Transformerless inverters offer higher efficiency and reduced weight by eliminating the bulky transformer, making them ideal for residential solar systems with space constraints. Transformer-based inverters provide galvanic isolation for enhanced safety, which may be preferable for installations requiring strict electrical isolation standards.
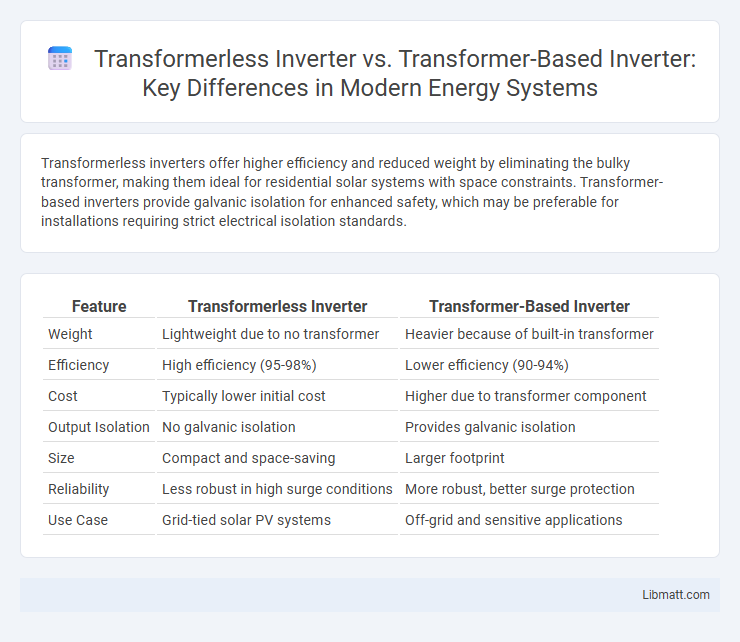
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Transformerless Inverter | Transformer-Based Inverter |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | Lightweight due to no transformer | Heavier because of built-in transformer |
| Efficiency | High efficiency (95-98%) | Lower efficiency (90-94%) |
| Cost | Typically lower initial cost | Higher due to transformer component |
| Output Isolation | No galvanic isolation | Provides galvanic isolation |
| Size | Compact and space-saving | Larger footprint |
| Reliability | Less robust in high surge conditions | More robust, better surge protection |
| Use Case | Grid-tied solar PV systems | Off-grid and sensitive applications |
Introduction to Inverter Technologies
Transformerless inverters offer higher efficiency and reduced weight compared to traditional transformer-based inverters by eliminating the bulky transformer component. Transformer-based inverters provide galvanic isolation, enhancing safety and reducing electromagnetic interference in solar power systems. Your choice depends on balancing efficiency, system safety, and application requirements for optimal energy conversion performance.
What is a Transformer-Based Inverter?
A transformer-based inverter includes a built-in transformer to step up or step down voltage levels, ensuring electrical isolation between the input and output. This design enhances safety and protects your connected devices from electrical faults or surges by isolating the grid from the load. These inverters are commonly used in applications requiring voltage conversion and reliable isolation for sensitive equipment.
Overview of Transformerless Inverters
Transformerless inverters are power electronics devices that convert DC to AC without using a traditional transformer, resulting in reduced weight, size, and cost. These inverters improve efficiency by minimizing energy losses associated with transformers and enable enhanced grid compatibility with advanced monitoring and safety features. Commonly used in residential and commercial solar PV systems, transformerless inverters support higher power densities and comply with strict grid regulations such as anti-islanding protection and leakage current detection.
Key Differences: Transformerless vs. Transformer-Based Inverters
Transformerless inverters offer higher efficiency and reduced weight compared to transformer-based inverters, making them ideal for residential solar systems seeking compact design and improved energy yield. Transformer-based inverters provide galvanic isolation, enhancing safety and electromagnetic compatibility, which is crucial in industrial and commercial applications with stringent grid requirements. Your choice depends on balancing efficiency, safety, and installation constraints specific to your solar power setup.
Efficiency Comparison: Transformerless vs. Transformer-Based
Transformerless inverters typically offer higher efficiency rates, often exceeding 98%, due to reduced energy losses associated with the absence of a heavy transformer component. Transformer-based inverters, while providing galvanic isolation and enhanced safety, generally exhibit lower efficiency levels around 94-96% because of energy dissipation in the transformer. Optimizing your PV system with a transformerless inverter can maximize energy output and minimize conversion losses for better overall performance.
Safety Considerations and Isolation Features
Transformer-based inverters provide galvanic isolation between the input and output, enhancing safety by preventing direct electrical faults and reducing the risk of electric shock. Transformerless inverters lack this inherent isolation, making it essential to rely on advanced grounding and monitoring systems to ensure user safety and meet regulatory standards. Your choice between the two affects the overall system protection strategy, especially in residential or sensitive environments where isolation is critical.
Cost Implications and Installation Complexity
Transformerless inverters generally offer lower cost implications due to reduced material requirements and smaller physical size, making them more budget-friendly compared to transformer-based inverters. The installation complexity is also minimized with transformerless models, as they are lighter and easier to mount, reducing labor time and expenses. Your choice between the two should consider the trade-off between initial investment and the specific safety isolation needs of your system.
Applications and Suitability for Different Projects
Transformerless inverters are widely used in residential and commercial solar power systems due to their higher efficiency, lighter weight, and lower cost, making them suitable for projects where space and budget constraints are critical. Transformer-based inverters provide galvanic isolation, enhancing safety and reliability, and are preferred in industrial applications or large-scale installations where grid compatibility and fault tolerance are paramount. The choice between transformerless and transformer-based inverters depends on project-specific requirements such as grid regulations, installation environment, and desired system efficiency.
Maintenance, Reliability, and Longevity
Transformerless inverters offer lower maintenance needs due to fewer components and simpler construction, enhancing overall reliability by reducing failure points. They typically exhibit longer operational lifespans since they avoid transformer-related heat and mechanical stresses that accelerate wear in transformer-based inverters. Your choice between the two should consider that transformer-based inverters, while more robust against certain electrical faults, often require more frequent maintenance and may have a shorter lifespan due to transformer aging.
Choosing the Right Inverter for Your Needs
Transformerless inverters offer higher efficiency and lighter weight due to the absence of heavy transformers, making them ideal for residential and commercial solar systems with space constraints. Transformer-based inverters provide galvanic isolation, enhancing safety and compatibility with specific grid requirements, which is crucial for installations demanding stringent electrical standards. Selecting the right inverter depends on your system's efficiency goals, safety requirements, and compliance with local regulations.
Transformerless inverter vs Transformer-based inverter Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com