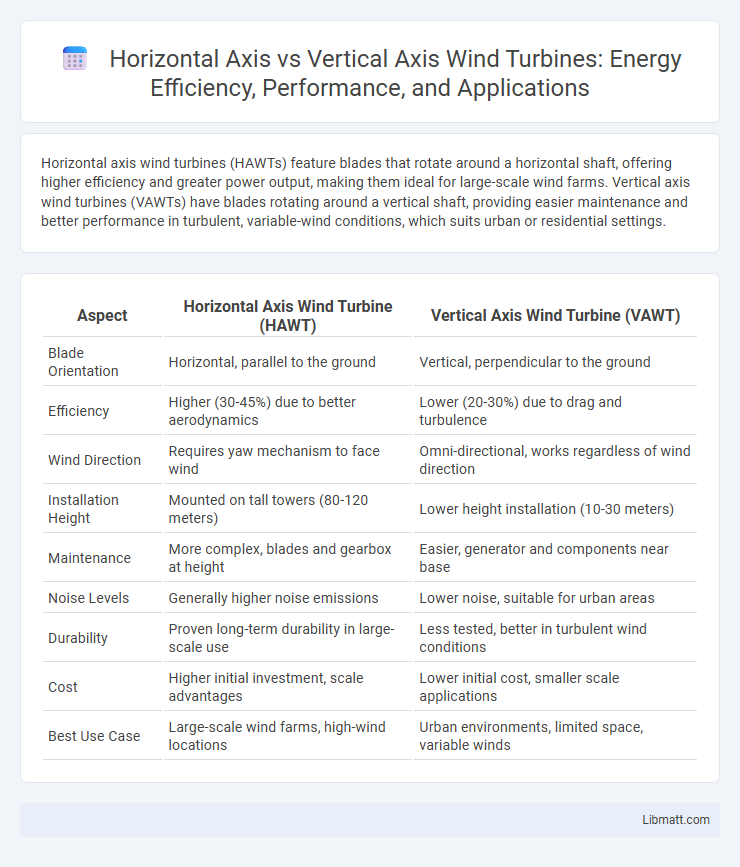
Horizontal axis wind turbines (HAWTs) feature blades that rotate around a horizontal shaft, offering higher efficiency and greater power output, making them ideal for large-scale wind farms. Vertical axis wind turbines (VAWTs) have blades rotating around a vertical shaft, providing easier maintenance and better performance in turbulent, variable-wind conditions, which suits urban or residential settings.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine (HAWT) | Vertical Axis Wind Turbine (VAWT) |
|---|---|---|
| Blade Orientation | Horizontal, parallel to the ground | Vertical, perpendicular to the ground |
| Efficiency | Higher (30-45%) due to better aerodynamics | Lower (20-30%) due to drag and turbulence |
| Wind Direction | Requires yaw mechanism to face wind | Omni-directional, works regardless of wind direction |
| Installation Height | Mounted on tall towers (80-120 meters) | Lower height installation (10-30 meters) |
| Maintenance | More complex, blades and gearbox at height | Easier, generator and components near base |
| Noise Levels | Generally higher noise emissions | Lower noise, suitable for urban areas |
| Durability | Proven long-term durability in large-scale use | Less tested, better in turbulent wind conditions |
| Cost | Higher initial investment, scale advantages | Lower initial cost, smaller scale applications |
| Best Use Case | Large-scale wind farms, high-wind locations | Urban environments, limited space, variable winds |
Introduction to Wind Turbine Types
Horizontal axis wind turbines (HAWTs) feature blades rotating around a horizontal shaft, commonly used in large-scale wind farms due to their higher efficiency and ability to capture stronger winds at greater heights. Vertical axis wind turbines (VAWTs) have blades rotating around a vertical shaft, offering advantages in urban environments with variable wind directions and lower noise levels. Your choice between these types depends on factors like installation space, wind conditions, and maintenance preferences.
What is a Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine (HAWT)?
A Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine (HAWT) features blades that rotate around a horizontally aligned axis, typically positioned at the top of a tall tower to capture stronger and steadier winds. HAWTs are the most common type of wind turbines, known for their high efficiency and ability to generate significant amounts of electricity in large-scale wind farms. Their design allows the rotor blades to face the wind direction, optimizing energy conversion from wind to electrical power.
What is a Vertical Axis Wind Turbine (VAWT)?
A Vertical Axis Wind Turbine (VAWT) features blades that rotate around a vertical shaft, allowing it to capture wind from any direction without needing to adjust its orientation. Unlike Horizontal Axis Wind Turbines (HAWT), VAWTs are typically more compact and operate efficiently in turbulent or urban environments where wind patterns are unpredictable. Your choice of a VAWT can be ideal for limited spaces or sites with variable wind directions, offering lower noise levels and easier maintenance.
Design Differences: HAWT vs VAWT
Horizontal Axis Wind Turbines (HAWT) feature blades that rotate around a horizontal shaft, typically positioned on tall towers to capture stronger winds at higher altitudes. Vertical Axis Wind Turbines (VAWT) have blades rotating around a vertical shaft, enabling omnidirectional wind capture and ground-level installation with simpler maintenance. The aerodynamic design of HAWTs maximizes efficiency in steady wind conditions, while VAWTs excel in turbulent and variable wind environments due to their adaptable rotor orientation.
Efficiency Comparison: Horizontal Axis vs Vertical Axis
Horizontal axis wind turbines (HAWTs) typically achieve higher efficiency due to their ability to capture stronger and more consistent wind speeds at elevated heights, reaching up to 45-50% aerodynamic efficiency. Vertical axis wind turbines (VAWTs) generally operate at lower efficiencies, around 30-40%, because of increased aerodynamic drag and less optimal blade orientation relative to wind direction. The superior efficiency of HAWTs makes them more suitable for large-scale power generation, while VAWTs find niche applications in urban or turbulent wind environments.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Horizontal axis wind turbines (HAWTs) typically require more complex installation involving tall towers and heavy lifting equipment, which can increase initial setup time and costs. Their maintenance often necessitates specialized technicians to access high-mounted components, posing safety considerations and potentially higher service expenses. Vertical axis wind turbines (VAWTs) offer easier installation on rooftops or urban environments due to their compact design and lower height, simplifying maintenance as key parts are closer to the ground, reducing downtime and operational challenges for your wind energy setup.
Performance in Various Wind Conditions
Horizontal axis wind turbines (HAWTs) typically perform better in consistent, high-speed wind conditions due to their efficient aerodynamic design and ability to yaw into the wind, maximizing energy capture. Vertical axis wind turbines (VAWTs) excel in turbulent or variable wind environments, such as urban areas, because they can capture wind from any direction without needing to reorient. Your choice between HAWT and VAWT depends on site-specific wind patterns and performance requirements for optimal energy generation.
Space and Location Considerations
Horizontal axis wind turbines (HAWTs) require larger open spaces with consistent wind flow and are typically installed in rural or offshore locations due to their taller height and wide rotor diameter. Vertical axis wind turbines (VAWTs) have a compact footprint and can be positioned closer together, making them suitable for urban or constrained environments with turbulent wind patterns. Site selection for HAWTs focuses on maximizing wind speed and minimizing turbulence, while VAWTs prioritize adaptability to changing wind directions and limited spatial availability.
Cost Analysis: HAWT vs VAWT
Horizontal Axis Wind Turbines (HAWT) generally have higher initial installation costs due to complex foundations and taller towers but offer greater energy output and efficiency, reducing long-term operational expenses. Vertical Axis Wind Turbines (VAWT) have lower upfront costs with simpler designs and easier maintenance, yet often yield less energy, impacting overall cost-effectiveness in large-scale applications. Lifecycle cost analysis reveals HAWTs tend to provide better return on investment for utility-scale projects, while VAWTs can be more economical in urban or low-wind environments.
Which Wind Turbine is Best for Your Needs?
Horizontal axis wind turbines (HAWTs) are ideal for large-scale energy production due to their high efficiency and ability to harness stronger, consistent wind speeds at higher elevations. Vertical axis wind turbines (VAWTs) excel in urban or turbulent environments where wind directions vary, offering easier maintenance and quieter operation. Selecting the best wind turbine depends on specific site conditions, energy requirements, and space availability, with HAWTs preferred for open, windy areas and VAWTs suited for compact, variable-wind locations.
Horizontal Axis vs Vertical Axis Wind Turbine Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com