Fossil fuels, derived from ancient organic matter, emit high levels of carbon dioxide contributing to climate change, while alternative fuels like biofuels, hydrogen, and electric power offer cleaner, renewable energy solutions with lower environmental impact. Choosing alternative fuels can significantly reduce your carbon footprint and support a sustainable future.
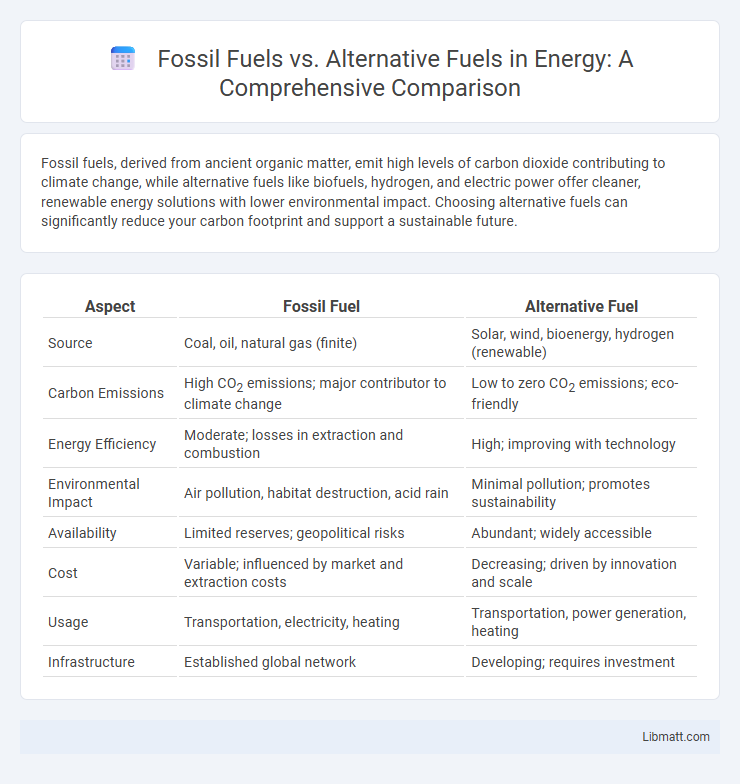
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Fossil Fuel | Alternative Fuel |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Coal, oil, natural gas (finite) | Solar, wind, bioenergy, hydrogen (renewable) |
| Carbon Emissions | High CO2 emissions; major contributor to climate change | Low to zero CO2 emissions; eco-friendly |
| Energy Efficiency | Moderate; losses in extraction and combustion | High; improving with technology |
| Environmental Impact | Air pollution, habitat destruction, acid rain | Minimal pollution; promotes sustainability |
| Availability | Limited reserves; geopolitical risks | Abundant; widely accessible |
| Cost | Variable; influenced by market and extraction costs | Decreasing; driven by innovation and scale |
| Usage | Transportation, electricity, heating | Transportation, power generation, heating |
| Infrastructure | Established global network | Developing; requires investment |
Introduction to Fossil Fuels and Alternative Fuels
Fossil fuels, including coal, oil, and natural gas, have been the primary energy sources for centuries due to their high energy density and established infrastructure. Alternative fuels, such as biofuels, hydrogen, and electricity derived from renewable sources, offer sustainable options that reduce greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on finite resources. Transitioning to alternative fuels is essential for mitigating climate change and promoting energy security in a rapidly evolving global energy landscape.
Types of Fossil Fuels: Coal, Oil, and Natural Gas
Coal, oil, and natural gas are the primary types of fossil fuels, each derived from ancient organic matter and widely used for energy production. Coal is mainly used for electricity generation, oil powers transportation and industrial processes, while natural gas serves heating, electricity, and as a cleaner alternative to coal and oil. Your energy choices influence environmental impact, as fossil fuels emit significant greenhouse gases compared to alternative fuels like solar, wind, and bioenergy.
Exploring Alternative Fuels: Solar, Wind, Biofuel, and More
Alternative fuels like solar, wind, and biofuel offer sustainable energy solutions that reduce greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on fossil fuels. Solar power harnesses sunlight through photovoltaic cells, wind energy utilizes turbines to convert wind into electricity, while biofuels are produced from organic materials, providing cleaner combustion. Exploring these renewable sources can significantly enhance your energy efficiency and contribute to a greener future.
Environmental Impact: Fossil Fuels vs. Alternative Fuels
Fossil fuels release high levels of carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, and nitrogen oxides, contributing significantly to air pollution and global warming. Alternative fuels, such as biofuels, hydrogen, and electricity from renewable sources, produce substantially lower greenhouse gas emissions and reduce dependence on finite resources. Transitioning to alternative fuels is essential for mitigating climate change and minimizing harmful environmental impacts.
Economic Factors: Costs and Investments
Fossil fuels often require lower initial investment costs due to established infrastructure but incur higher long-term expenses from price volatility and environmental regulations. Alternative fuels usually demand higher upfront capital for technology development and infrastructure but offer greater cost stability and potential savings through government incentives. Your investment in alternative energy can lead to long-term economic benefits by reducing dependence on fluctuating fossil fuel markets.
Energy Efficiency and Performance Comparison
Alternative fuels such as electric and hydrogen power exhibit higher energy efficiency compared to fossil fuels, converting a larger percentage of input energy into usable power. Fossil fuels like gasoline and diesel, while delivering high energy density and reliable performance, typically suffer from lower combustion efficiency and higher greenhouse gas emissions. Advances in battery technology and fuel cell systems are rapidly closing the performance gap, making alternative fuels increasingly viable for transportation and industrial applications.
Accessibility and Infrastructure for Different Fuels
Fossil fuels benefit from well-established, widespread infrastructure including refineries, pipelines, and distribution networks, making them highly accessible globally. Alternative fuels such as hydrogen, electric, and biofuels face limited infrastructure development and accessibility challenges, often requiring new technology investments and localized distribution systems. Expanding charging stations for electric vehicles and hydrogen refueling networks is critical to improving alternative fuel accessibility.
Government Policies and Global Trends
Government policies increasingly favor alternative fuels through subsidies, tax incentives, and stringent emissions regulations targeting fossil fuel consumption. Global trends highlight a significant shift towards renewable energy adoption, driven by international agreements such as the Paris Accord aiming to reduce carbon emissions. Investments in clean energy infrastructure and technology innovation are accelerating the transition from fossil fuels to sustainable alternatives worldwide.
Future Prospects: Innovation and Transition
Innovation in alternative fuels, such as hydrogen, biofuels, and advanced battery technologies, is accelerating the transition away from fossil fuels, driven by global climate goals and regulatory pressures. Advances in energy storage, carbon capture, and renewable infrastructure are reshaping the energy landscape, making alternative fuels increasingly viable and cost-effective. Your investment in renewable energy technologies aligns with the growing market demand for cleaner, sustainable sources that promise long-term environmental and economic benefits.
Conclusion: Choosing the Sustainable Path Forward
Fossil fuels contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions, accelerating climate change and depleting finite natural resources, while alternative fuels like solar, wind, and bioenergy offer cleaner, renewable solutions that reduce environmental impact. Transitioning to alternative fuels supports energy security, lowers pollution, and promotes sustainable economic growth. Your commitment to adopting clean energy sources drives the global shift toward a more sustainable and resilient future.
Fossil fuel vs Alternative fuel Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com