapters, and industrial machinery where voltage and current conversion is essential for efficient operation.
Inverter vs Converter: Key Differences
Inverter vs Converter: Key Differences lie primarily in their core functions--an inverter converts direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC), while a converter changes AC to DC or alters voltage levels. Your choice depends on specific application needs such as powering AC appliances from a DC source or charging batteries with AC power. Understanding these distinctions helps optimize energy efficiency and compatibility in electrical systems.
Working Principle of Inverters
Inverters operate by converting direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) using electronic components such as transistors and oscillators to generate a sine wave output suitable for household appliances and industrial equipment. The working principle involves switching the DC input rapidly through a series of transistors in an H-bridge configuration to produce a high-frequency AC signal, which is then filtered to create a smooth sinusoidal waveform. This process enables efficient energy conversion for applications like solar power systems, uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), and motor drives.
Working Principle of Converters
Converters function by altering the voltage level of electrical power, either stepping it up or stepping it down through electromagnetic induction or semiconductor switching devices such as diodes and transistors. The working principle involves converting alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) or vice versa, depending on the type of converter--rectifiers for AC to DC and choppers or DC-DC converters for DC voltage regulation. Efficient energy transformation in converters relies on controlled switching mechanisms to minimize losses and maintain stable output voltage and current for various electronic applications.
Applications of Inverters
Inverters are widely used in renewable energy systems, converting DC from solar panels or batteries into AC for household appliances and grid compatibility. They play a crucial role in uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) by providing backup power during outages, ensuring continuous operation of critical equipment. Industrial applications also utilize inverters to control motor speeds, improving energy efficiency and process precision.
Applications of Converters
Converters are essential in applications requiring the transformation of direct current (DC) voltage levels, such as battery-powered devices, electric vehicles, and renewable energy systems like solar power installations. They enable efficient energy transfer between different voltage levels, ensuring compatibility between power sources and loads, which is critical for maintaining system performance and efficiency. Your choice of converters impacts the reliability and effectiveness of power management in portable electronics and industrial equipment.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Inverters efficiently convert DC to AC, making them ideal for renewable energy systems and electronics but can produce harmonic distortion and require complex circuitry, increasing cost. Converters transform AC to DC, providing stable power for battery charging and electronic devices, though they may cause reduced efficiency and heat generation due to energy loss. Selecting between an inverter and a converter depends on application requirements like energy efficiency, power quality, and device compatibility.
Choosing Between Inverter and Converter
Choosing between an inverter and a converter depends on the specific power requirements and application needs. Inverters convert DC to AC, ideal for devices requiring alternating current like household appliances and renewable energy systems, while converters transform AC to DC, essential for powering electronic gadgets and charging batteries. Evaluating voltage compatibility, power output, and efficiency will help determine the best solution for your electrical setup.
Inverter vs Converter Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com