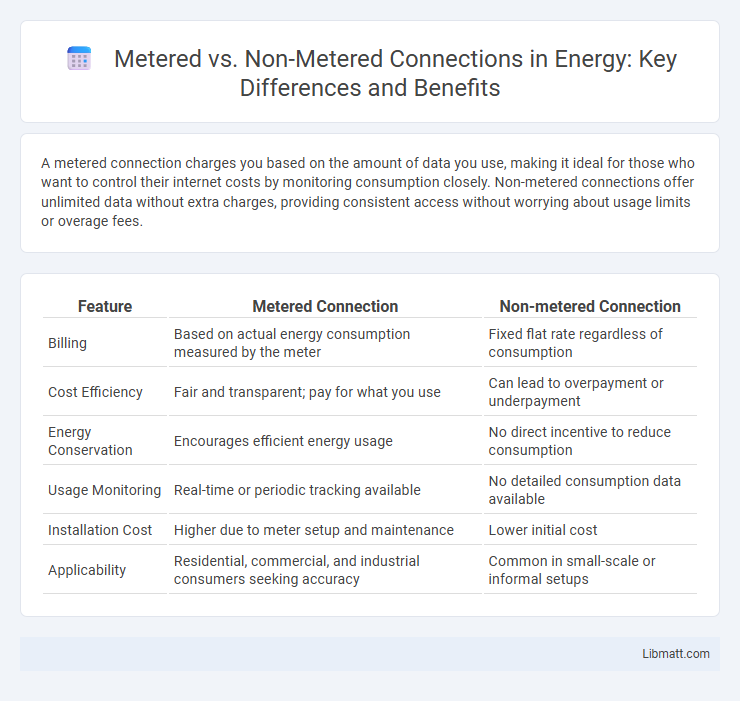
A metered connection charges you based on the amount of data you use, making it ideal for those who want to control their internet costs by monitoring consumption closely. Non-metered connections offer unlimited data without extra charges, providing consistent access without worrying about usage limits or overage fees.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Metered Connection | Non-metered Connection |
|---|---|---|
| Billing | Based on actual energy consumption measured by the meter | Fixed flat rate regardless of consumption |
| Cost Efficiency | Fair and transparent; pay for what you use | Can lead to overpayment or underpayment |
| Energy Conservation | Encourages efficient energy usage | No direct incentive to reduce consumption |
| Usage Monitoring | Real-time or periodic tracking available | No detailed consumption data available |
| Installation Cost | Higher due to meter setup and maintenance | Lower initial cost |
| Applicability | Residential, commercial, and industrial consumers seeking accuracy | Common in small-scale or informal setups |
Introduction to Metered and Non-metered Connections
Metered connections track actual usage through devices like electricity or water meters, allowing consumers to pay based on consumption, promoting efficient resource management. Non-metered connections involve fixed charges regardless of usage, often leading to less precise billing and potential overconsumption. Understanding these differences is crucial for consumers aiming to optimize their utility expenses and for service providers managing resource allocation.
Defining Metered vs Non-metered Internet
Metered internet connections charge you based on the amount of data used, making them ideal for users with predictable or low data consumption. Non-metered internet connections offer unlimited data usage for a fixed price, providing convenience for heavy data users or households with multiple devices. Understanding the difference between metered and non-metered internet ensures you select a plan that aligns with your data needs and budget.
Key Differences Between Metered and Non-metered Connections
Metered connections measure electricity consumption with a digital or analog meter, enabling precise billing based on usage, while non-metered connections charge a fixed amount regardless of actual consumption. Metered connections promote energy efficiency and cost accountability, whereas non-metered connections often lead to flat-rate billing without usage tracking. The key difference lies in consumption transparency and billing accuracy, impacting consumer behavior and utility management.
Advantages of Metered Connections
Metered connections offer precise tracking of your water or electricity usage, enabling efficient resource management and cost control. They help identify consumption patterns, encouraging conservation and reducing unnecessary expenses. With metered connections, you only pay for what you use, which promotes fair billing and accountability in utility services.
Drawbacks of Metered Connections
Metered connections often result in unpredictable costs due to usage-based billing, which can lead to higher expenses during peak consumption periods. Limited data allowances may cause service interruptions or additional charges when exceeded, affecting continuous access. These drawbacks make budgeting for internet or utility costs challenging compared to the fixed pricing of non-metered connections.
Benefits of Non-metered Connections
Non-metered connections offer the advantage of fixed monthly billing, eliminating unexpected spikes in your utility costs and facilitating easier budgeting. They provide uninterrupted service without the need for constant consumption monitoring, ideal for consumers with consistent usage patterns. This type of connection simplifies managing expenses by providing predictable payments regardless of actual consumption fluctuations.
Limitations of Non-metered Connections
Non-metered connections often lead to unregulated electricity consumption, resulting in inefficiencies and increased strain on power grids. These connections lack precise measurement, making it difficult to monitor usage patterns or identify energy wastage. Consequently, consumers with non-metered connections face potential issues with billing accuracy and limited incentives for energy conservation.
Choosing the Right Connection: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right connection between metered and non-metered options depends largely on your usage patterns, budget, and need for cost control. Metered connections charge based on actual consumption, ideal for low or variable data users aiming to avoid unnecessary expenses. Non-metered connections offer unlimited access with a fixed fee, better suited for high data consumption scenarios where consistent connectivity is essential.
Impact on Data Usage and Cost
Metered connections track and limit data usage, often resulting in lower costs for users who consume minimal data, while non-metered connections offer unlimited data but may lead to higher expenses due to unregulated usage. Data usage in metered plans is carefully monitored, making them cost-effective for light users, whereas non-metered plans suit heavy data consumers despite potentially increased costs. Understanding the difference can optimize expenses by aligning connection type with individual or business data consumption patterns.
Conclusion: Which Connection Suits Your Needs?
Choosing between metered and non-metered connections depends on your usage patterns and budget preferences. Metered connections offer cost control and are ideal for those with variable or low internet consumption, while non-metered connections provide unlimited access suited for heavy usage without worrying about data limits. Assess your internet needs, considering factors like online activities, data consumption, and cost sensitivity to select the connection that best aligns with your lifestyle.
Metered vs Non-metered Connection Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com