Passive solar design uses natural elements like sunlight, building orientation, and materials to heat and cool your home without mechanical systems, offering energy savings and environmental benefits. Active solar systems rely on mechanical components such as pumps and fans to collect, store, and distribute solar energy, providing more control and efficiency for heating, cooling, or electricity generation.
Table of Comparison
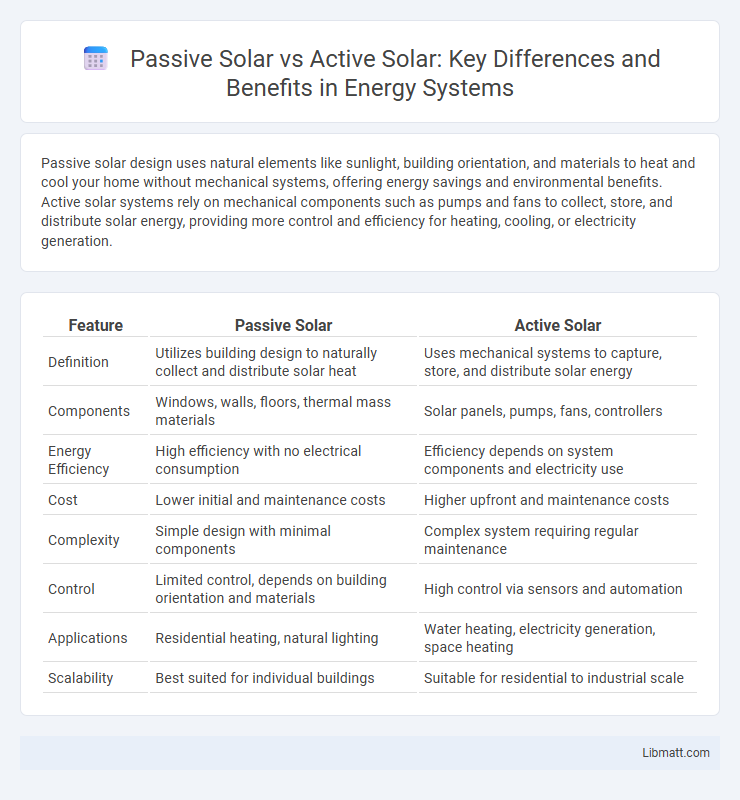
| Feature | Passive Solar | Active Solar |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Utilizes building design to naturally collect and distribute solar heat | Uses mechanical systems to capture, store, and distribute solar energy |
| Components | Windows, walls, floors, thermal mass materials | Solar panels, pumps, fans, controllers |
| Energy Efficiency | High efficiency with no electrical consumption | Efficiency depends on system components and electricity use |
| Cost | Lower initial and maintenance costs | Higher upfront and maintenance costs |
| Complexity | Simple design with minimal components | Complex system requiring regular maintenance |
| Control | Limited control, depends on building orientation and materials | High control via sensors and automation |
| Applications | Residential heating, natural lighting | Water heating, electricity generation, space heating |
| Scalability | Best suited for individual buildings | Suitable for residential to industrial scale |
Introduction to Passive and Active Solar Systems
Passive solar systems use building design elements like windows, walls, and floors to naturally collect, store, and distribute solar energy without mechanical devices. Active solar systems rely on mechanical components such as pumps and fans to capture and transfer solar energy through solar panels or collectors. Understanding the difference helps you choose the most efficient and cost-effective solar solution for your energy needs.
How Passive Solar Energy Works
Passive solar energy works by designing buildings and spaces to naturally collect, store, and distribute solar heat without mechanical systems. It utilizes architectural elements like south-facing windows, thermal mass materials, and proper insulation to optimize sunlight absorption during the day and release warmth at night. This approach reduces heating costs and energy consumption by leveraging natural solar patterns efficiently.
How Active Solar Energy Works
Active solar energy systems use photovoltaic panels or solar thermal collectors to capture sunlight and convert it into electricity or heat. These systems rely on mechanical components like pumps and fans to circulate fluids or air, enhancing energy transfer and storage efficiency. By integrating batteries or thermal storage, active solar setups provide consistent power supply regardless of sunlight availability.
Key Differences Between Passive and Active Solar
Passive solar energy harnesses sunlight through architectural design elements like large south-facing windows and thermal mass materials, requiring no mechanical systems to capture or distribute heat. Active solar energy relies on photovoltaic panels or solar thermal collectors combined with mechanical equipment such as pumps or fans to convert and transfer solar energy into usable electricity or heat. The key differences lie in their approach: passive solar uses design features to naturally collect and store energy, while active solar employs technological devices to enhance energy capture and distribution.
Efficiency Comparison: Passive vs Active Solar
Passive solar systems use building design elements like windows, walls, and floors to naturally collect and store solar energy without mechanical devices, making them highly efficient with minimal energy input. Active solar systems rely on mechanical components such as pumps and fans to capture and distribute heat or electricity, which can yield higher energy output but involves increased maintenance and operational costs. Your choice between passive and active solar depends on desired efficiency balanced with system complexity and energy needs.
Cost Analysis: Installation and Maintenance
Passive solar systems have lower installation costs since they utilize building design elements like windows, walls, and floors to collect and store solar energy without mechanical components. Active solar systems require a higher upfront investment due to solar panels, pumps, and controllers, along with ongoing maintenance expenses for mechanical parts to ensure optimal performance. Your choice between passive and active solar must consider long-term cost efficiency, balancing installation complexity against maintenance commitments.
Environmental Impact of Both Systems
Passive solar systems harness natural sunlight for heating and lighting without mechanical components, resulting in minimal environmental impact and zero greenhouse gas emissions during operation. Active solar systems, which use photovoltaic panels or solar thermal collectors combined with pumps or fans, have a higher embodied energy due to manufacturing and maintenance but still significantly reduce carbon footprints compared to fossil fuels. You can maximize sustainability by choosing passive solar design strategies when possible and supplementing with active solar technologies for energy needs requiring mechanical support.
Best Use Cases for Passive Solar
Passive solar design excels in residential buildings located in mild to moderate climates, where maximizing natural sunlight for heating and daylighting reduces energy consumption. It is ideal for homes with large south-facing windows, thermal mass materials like concrete or brick, and proper shading devices to prevent overheating in summer. This approach works best for long-term energy savings without reliance on mechanical systems, making it suitable for sustainable and cost-effective heating in solar-rich regions.
Best Use Cases for Active Solar
Active solar systems are best suited for applications requiring reliable, controllable energy output, such as residential water heating, commercial HVAC systems, and off-grid power generation. These systems use mechanical components like pumps and fans to optimize energy collection and distribution, making them ideal for locations with variable sunlight or high energy demands. Active solar technology excels in scenarios where precision and efficiency in energy management are critical to performance.
Choosing the Right Solar Solution for Your Needs
Passive solar systems use design elements like windows, walls, and floors to naturally collect and store solar energy, requiring minimal maintenance and no mechanical components. Active solar systems incorporate solar panels and mechanical devices such as pumps or fans to actively capture and distribute energy, offering higher efficiency and control but with increased installation and operational costs. Your choice depends on factors like climate, budget, energy needs, and whether you prioritize simplicity or maximum energy output.
Passive solar vs Active solar Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com